Chemical etching is a versatile and precise manufacturing technique used across various industries for the production of intricate metal parts, microelectronic components, and more. This process involves selectively removing material from a substrate using chemical reactions. Here are eight frequently asked questions about chemical etching:
1. What is Chemical Etching, and How Does It Work?
Chemical etching, also known as chemical milling or chemical machining, is a subtractive manufacturing process that uses chemical solutions to selectively remove material from a metal surface. It involves several key steps: cleaning the metal surface, applying a maskant (resist) to protect areas not to be etched, exposing the material to an etchant (acid or chemical solution), and finally removing the maskant to reveal the etched pattern.
2. What Materials Can Be Etched Using Chemical Etching?
Chemical etching is primarily used on metals and alloys such as stainless steel, copper, brass, aluminum, nickel, and various specialty alloys. While it’s most commonly applied to metals, it can also work on other materials like glass, ceramics, and certain polymers under specific conditions.
3. What Are the Advantages of Chemical Etching Over Other Manufacturing Methods?
Several advantages make chemical etching a preferred method for precision manufacturing. It offers high precision and repeatability, allowing for intricate and complex designs. The process doesn’t induce mechanical stress on materials, resulting in parts with superior burr-free edges. Additionally, it’s a cost-effective solution for producing small to medium-sized batches of parts with minimal tooling investment.
4. What Factors Influence the Etching Rate and Quality of the Resulting Parts?
Several variables affect the chemical etching process, including the type and concentration of the etchant, temperature, agitation, and the composition and surface finish of the material being etched. Controlling these factors ensures the desired etching rate and quality, preventing over-etching or under-etching.
5. How Accurate and Repeatable is Chemical Etching?
Chemical etching offers exceptional accuracy and repeatability. The process is highly controllable, allowing for precise etching of intricate and fine features with tolerances as tight as a few microns. Modern advancements in technology and process control have further enhanced its accuracy and repeatability.
6. Are there Limitations or Challenges with Chemical Etching?
While chemical etching is a versatile manufacturing method, it has some limitations. It may not be suitable for large-scale production due to longer processing times compared to some alternative methods like stamping or laser cutting. Also, certain geometries or extremely thick materials may pose challenges in achieving uniform etching.
7. What Surface Finishes Can Be Achieved Through Chemical Etching?
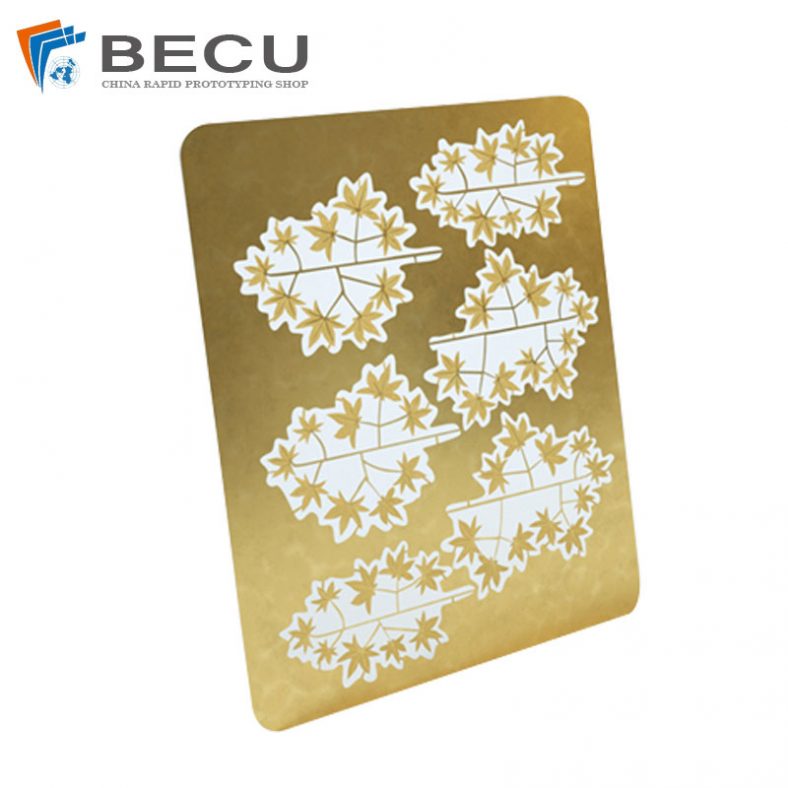
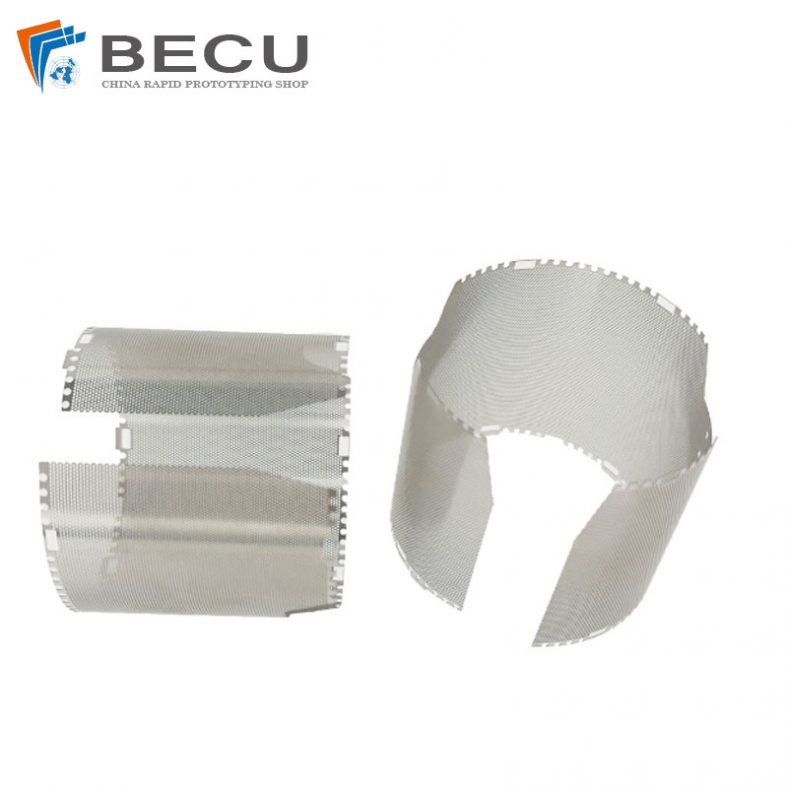
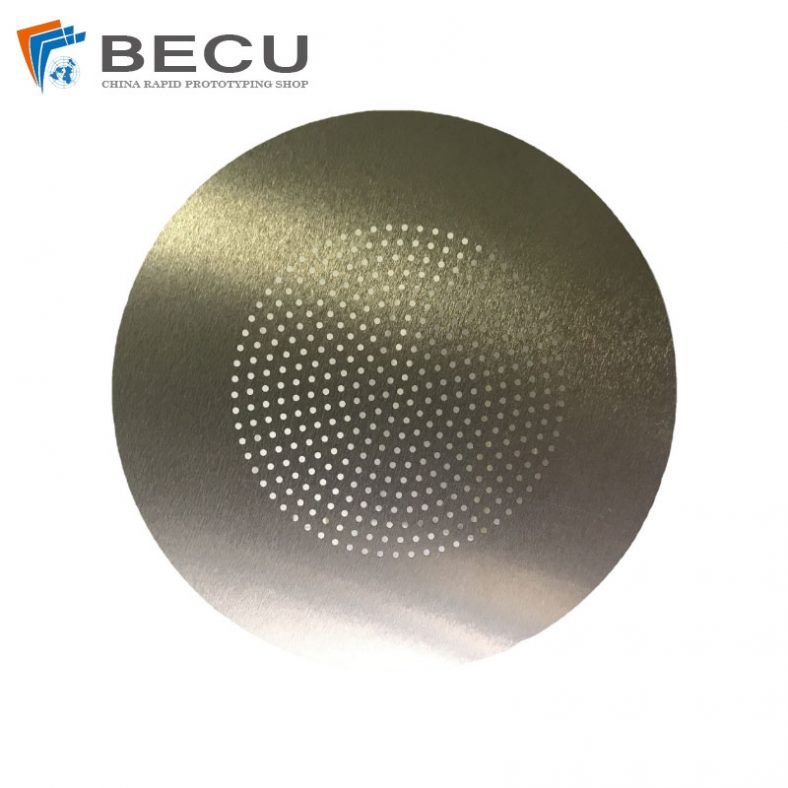
Chemical etching can produce various surface finishes, including matte, satin, or mirror finishes, depending on the material and etching conditions. The process can also create textures and patterns on the surface, providing functional or aesthetic properties to the finished parts.
8. What Industries Benefit Most from Chemical Etching?
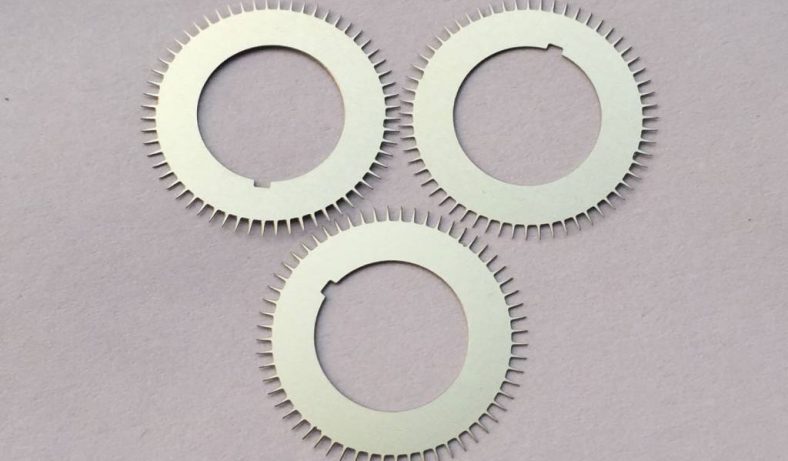
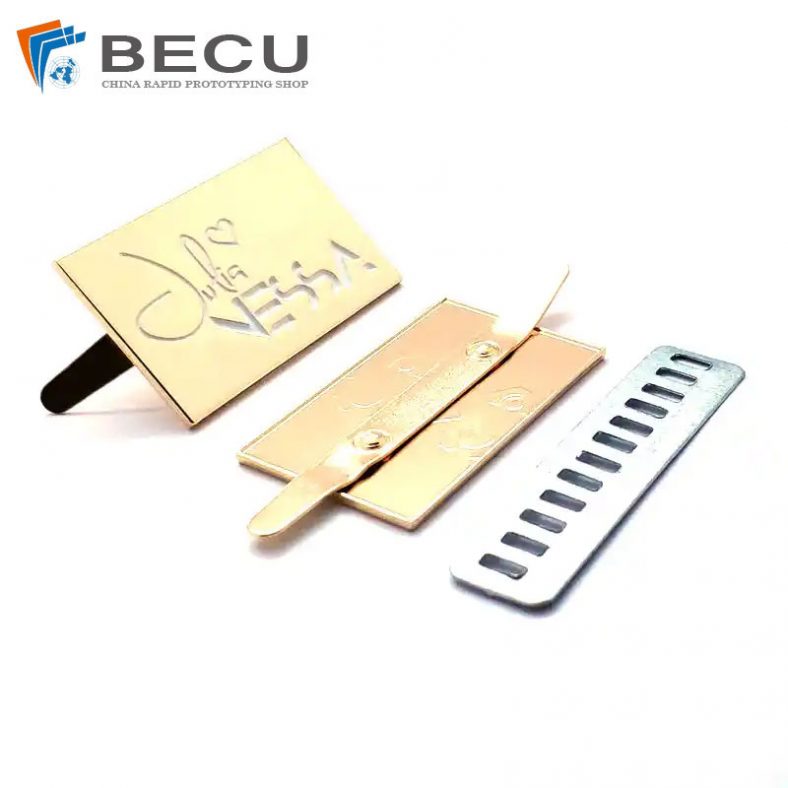
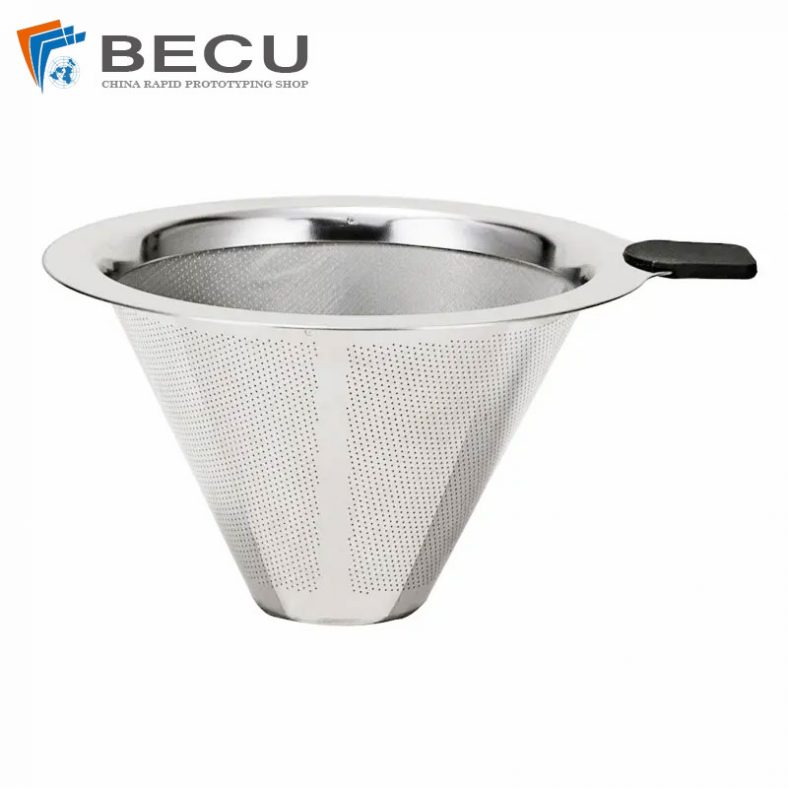
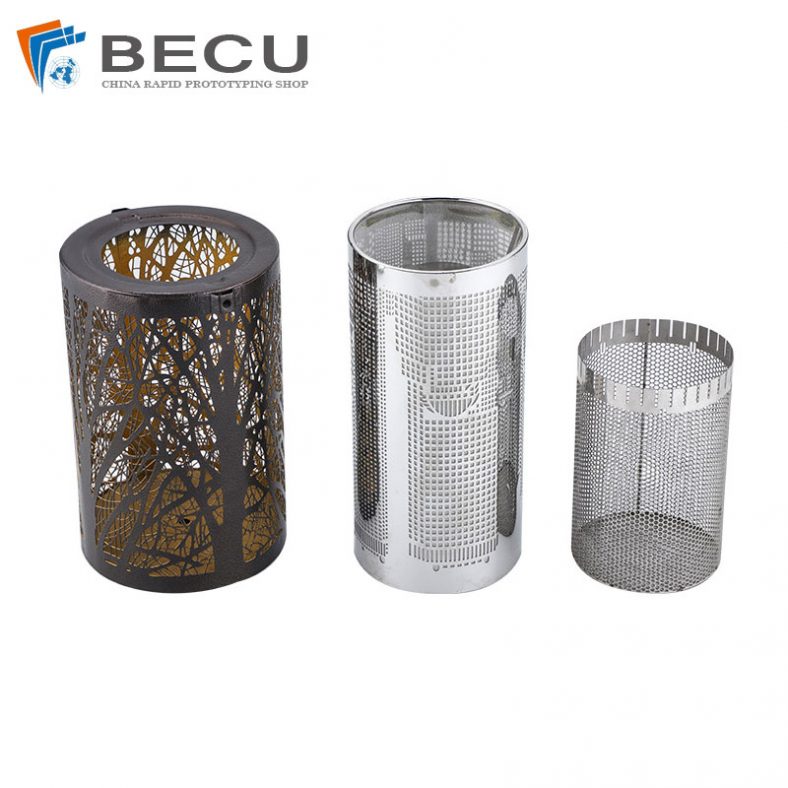
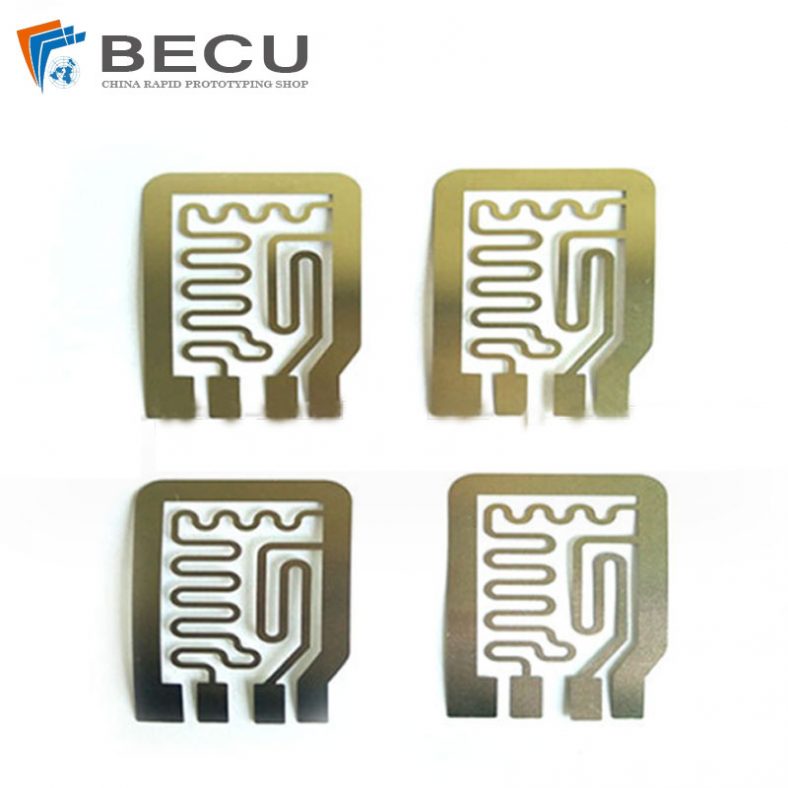
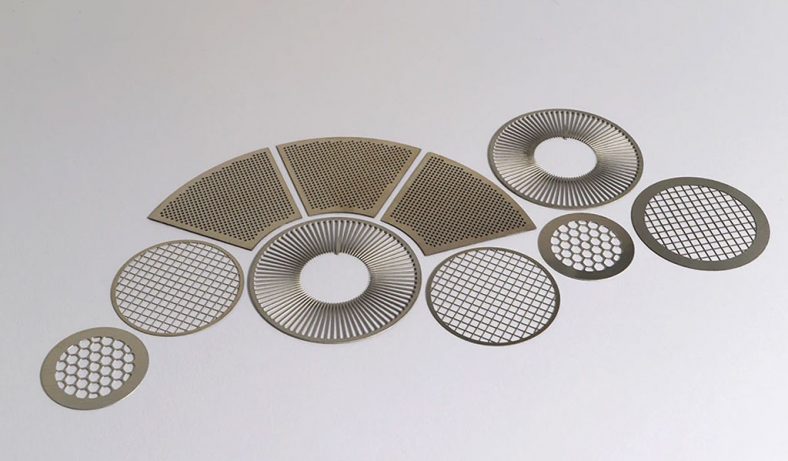
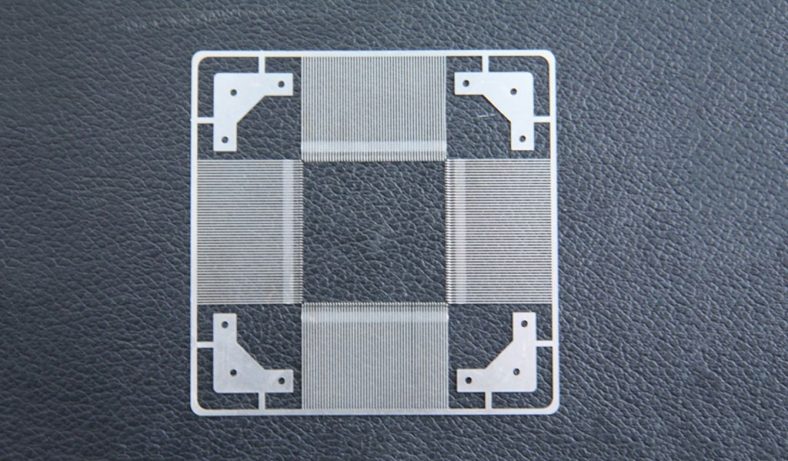
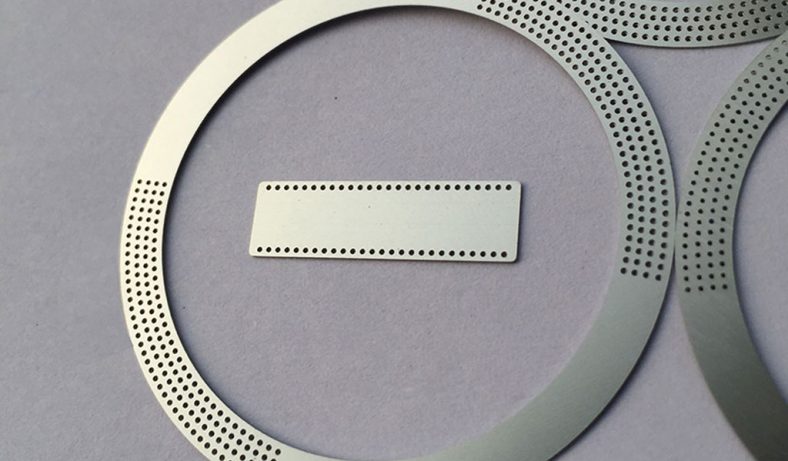
Chemical etching finds applications in diverse industries such as aerospace, electronics, automotive, medical devices, and consumer goods. It’s commonly used to manufacture intricate components like stencils, filters, springs, precision metal parts, electronic circuitry, and decorative items.
In conclusion, chemical etching is a versatile and precise manufacturing technique with wide-ranging applications across industries. Its ability to produce intricately detailed parts with high precision and repeatability makes it a preferred choice for many manufacturing needs.