Homepage » Metal Etching »

What Is Photo Etching
Photo etching, also known as photochemical machining (PCM), chemical milling, or photochemical etching, is a highly precise and versatile manufacturing process used to produce intricate and detailed components from various types of materials, primarily metals and non-metals. This method is characterized by its ability to create complex shapes and features with high precision and repeatability, making it an essential technique in numerous industries.
At its core, photo etching involves the use of a chemical etchant to selectively remove material from a sheet or plate, leaving behind the desired pattern or design. The process is controlled through photolithography, where a photosensitive resist, often a light-sensitive polymer or dry film, is applied to the material’s surface. The resist is exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light through a mask or phototool, which carries the design to be transferred onto the material. This exposure hardens the resist in certain areas while leaving others unhardened.
Custom Photo Etching Services
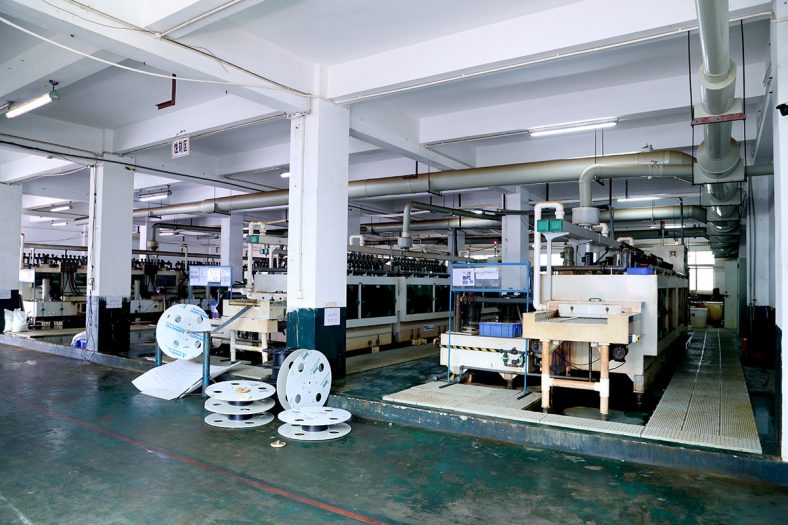
At Metal-etch.com, we offer custom photo etching services and materials — our complete manufacturing facility allow us the opportunity to manufacture parts to drawing specifications.
When you’re considering partnering with a company to help you with custom precision etching services, it’s important to know what type of facility they have.Photo etching has evolved throughout the years so we’ve invested heavily in technology and the team necessary to offer advanced electrical component etching services. As a result, our electrical etching capabilities are unparalleled in our industry and meet the requirements of some of the most demanding organizations.
BE-CU ETCH offering photo-chemical etching and chemical machining services for mechanical products, perforated metals, thermal components, decorative and electronics.Works any type of metal, such as stainless steel,copper,steel,aluminum, molybdenum, brass, ceramic, nickel, titanium, Inconel® and Kovar® materials, with details as small as 0.030 in. to depths ranging between 0.001 to 0.060 in.Capable of handling parts up to 24 x 60 in. sizes and 25,000 lbs. Capabilities for contoured surface, color fill, 2D graphics and image, artwork and pattern, and inside bore and wall etching. Suitable for small and large format projects. Serves the signage, interior and exterior architectural, aerospace, medical, and general industrial markets.Other services include blasting, chemical milling, cleaning, CNC machining, stamping, laser machining, bending, water jet machining, electronic and laser welding, heat treating and electro polishing.
Whether you need the material to create your part, the custom photo etching service to create your part, or both, BE-CU has everything you need to get the particular parts you need.
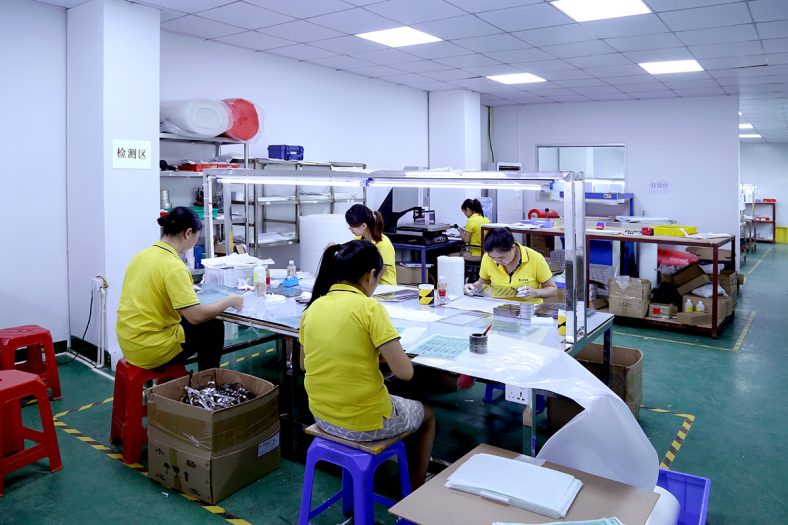
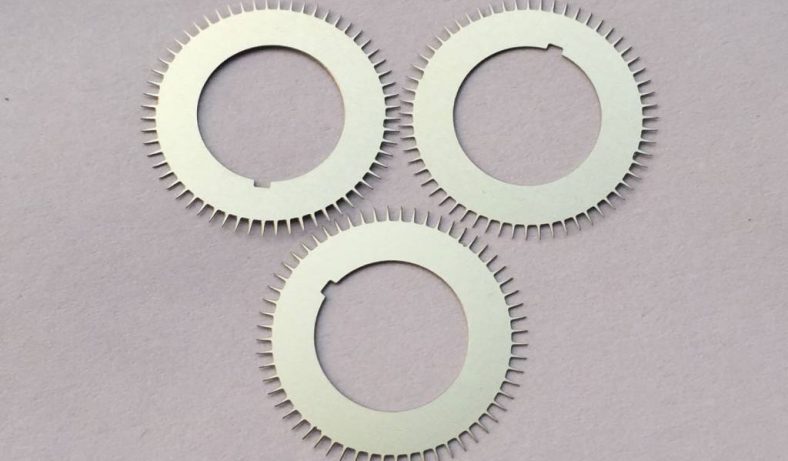
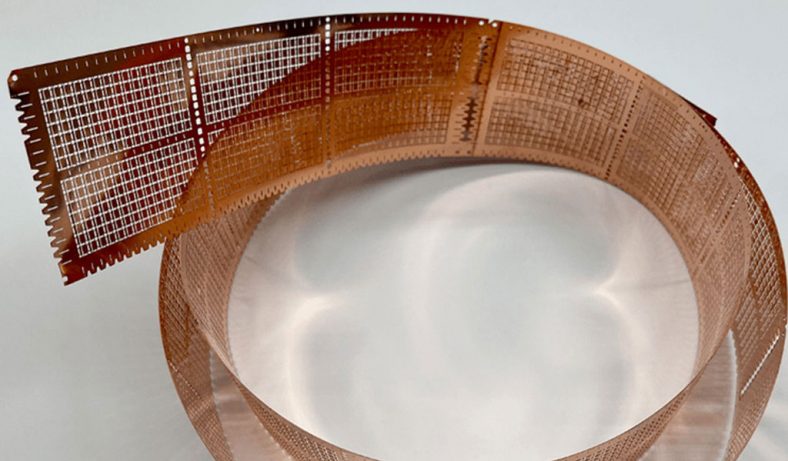
Photo-Chemical Etching Parts
With our photo etching service, we can cater to both one-off prototypes and high-volume production requirements, enabling us to serve a diverse range of specialist component applications.
-
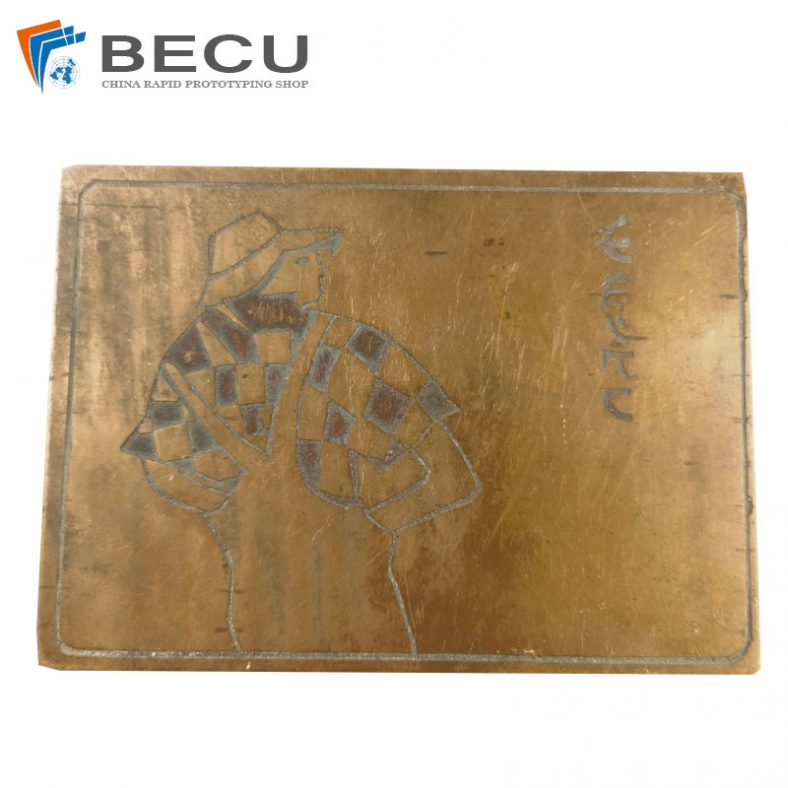

Copperplate Engravings Of World Famous Works
-
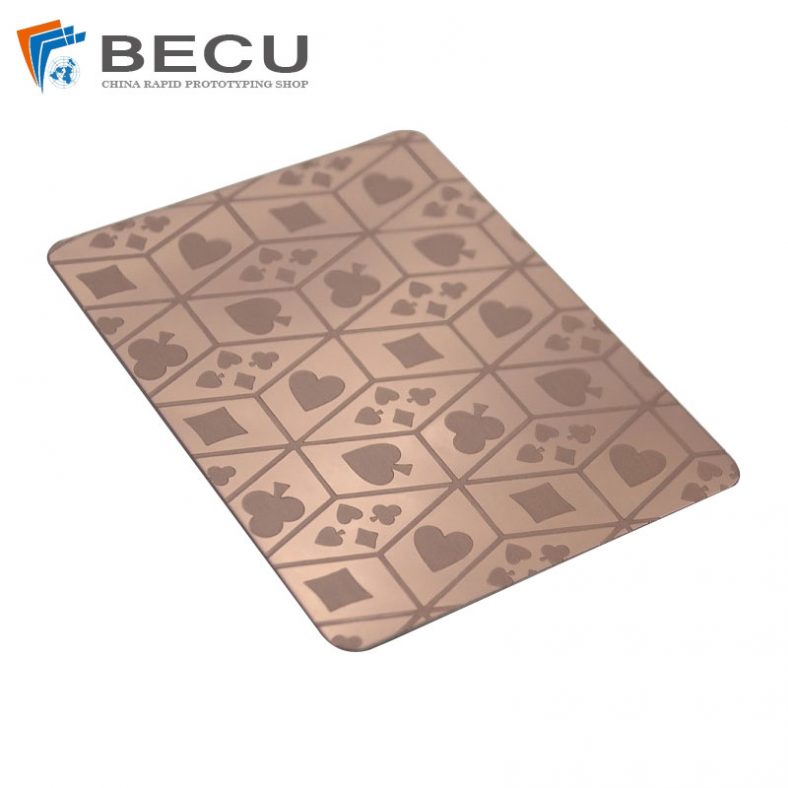

Artistic Etched Copper Shielding Electronics Playing Cards with Patterns
-
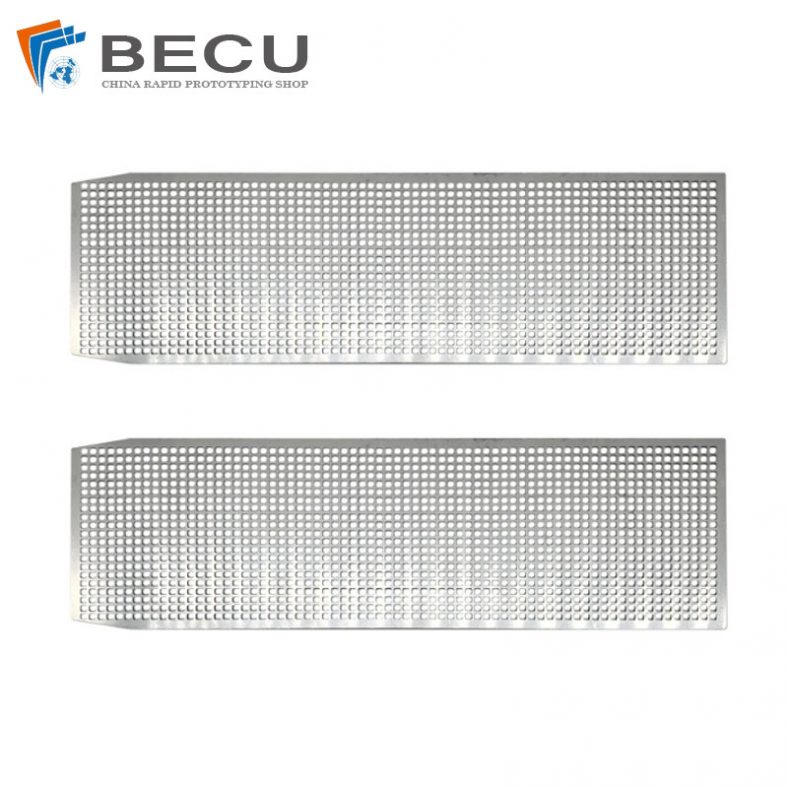

Precision Etched Titanium Alloy Odor Eliminator Perforated Plates
-
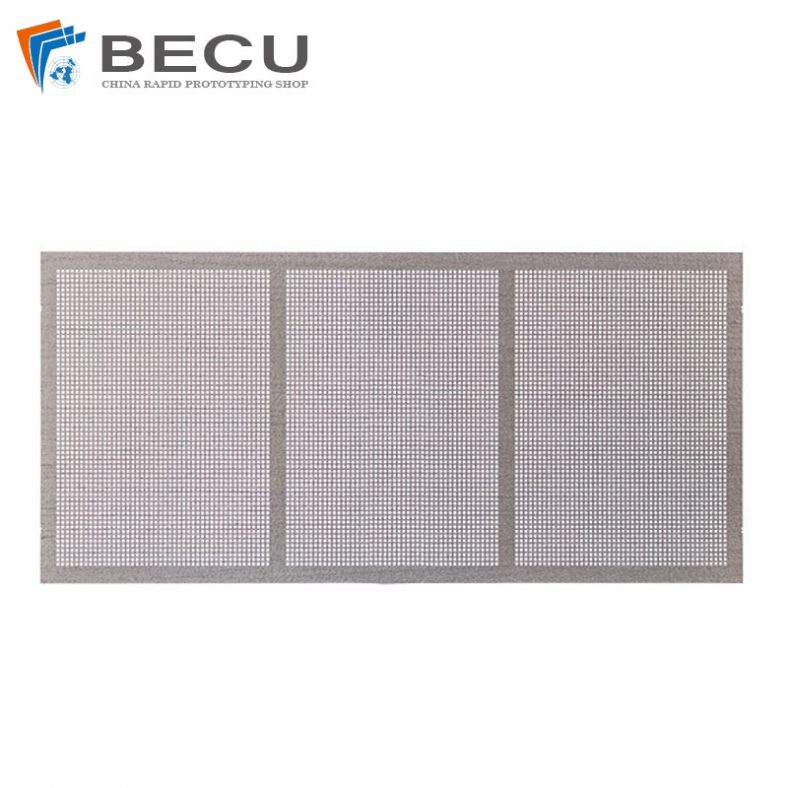

High-End Etched TC4 Titanium Alloy Filters
-
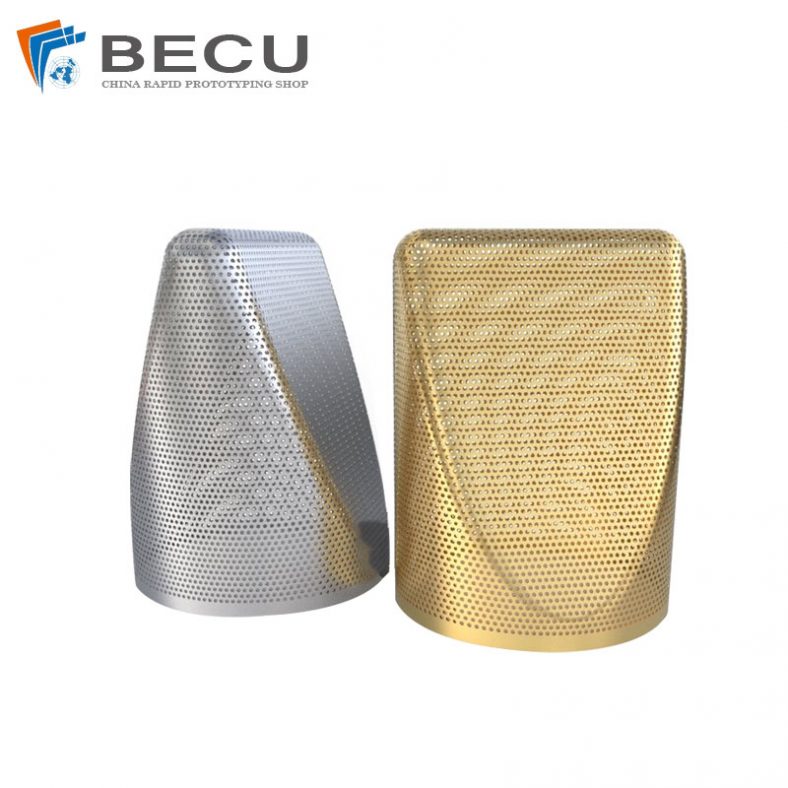

Aluminum Alloy 7075 Etched Microphone Grille
-
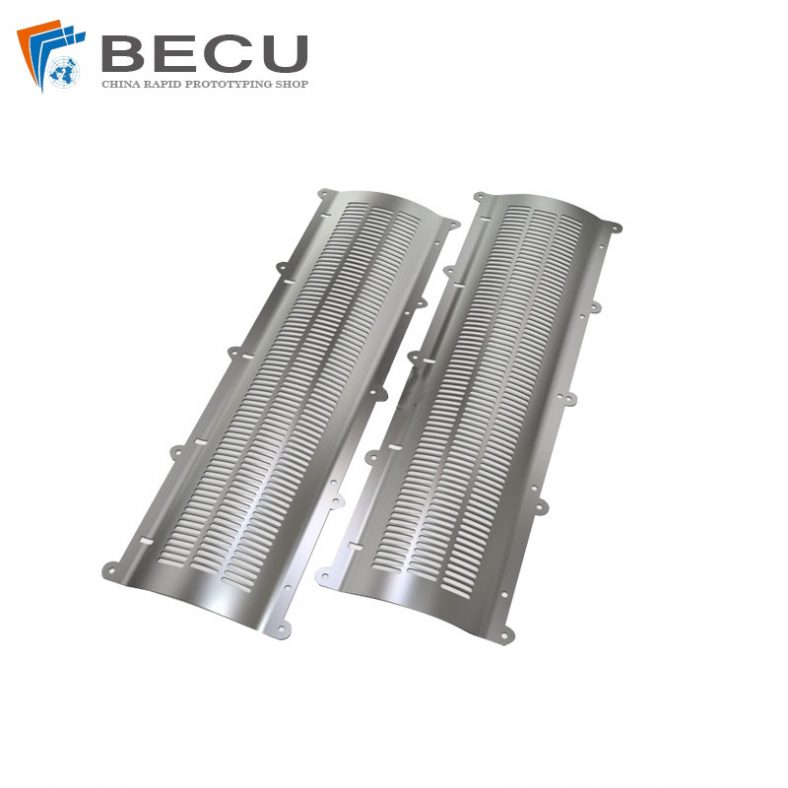

Molybdenum Screen and Spacecraft Electron Tube Grid Etching
-
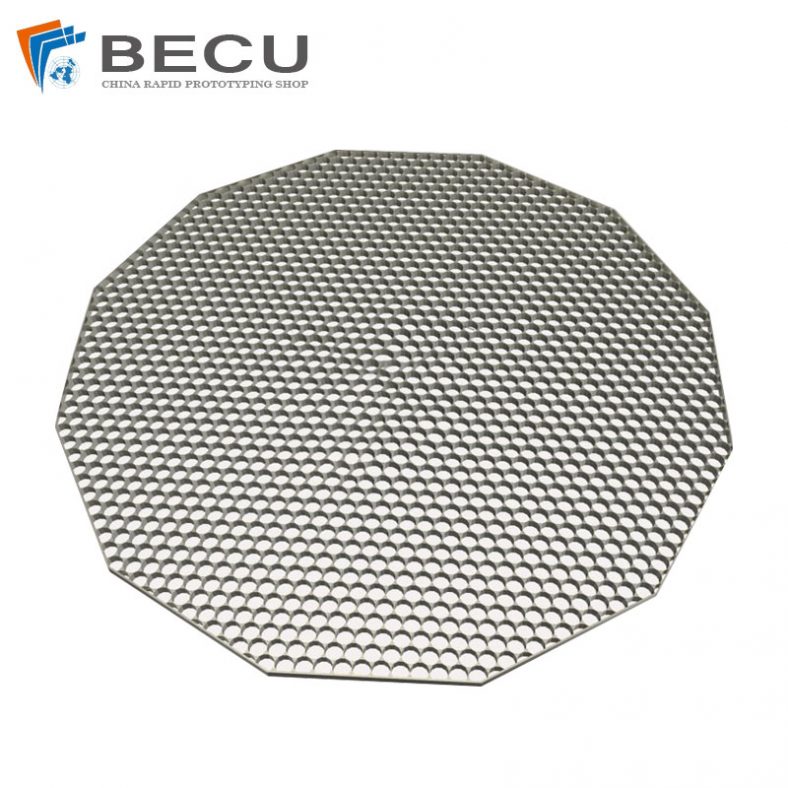

Metal Etching Car Audio Modified Insulation Chips Shock Absorber Board Acoustic
-
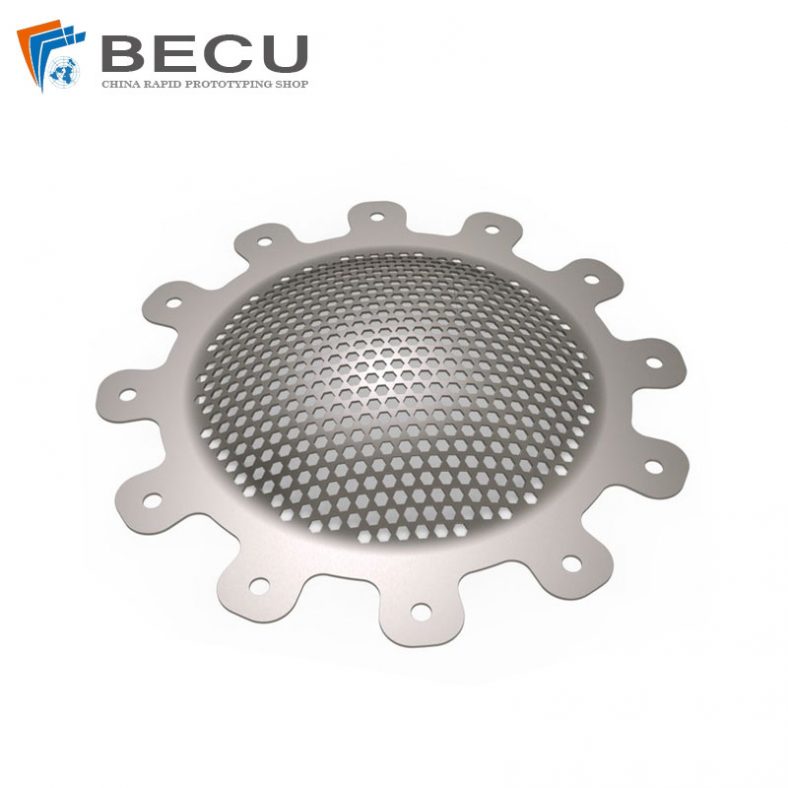

Etching 6.0 Inch Molybdenum Alloy Subwoofer Speaker Grill Guard Protector Cover for Home Audio
-
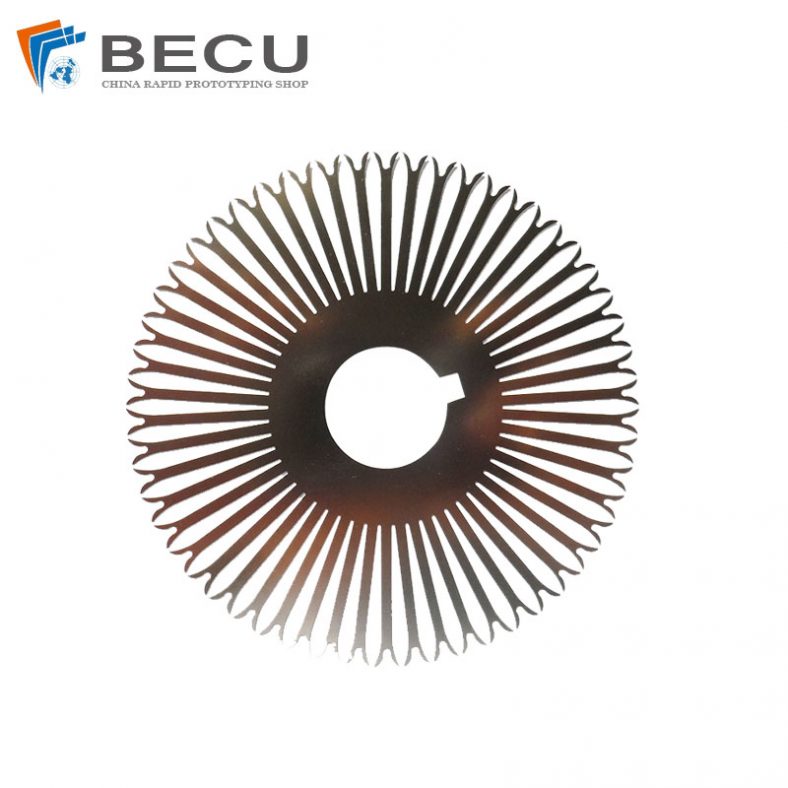

Precision Etching Titanium Alloy Hanging Fixture for Anodizing
-
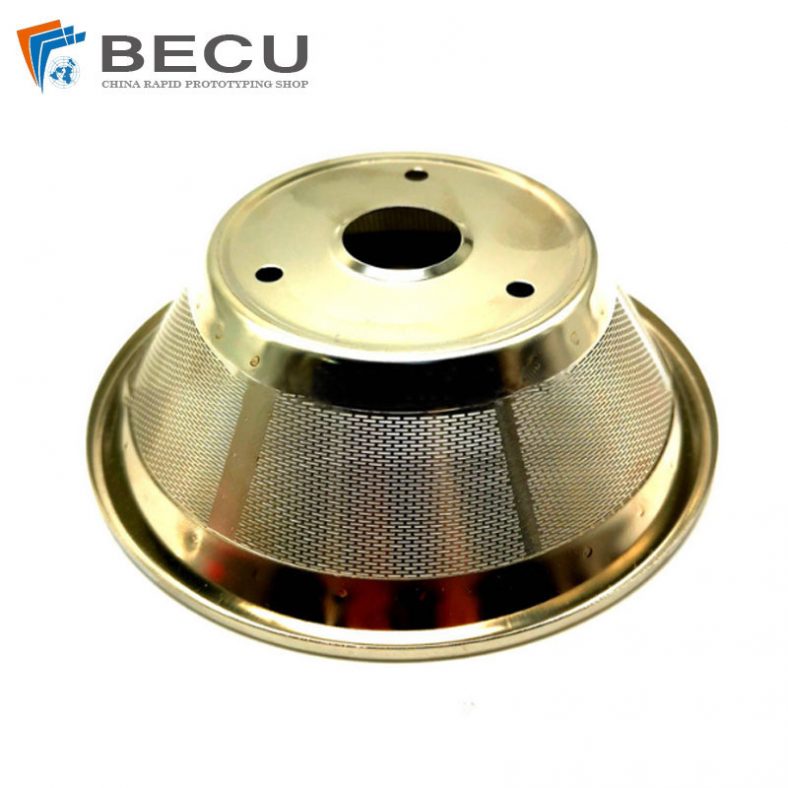

Stainless Steel 316L Etching Tea Strainer
-
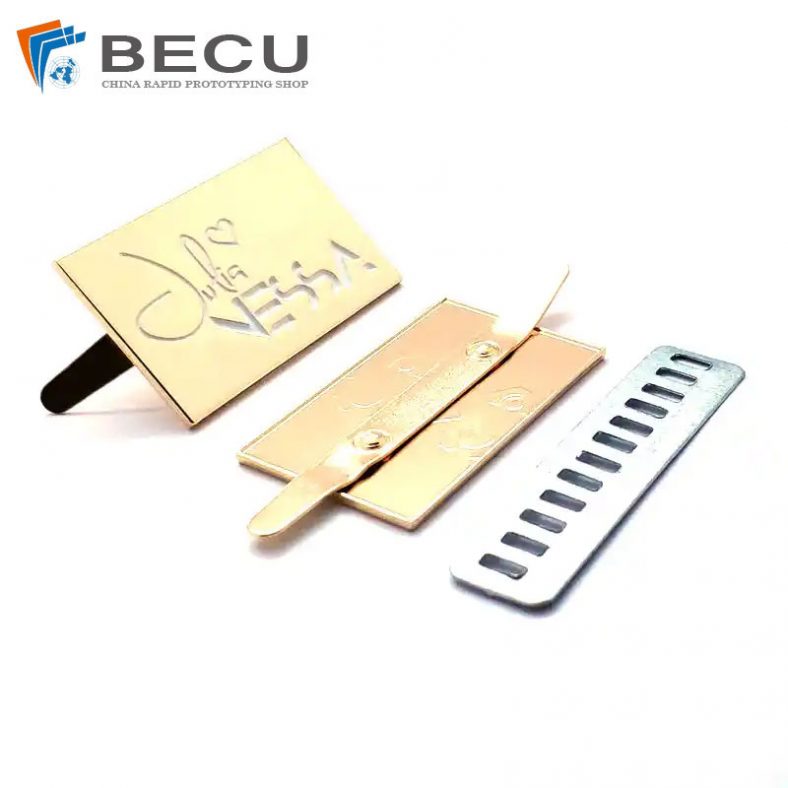

Zinc Alloy Nameplate Etching For Bags Logo/Signs
-

Russian Mythology Character Metal Nameplate Badge Etching
How To Photo Etching – Our Photo Etching Process
Photo etching, also known as photochemical machining (PCM), is a precise manufacturing process used to create intricate components from various materials. To perform photo etching, you’ll need access to the necessary equipment, materials, and a clear understanding of the process. Here are the steps involved in photo etching:
#1 Utilize Computer-Aided Design (CAD)
The process of photochemical metal etching begins with creating a design using CAD or Adobe Illustrator. Although design is the first step in the process, it is not the end of computer calculations.
Once the rendering is complete, the thickness of the metal and the number of parts that will fit on a sheet of metal are determined, a necessary factor in keeping production costs down.
Another aspect of sheet metal thickness is the determination of part tolerances, which depend on the size of the part.
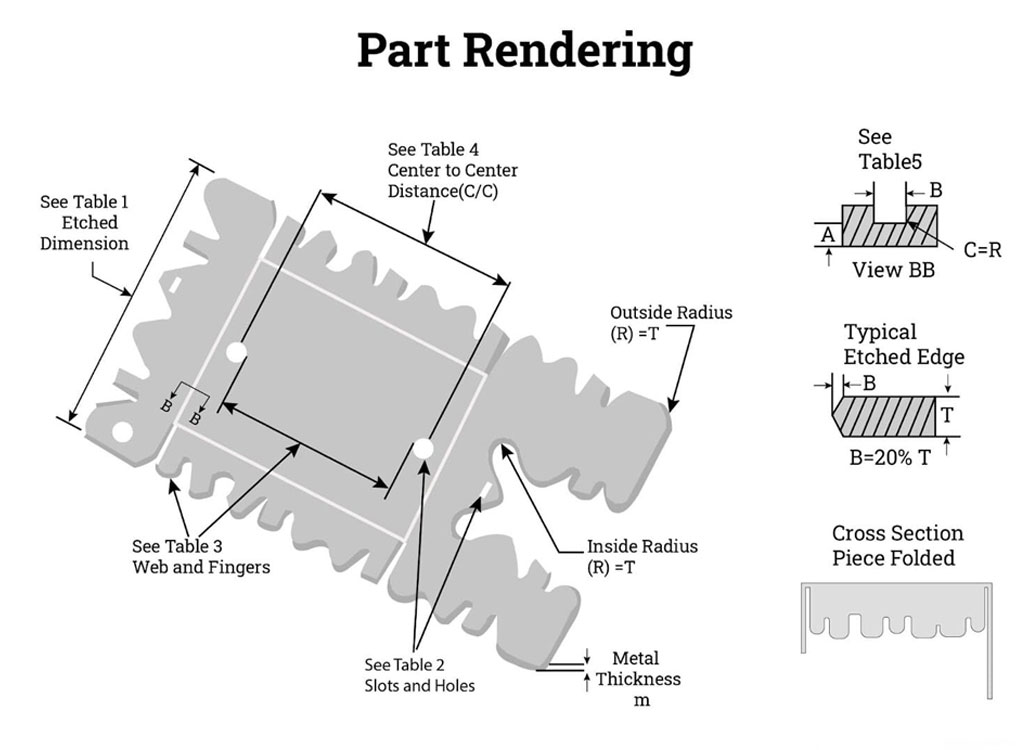
The process of photochemical metal etching begins with creating a design using CAD or Adobe Illustrator. However, this is not the only step involving computer calculations. Once the design is complete, the thickness of the metal and the number of parts that will fit on a sheet of metal are determined to reduce production costs. Additionally, part tolerances depend on part size, which is also related to the thickness of the metal sheet.
#2 Metal Preparation Before Photo Etching Process
As with acid etching, the metal must be thoroughly cleaned before photo machining. Each piece of metal goes through a process of brushing, cleaning and washing with water pressure and mild solvents. This process removes oil, impurities and tiny particles. This is to provide a smooth, clean surface to which the photoresist film can safely adhere.
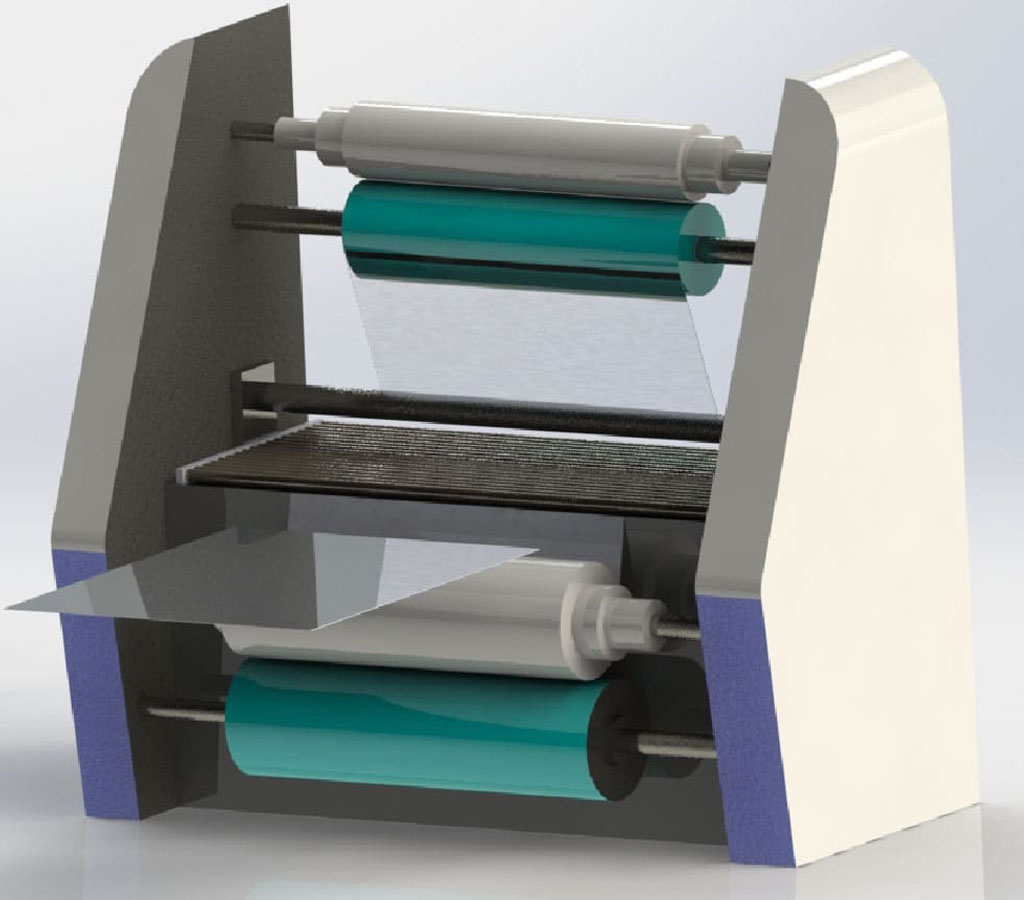
#3 Cover The Metal Plate With A Layer Of Photoresist
Lamination is the application of a photoresist film layer to a metal plate. The metal sheet is moved between rollers, coating and laminating evenly applied. To avoid unnecessary exposure of the metal sheets, the process is carried out in a room illuminated with yellow light to protect it from UV rays. Punch holes on the edge of the metal sheet provide the correct alignment of the sheet. By vacuum sealing the metal panels, air bubbles in the laminate coating are avoided, which results in a smooth laminate layer.
To prepare metal for photochemical metal etching, it must be thoroughly cleaned to remove oil, impurities, and particles. Each piece of metal is brushed, cleaned, and cleaned using mild solvents and water pressure to ensure a smooth, clean surface for photoresist film application.
The next step is lamination, which involves applying a photoresist film to the metal plate. The metal plate moves between rollers to evenly coat and apply the adhesive film. The procedure is performed in a room illuminated by yellow light to prevent UV exposure. Perforating the sheet metal edges provides proper alignment, while vacuum sealing flattens the laminate layers and prevents air bubbles from forming.
#4 Photoresist Film Machining
During photoresist machining, an image from a CAD or Adobe Illustrator rendering is placed over a photoresist layer on a metal plate. The image is printed on both sides of the metal plate by sandwiching CAD or Adobe Illustrator renderings to the upper and lower sides of the metal plate. Once the image has been applied to the metal plates, they are exposed to UV light to permanently fix the image. When UV light is shined through the clear areas of the laminate, the photoresist film hardens and cures. The black areas in the laminate are not affected by UV light and remain soft.
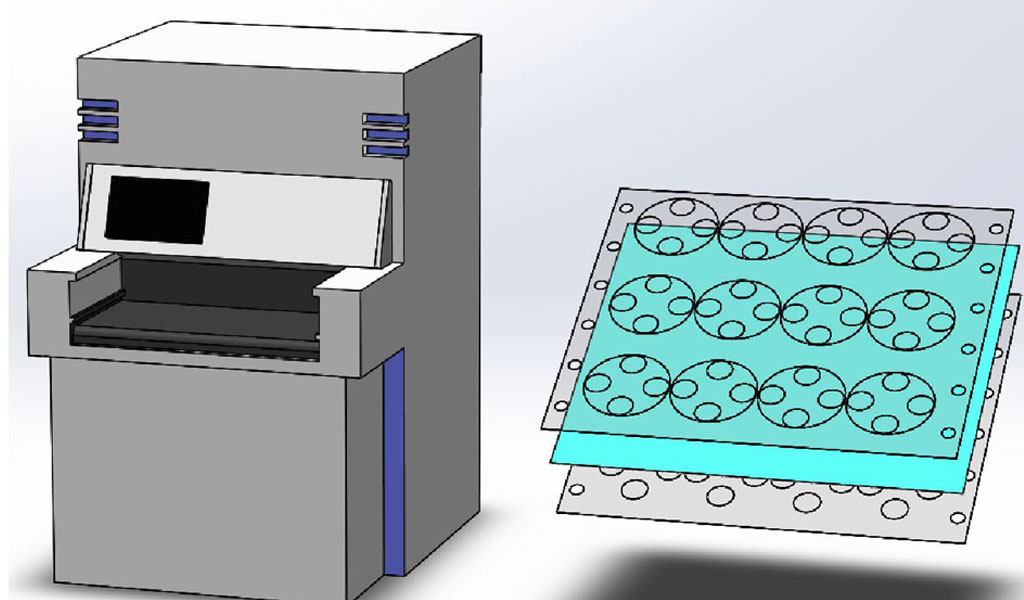
In the photoresist film machining stage of photochemical metal etching, the image of the CAD or Adobe Illustrator design is transferred to the photoresist film layer on the metal plate. This is done by clamping the design to the upper and lower sides of the metal plate. Once the image is applied to the metal plate, it is exposed to UV light, making the image permanent.
During UV exposure, transparent areas in the laminate layer allow UV light to pass through, causing the photoresist film to harden and become stronger. In contrast, the black areas in the laminate layer remain soft and unaffected by UV light. This process creates a pattern that guides the etching process, where hardened areas will remain and soft areas will be etched away.
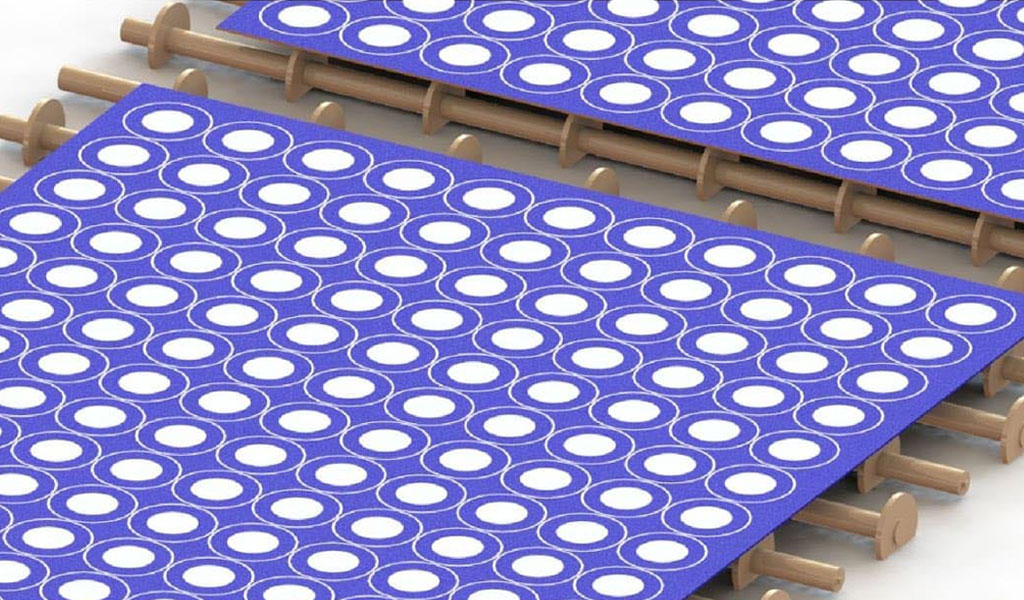

#5 Developed Metal Plate
After being treated with the photoresist film, the metal plate is moved to a developing machine, which uses an alkaline solution, mainly sodium carbonate or potassium carbonate solution, to rinse the metal plate and wash away the soft photoresist film, exposing the part to be etched. come out. This process removes the soft film, leaving only the hardened film, which is the part to be etched. In the image below, hardened areas are colored blue and soft areas are gray. The areas not protected by the hardened layer are exposed metal and will be removed during the etching process.
After the photoresist film machining stage, the metal plate is transferred to a developing machine, where an alkaline solution is used, usually sodium or potassium carbonate. This solution rinses the metal plate, washing away the soft photoresist film and exposing the parts to be etched.
Therefore, the soft adhesive film is removed, while the hardened adhesive film, corresponding to the area to be etched, remains. In the resulting pattern, hardened areas appear in blue and soft areas in gray. The areas not protected by the hardened film represent the exposed metal that will be removed during the etching process.
#6 Precision Etching
Similar to the acid etching process, the developed metal plate is placed on a conveyor belt and passed through a machine where the etchant is poured onto the metal plate. When the etchant comes into contact with exposed metal, it dissolves the metal, leaving the protected parts unaffected.In most photochemical processes, the etchant used is ferric chloride, which is sprayed from the bottom and top of the conveyor belt. Ferric chloride was chosen as the etchant because it is safe to use and recyclable. Copper chloride is used to etch copper and its alloys.
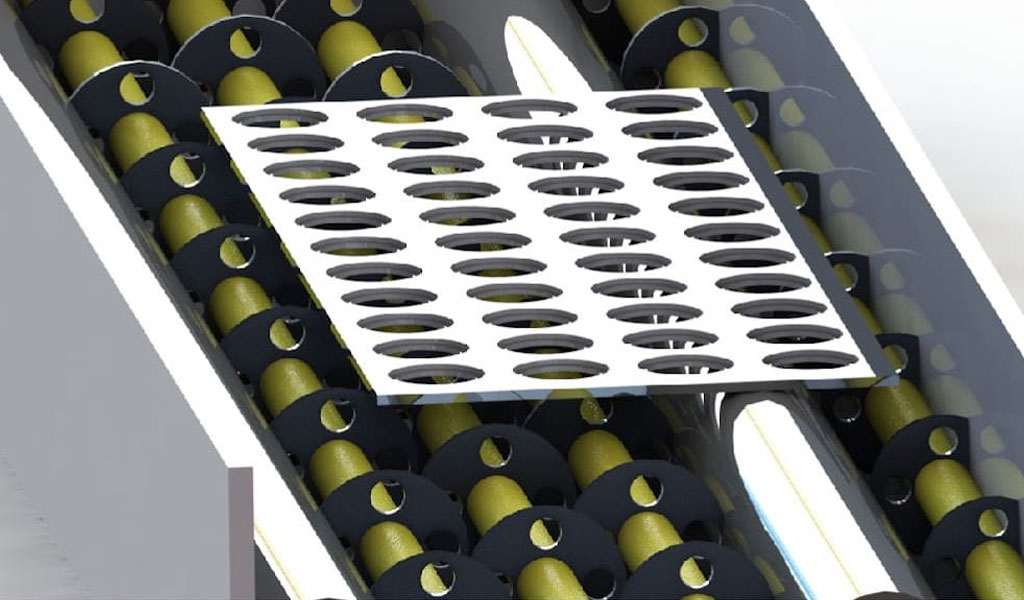
The etching process must be carefully timed and controlled based on the metal being etched, as etching times may vary for different metals. For the success of photochemical etching, careful monitoring and control are crucial.
In the etching stage of photochemical metal etching, the developed metal plate is placed on a conveyor belt and passed through a machine where the etchant is poured onto the metal plate. The etchant dissolves the exposed metal, leaving a protected area on the metal plate.
In most photochemical processes, a commonly used etchant is ferric chloride because it is safe to use and recyclable. For copper and its alloys, cuprous chloride is commonly used as an etchant.
The etching process must be carefully timed and controlled based on the type of metal being etched, as some metals require longer etching times than others. To ensure the success of the photochemical etching process, careful monitoring and control are crucial.
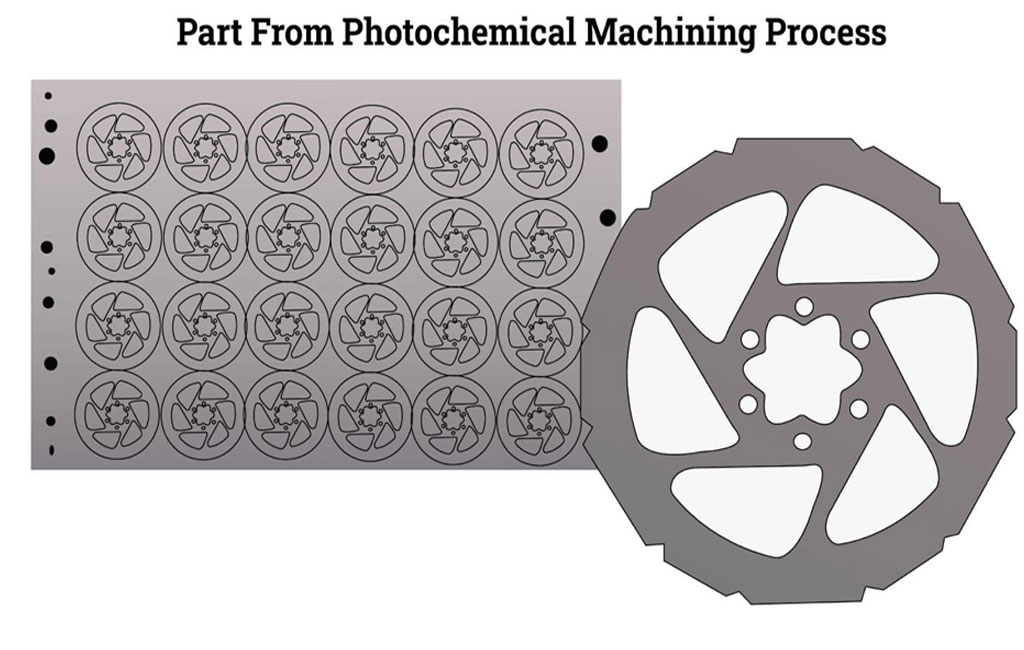
#7 Remove Surplus Adhesive Film
In the process of removing the remaining film, a film remover will be used to remove the remaining film. Once the removal is complete, the final part is obtained, as shown in the image to the right.After the etching process is complete, remove the remaining adhesive film from the metal plate by applying adhesive film remover. This process will remove any remaining adhesive film from the surface of the metal plate.Once the process of removing the adhesive film is complete, the final metal part is left behind and can be seen in the resulting image.
Online Cooperate With Photo Etching Company
We are not resellers of other companies’ parts.That’s because we enjoy making a living by producing, not by earning commissions on other people’s work. We are a true Photo etching service.
Your confidential files won’t be shared with third parties.
Be-cu works with customers all over the world to bring customers ideas to life with the highest quality precision Photo etching on the planet. If you are looking for a partnership to help you apply new tools and technologies, or help you fully realize your design vision, let us help you move your business forward, contact our team ([email protected])or quote online today to get the conversation started.
Metal Etching Certification,Equipment List and Quality
We are committed to enlisting the full support of all employees to continuously improve our processes and enhance quality, thereby fulfilling our customer's needs with defect free products and services, on time and every time
- ISO 9001:2015 certified
- Compliance in DFARS materials sourcing requirements
- Strict compliance with PPAP and Process FMEA
- Fully compliant with the exacting requirements of our customers
- ITAR registered
- NIST cybersecurity standard compliant
- Proprietary Patented quality systems
- Skilled in KanBan and other customer driven quality and inventory management systems
Metal Etching Material
BE-CU is experienced in precision etching various metals, allowing customers the freedom to specify components in hundreds of different materials.
The Surface Treatment Of Metal Etching Parts
Do you want your etching parts to be more corrosion-resistant or get a specific look? Metal finishing service is a essential choice to achieve your design perfectly. BE-CU – metal-etch.com is an accomplished finished parts manufacturer, our workers and craftsman are capable to provide precision metal etching services and a wide range of finishing services including aluminum anodizing, painting, passivation, electroplating, powder coating, polishing, black oxide, conversion coating, abrasive blasting, etc. We offers several common surface finishes to help improve functionality and aesthetics.
- Anodizing (Anodized)
- Passivation
- Plating (Electroplating)
- Painting
- Black Oxide (Hot Blackening)
- Polishing
- Powder Coating
- Heat Treatment
- Satin Finish
- Abrasive blasting (Sandblasting)
- Conversion coating
- Tungsten carbide coating
After browsing a list of metal finishing services, select a process based on essential considerations, like production time, cost-effectiveness, part tolerance, durability and applications. High-tolerance metal etching parts are not recommended to apply secondary metal surface finish, because the treatment may change the sizes of the finished part through removing or adding a small amount of materials.
Other requirements or custom designs, welcome to contact us for a free quote fast!