Homepage » Metal Etching »
Metal Etching Process – The BE-CU Solutions For Etching Parts
Metal etching is a technique that removes material using a chemical reaction or physical impact. Metal etching technology can be divided into two categories: wet etching and dry etching. Metal etching is composed of a series of complex chemical processes. Different corrosives have different corrosion properties and strengths for different metal materials.
Different types of metal have different etching processes, but the general process is as follows: Metal etching plate → Clean and remove oil → Wash → Dry → Apply film or screen printing ink → Dry → Expose pattern → Develop → Washing and drying → etching → film removal → drying → inspection → finished product packaging.
Usually referred to as metal etching, also known as photochemical metal etching, it refers to removing the protective film from the area to be metal etched through exposure plate making and development. During metal etching, it is exposed to chemical solutions to achieve the effect of dissolving corrosion and forming concave and convex or hollow forming effects. It was first used to make printing embossed plates such as copper plates and zinc plates. It is also widely used to reduce the weight of instrument panels, nameplates and thin workpieces that are difficult to process with traditional processing methods. After continuous improvement and development of process equipment, it can also be used Used for the processing of precision metal etching products for electronic wafer parts in the aviation, machinery, and chemical industries. Especially in the semiconductor manufacturing process, metal etching is an indispensable technology.
How Does Precision Metal Etching Work?
Different types of metal have different etching processes, but the general process is as follows:
1.Cleaning Process Before Metal Etching
The process before etching stainless steel or other metals is cleaning. The main function is to remove dirt, dust, oil stains, etc. on the surface of the material. Whether this first process is completed well is a key process to ensure that the film or screen printing ink has good adhesion to the metal surface. Therefore, the oil stains and oxide film on the metal etching surface must be completely removed. The degreasing plan should be determined according to the oil stain of the workpiece. It is best to conduct electrolytic degreasing before the screen printing ink to ensure the effect of degreasing. To remove the oxide film, the best etching solution must be selected according to the type of metal and film thickness to ensure that the surface is clean. It must be dried before screen printing. If there is moisture, it will also affect the adhesion of the ink, and it will also affect the effect of subsequent pattern etching and even aliasing, affecting the etching effect.
2.Apply Dry Film Or Screen Printing Ink Photosensitive Adhesive Layer
According to the actual product material, thickness and precise width of the graphics, dry film or wet film screen printing should be used. For different thickness products, when applying the photosensitive adhesive layer, factors such as the etching processing time required for the product graphics should be taken into consideration, so that Make a thicker or thinner photosensitive adhesive layer, so that the covering performance is good and the pattern produced by metal etching is high-definition.
3.Dry
After the film or roller coating of screen printing ink is completed, the photosensitive adhesive layer needs to be thoroughly dried to prepare for the exposure process. At the same time, it is necessary to ensure that the surface is clean and free of adhesion, impurities, etc.
4.Exposure
This process is an important process for metal etching. The amount of exposure energy will be considered based on the thickness and precision of the product’s material. This is also a reflection of the technical capabilities of an etching processing enterprise. The exposure process determines whether etching can ensure good dimensional control accuracy and other requirements.
5.Develop
After the photosensitive adhesive layer on the surface of the metal etching plate is exposed, the pattern adhesive layer is solidified on the metal plate after being exposed to light. After that, the unnecessary parts of the pattern, that is, the parts that need to be corroded, are exposed. The development process also determines whether the final size of the product can meet the requirements. This process will completely remove the unnecessary photosensitive adhesive layer covering the product.
6.Etching Or Corrosion Process
The most critical process is after the product pre-production process is completed. Chemical liquid etching will be performed. This process determines whether the final product is qualified or not. The entire process involves parameters such as the concentration of the etching solution, temperature, pressure, speed, etc. The quality of the product needs to be determined by these parameters.
7.Remove film
After etching, the surface of the product is still covered with a layer of photosensitive adhesive. This process requires removing the photosensitive adhesive layer on the surface of the product after etching. Since the photosensitive adhesive layer is an acidic substance, most of them use acid-base neutralization method for bulking. After overflow water washing and ultrasonic cleaning, the surface photosensitive adhesive layer is removed. This process mainly prevents photosensitive adhesive residue.
8.After The Film Removal Is Completed
The rest is inspection and packaging. Dimensional inspection ensures that no defective products will flow out to customers.
Common Metal Etching Operations
Understanding Metal etching operations is essential to grasp the full concept of Metal etching. There are three significant operations that you need to be aware of, and we will demystify them for you below.
1.Reduce side etching and protruding edges, and improve metal etching processing coefficient
Lateral erosion produces a bulging edge. Generally, the longer the printed board is in the metal etching solution (or using an old-fashioned left-right etching machine), the more serious the side etching will be. Undercutting seriously affects the accuracy of printed conductors, and severe undercut will make it impossible to produce fine conductors. When the side etching and protruding edges are reduced, the etching coefficient increases. A high etching coefficient indicates the ability to maintain thin wires, making the etched wires close to the original size. Whether the electroplating etching resist is tin-lead alloy, tin, tin-nickel alloy or nickel, excessive protrusion will cause a short circuit in the wire. Because the protruding edge breaks off easily, an electrical bridge is formed between the two points of the wire.
2.Improve the consistency of etching processing rates from board to board
In continuous board etching, the more consistent the metal etching processing rate is, the more uniformly etched boards can be obtained. To meet this requirement, it is necessary to ensure that the etching solution is always in the best etching state during the entire etching process. This requires choosing an etching liquid that is easy to regenerate and compensate, and the etching rate is easy to control. Select processes and equipment that can provide constant operating conditions and automatic control of various solution parameters. This is achieved by controlling the amount of dissolved copper, pH value, solution concentration, temperature, uniformity of solution flow (spray system or nozzle and nozzle swing), etc.
3.Improve the uniformity of metal etching processing rate on the entire board surface
The uniformity of etching on the upper and lower sides of the board and various parts of the board is determined by the uniformity of the metal etchant flow rate on the surface of the board. During the etching process, the etching rates on the upper and lower plates are often inconsistent. Generally speaking, the etching rate of the lower plate surface is higher than that of the upper plate surface. Because there is accumulation of solution on the upper plate surface, the etching reaction is weakened. The phenomenon of uneven etching on the upper and lower plate surfaces can be solved by adjusting the spray pressure of the upper and lower nozzles. A common problem with etching printed circuit boards is that it is difficult to etch the entire board surface cleanly at the same time. The edges of the board etch faster than the center of the board. Using a sprinkler system and oscillating the nozzles is an effective measure. Further improvement can be achieved by making the spray pressure different between the center of the board and the edge of the board, and intermittent metal etching at the front and rear ends of the board to achieve etching uniformity across the entire board.
Pros and Cons of Metal Etching
Understanding the basics of metal etching involves recognizing its advantages and disadvantages, just like any other manufacturing process. Here are some of the pros and cons of utilizing metal etching.
Regarding Mold Opening And Cost: The mold opening cost is relatively low, ranging from 200 to 1,000 yuan under normal circumstances (special glass masks will be more expensive). The design update time is fast, and the design update and template production can be completed within one day at the fastest, and the cost is relatively small.
New Product Development Cycle: New product development for metal etching processing processes can be more flexible and cost-effective. Designers can communicate with us in advance when developing new products, so that some design defects can be avoided through discussions between both parties. For example: the designed material thickness, the designed processing control accuracy, the smallest hole that can be etched, the smallest gap, etc. You can send the design drawing to the email address: [email protected] in advance for pre-discussion. Or contact: Liu Sheng 135 3425 7051
Some Special Functions That Metal Etching Manufacturing Can Achieve: Metal etching processing can achieve concave and convex effects that cannot be achieved by stamping, cutting or CNC: such as some LOGOs, brand logos, etc., with strong three-dimensional effect, arbitrary patterns, and high precision.
Some Common Controllable Accuracies For Metal Etching Manufacturing: Based on the material material and thickness, the processing accuracy of our factory can be converted into approximately 10% of the material thickness. For example, for 0.1mm thick stainless steel, the controllable accuracy is +/-0.01mm.
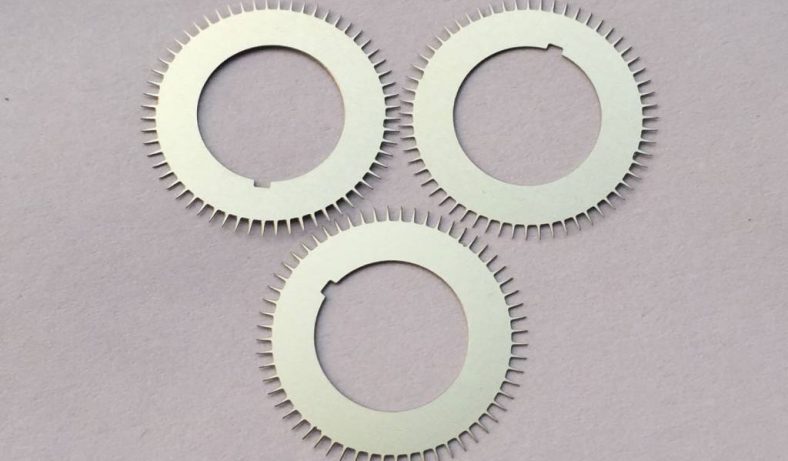
Some Shapes That Can Be Machined By Metal Etching: almost any shape. Depending on the thickness of the material, the smallest opening that can be opened in the shape will be different. The thicker the board, the larger the shape gap that can be opened. Products with complex shapes can also be etched without additional costs.
Metal Etching Can Process Some Material Thicknesses: the most ideal state is: 0.05mm-0.5mm thickness range. At present, the thickness of the materials that our factory can process is controlled at 0.02mm-2.0mm. The thicker the plate, the longer the etching process will take and the relative cost will be higher. At the same time, the processing cost of ultra-thin materials will not be low, and operations such as process control and deformation prevention require special treatment.
Etching Can Process Some Materials: In theory, all metal materials can be corroded or etched. It’s just that different chemical formulas are used for different materials. Materials with good corrosion resistance, such as gold and silver, even require aqua regia-type etching formulas to etch. Considering risk factors and mass production, most of our factory uses SUS304 and SUS316 stainless steel for etching processing, and all copper materials, copper alloys, and molybdenum sheet materials can be etched.
Special Advantages Of Etching: Because metal etching is etched with chemicals.
- The most significant advantage is that the product is highly consistent with the raw materials. It does not change the properties of the material, does not change the stress of the material (except for semi-etched surfaces), does not change the hardness, tensile strength, yield strength and ductility of the material. During the base processing process, etching is carried out in an atomized state in the equipment, and there is no obvious pressure on the surface.
- No burrs: There is no punching force throughout the product processing process, so there will be no curling, protrusions, or pressure points.
- It can be used in conjunction with post-process stamping to complete the separate molding action of the product. It can use hanging points to perform full-page electroplating, adhesive backing, electrophoresis, blackening, etc., which is relatively more cost-effective. For details on how to design hanging points, please contact Mr. Liu: [email protected];135 3425 7051
- Miniaturization and diversification can also be dealt with, and the cycle is short and the cost is low. This provides a better solution for some small or unicorn companies at home and abroad, using our specialized sample preparation team to achieve fast delivery while ensuring product quality.
Connection Point Design Method For Metal Etching Machining
| Thickness mm | Concave Design | Concave Design | Protruding Design | Protruding Design |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness mm | Erosion Depth | Eclipse Width | Projection Height | Bulge Width |
| 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.60 | 0.05-0.15 | 0.12-0.15 |
| 0.15 | 0.2 | 0.75 | 0.05-0.15 | 0.12-0.15 |
| 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.90 | 0.05-0.15 | 0.12-0.15 |
| 0.25 | 0.2 | 0.90 | 0.20 | 0.12-0.15 |
| 0.30 | 0.3 | 1.00 | 0.20 | 0.2 |
| 0.40 | 0.35 | 1.30 | 0.20 | 0.3 |
| 0.50 | 0.4 | 1.50 | 0.30 | 0.4 |
| 0.60 | 0.4 | 1.60 | 0.36 | 0.4 |
| 0.70 | 0.4 | 1.65 | 0.30 | 0.5 |
| 0.80 | 0.45 | 2.40 | 0.40 | 0.5 |
| 1.00 | 0.45 | 2.50 | 0.40 | 0.5 |
Chemical Etching Solution Formula And Process Conditions
Etching different metals requires different solution formulas and process conditions. The etching solution formulas and process conditions for commonly used metal materials are shown in Table 6-4~Table 6-6.
| Solution Composition And Process Conditions | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferric Chloride(FeCl3)/(g/L) | 800~900 | 450~ 560 | 600~ 800 | 600~ 650 | 450~ 550 |
| Hydrochloric acid (HC)/(g/L) | 100~ 120mL/L | 5~ 10mL/L | 80~ 120 | ||
| Hydrofluoric acid (HF)/ (mL/L) | 80~ 120 | ||||
| Phosphoric Acid (H3P04)/(g/L) | 20~30 | ||||
| Copper Sulfate (CuS04)/(g/L) | |||||
| Copper Sulfate (CuS04)/(g/L) | 200~ 300 | ||||
| Sulfuric Acid (H2S04)/(g/L) | 90~ 100 | 10~20 | |||
| Nitric Acid(HN03)/(g/L) | 8~ 12 | ||||
| Etching Accelerator/(g/L) | 5~ 8(Leveling Agent) | 80~ 100 | |||
| Kerosene/(g/L) | Small Amount | ||||
| Solution Temperature/C | 20~ 50 | 20~ 50 | 10~45 | 15~ 50 | 20~40 |
| Processing Time/min | 15~25 | 15~ 20 | 10~15 | 10~ 20 | |
| Applicable Materials | Steel | Die Steel | Stainless Steel | Copper Alloy | Cast Aluminum |
| Solution Composition And Process Conditions | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitric Acid(HN03)/(mL/L) | 1000 | 1000 | – | 50 |
| Sulfuric Acid (HzS04)/ (mL/L) | 20 | – | 900~ 1000 | |
| Chromic Anhydride (Cr03)/(g/L) | – | 50 | ||
| Sodium Chloride (NaC)/ (g/L) | 45 | 40~ 50 | 400 | 10~20 |
| Solution Temperature/C | 20~ 30 | 60~ 80 | 20~ 30 | 60~ 80 |
| Etching Time/min | 15~20 | 10~15 | 15~20 | 10~ 15 |
| Solution Composition And Process Conditions | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitric acid (HN03,65%)/ (mL/L) | 800~ 1000 | ||
| Hydrochloric acid (HC!, 37%)/(9/L) | 210~ 240 | 150~ 300 | |
| Solution Temperature/C | 20~ 30 | 20~30 | 25~ 50 |
| Etching Time/min | Depends On Etching Depth | Depends On Etching Depth | Depends On Etching Depth |
The Effect Of Process Operating Conditions
Etching is the key to the pattern decoration process of metal templates. If you want to obtain patterned products with clear stripes and strong decorative properties, you must pay attention to controlling the conditions of the etching process. Mainly the temperature of the etching solution and the etching time. Slightly higher temperature of the solution can increase the speed of metal dissolution, that is, the speed of etching, and shorten the time required for etching. However, etching solutions are generally strong acid solutions. Strong acid solutions are highly corrosive at high temperatures and can easily cause damage to protective equipment. The coating or corrosion-resistant ink softens or even dissolves, which reduces the adhesion of the corrosion-resistant layer on the non-etched parts of the metal, causing the corrosion-resistant coating at the junction of etching and non-etching to fall off or melt, making the etching pattern blurry and distorted, affecting the pattern. It has a beautiful, real and decorative effect, so the temperature should not exceed 45℃.
Similarly, if the etching time is too long, especially when the temperature of the etching solution is high, the corrosion-resistant ink or protective coating will be immersed for too long, which will also have the above-mentioned side effects and adverse consequences. Therefore, time control must also be appropriate. , should not be soaked for too long, generally not more than 20 to 25 minutes.
The Discovery Of The Principle Of FeCl3 Metal Etching
Fecl3 metal etching is one of the earliest processing methods used for copper and Taiwan gold etching. With this method, raw materials are easy to obtain, cheap, simple to prepare, and easy to operate. Therefore, this method has been widely used, even now It is also used by many copper etching factories. However, this method causes serious environmental pollution and is gradually replaced by other corrosion methods.
Fecl, the corrosion of copper is a redox process. On the copper surface, Fe3+ is oxidized to Cucl3 and Fe3 is reduced to Fe3+.
Introduction To FeCl3 Etching Principle
1.The effect of FeCL3 concentration on etching speed
As the concentration of FeCL3 in the FeCL3 etching solution increases, the etching speed accelerates. When the FeCL3 content exceeds a certain concentration, the etching speed decreases due to the increase in solution viscosity.
2.The effect of the amount of hydrochloric acid added on the etching speed
adding hydrochloric acid to the etching solution can, on the one hand, inhibit the hydrolysis of FeCL3 and CuCL2; on the other hand, it can increase the etching speed. Especially when the copper content in the etching solution reaches 37.4g/L, the effect of hydrochloric acid becomes more obvious.
3.Effect of temperature on etching speed
In the FeCL3 etching process, as the temperature increases, the etching speed also accelerates. For example, when the temperature is 50 degrees, the etching speed of copper with a new etching solution can reach 10um/min. However, in actual production, room temperature etching method is used. The etching of copper by FeCL3 is an exothermic reaction. As the etching proceeds, the temperature of the etching solution will gradually increase and the etching speed will accelerate. As FeCL3 is consumed, the etching rate decreases. At the same time, this temperature rise process is relatively slow, so the etching speed does not change much during the entire etching process.
4.Effect of stirring on etching speed
The speed and etching quality of static etching are relatively poor. This is because during the etching process, on the one hand, there will be precipitates on the etched copper surface and in the etching solution, which affects the normal etching of copper; on the other hand, during the etching process of copper, the solution on the etched surface will gradually turn dark green. , which indicates that the FeCL3 on the etched surface has undergone a reduction reaction with the copper surface and lost its oxidizing ability.
Cu+FecI,一cucl十Fe~:1
Cucl ions have reducing properties and further react with Fe¨ in the corrosion liquid leaf J to generate cucl.
Cucl+FeCl、一Cucl2+FeCl 2
The generated Cucl2 is oxidizing and will also undergo a redox reaction with copper.
Cu+c∞12——2cucl (5—43)
Conclusion On Metal Etching Principles:
FeC: l, the metal etching liquid relies on Fecl and cucl: to be completed at the same time. Among them, n¨ has strong oxidation ability, fast etching speed and good etching quality. Relatively speaking, the etching speed of CucI2 here is relatively slow and the etching quality is poor. With the consumption of Fe3 in the etching solution and the increase of cuCL2, the etching speed gradually slows down and the etching quality deteriorates. When Fe3 consumption reaches 50%, both the etching speed and etching quality will be detrimental to continuing the etching process. Instead, the etching fluid should be replaced.
In actual production, the etching efficiency of the metal etching solution is not measured by the consumption of Fe3, but by the dissolved amount of copper in the etching solution (unit: g/l). When copper is in FeCl3 etching solution, the initial etching rate is constant. However, with the consumption of Fe¨ in the etching solution, the copper content in the etching solution continues to increase. When the amount of dissolved copper reaches 60g/L, the etching speed will slow down. When the consumption of Fe3 in the etching solution reaches 40%, or the dissolved copper When the amount reaches 83g/L, the etching speed will drop sharply. At this time, the etching solution can no longer be used, and the regeneration or update of the etching solution should be considered.
The acidity of the commonly used FeCl 3 etching solution is not high, so when the FecL3 etching solution is etching copper, it is also accompanied by the hydrolysis side reaction of FeCl and CuCl:
- Fecl,+3H:O—Fe(OH)3 J+3HCI
- cucl2+2H20一cu(on)2 +2HC:l
The generated oxychloride is unstable and easily decomposes into corresponding oxides and water when heated. Some of these oxides precipitate at the bottom of the etching tank to form loess-like sediments, and some are suspended in the etching liquid, causing certain damage to the resist layer.
- 2Fe(OH),一Fe202+3H3O
- cu(OH)2—cuO +H2O
The Characteristics Of Metal Etching Process
- Targetedness. The so-called targeted nature means that there is a clear output through the entire process of a certain process, or that a certain specific purpose is to be achieved. For metal etching, this purpose is to meet the product requirements of its design drawings. More specifically, these requirements include the etching size requirements of the product, the surface roughness requirements after etching, etc.
- Inherence. The so-called immanence means that a technological process must have its own specific content, which can also be said to be the reality of the content. These contents are included in each step of the process and the behavior of all operators involved in these steps.
- Integrity. The so-called integrity means that the process flow must consist of at least two or more processes. Because, as a process, the technological process cannot be completed by one processing step, and at the same time, one processing step cannot complete the flow in the technological process. At least two or more steps and their related activities are required to establish a process. Only the basic structure or relationship can be transferred. For the metal etching process, it is also a complete process specification unity composed of multiple processes, process parameters of each process, tools and related equipment specified in each process, and they are inseparable from each other.
Exposure Principle Of Metal Etching
First, the pattern to be etched is transferred to two identical film films by photolithography, or transferred to two identical glass films by photolithography. Then align the film through manual alignment or machine alignment. Then place the steel piece that has been coated with photosensitive ink or photosensitive dry film in the middle of the film, and it can be exposed after inhalation. During exposure, the steel sheet corresponding to the black part of the film is not exposed to light, and the steel sheet corresponding to the white part of the film is exposed to light, and the ink or dry film in the photosensitive area of the steel sheet undergoes a polymerization reaction. Finally, after passing through the developing machine, the photosensitive ink or dry film on the steel sheet is not dissolved by the developer, and the unsensitized ink or dry film is dissolved and removed by the developer. In this way, the pattern to be etched is transferred to the steel sheet through exposure.
Exposure is under ultraviolet light irradiation. The photoinitiator absorbs light energy and decomposes into free radicals. The free radicals then initiate the polymerization and cross-linking reaction of non-polymerizable monomers. After the reaction, a macromolecular structure insoluble in dilute alkali solution is formed. Exposure is generally carried out in an automatic surface exposure machine. Today’s exposure machines are divided into air-cooled and water-cooled according to the cooling method of the light source. Exposure imaging quality In addition to the performance of the dry film photoresist, the selection of the light source, the control of the exposure time (exposure amount), and the quality of the photographic plate are all important factors that affect the exposure imaging quality.
When the exposure is insufficient, due to incomplete monomer polymerization, the film swells and becomes soft during the development process, the lines are unclear, the color is dim, and even degummed. During the etching process, the film warps, bleeds, and even falls off; when exposed, Excessive use will cause problems such as difficulty in developing, brittleness of the film, and residual glue. Exposure will produce deviations in image line width. Excessive exposure will make graphic lines thinner and product lines thicker. The appropriate exposure time is determined based on the brightness of the dry film after development, whether the image is clear, and whether the image line width is consistent with the original film.
Principle Of Roller Coating Protective Oil Before Etching Process
Make the rubber roller and the steel wheel parallel and rotate inward at a constant speed. The ink is sprayed from the rubber tube to the steel wheel. By evenly adjusting the tightness between the rubber roller and the steel roller, you can control the thickness of the ink adhering to the rubber roller. and uniformity; the steel sheet is pushed forward by the conveyor belt at a constant speed and properly contacts the rubber roller, and the ink on the rubber roller is evenly transferred to the surface of the steel sheet. Coating technology is widely used in the production of etching anti-corrosion layers. Commonly used coating methods include silk screen printing, dip coating, spray coating, electrophoretic coating, etc. The surface of the coated anti-corrosion layer should be uniform and complete, without blisters, white spots, etc. If the anti-corrosion layer is found to have the above quality defects, and these defects are near graphic lines, especially fine graphic lines, the anti-corrosion layer should be removed. Layers are recoated. After the photosensitive ink sprayed on the workpiece dries, a quality inspection is performed before exposure. Inspection items include no scratches or pores on the ink surface, and the uniformity of the ink roll coating. If this requirement is not met, the ink on the entire board should be removed and re-rolled.
- *The adhesion between the photoresist and the steel sheet is achieved by the flow of the photoresist film along the surface of the steel sheet.
- *Heating can reduce the viscosity of the photoresist and increase its fluidity, and pressure can squeeze the fluid photoresist into the surface of the steel sheet.
The Principle Of Roller Coating Before Metal Etching
When applying the film, first peel off the polyethylene film from the film, and then paste the dry resist layer on the stainless steel material under heating and pressure conditions. The photoresist layer in the dry film softens after being heated and its fluidity increases. The film application process is completed with the help of the pressure of the hot roller and the action of the adhesive in the photoresist layer. Dry film photoresist is a photosensitive material developed in the early 1970s. So far, a variety of products have been used to meet different production needs. Dry film has good process performance, excellent imaging properties and chemical resistance, and has been widely used in circuit board manufacturing, graphic production and cutting of precision parts.
Metal Etching Cannot Be Used To Machine Narrow And Deep Grooves
This is because the bubbles generated during the chemical etching reaction of the metal will accumulate under the edge of the anti-corrosion layer, and these bubbles blocked under the anti-corrosion layer actually act to isolate the metal surface from the corrosive agent. As a result, a very irregular corrosion is caused and a very irregular edge is formed, which is a troublesome problem for large-depth additions. Although some anti-corrosion materials with good performance are soft and easy to discharge bubbles, after processing to a certain depth, even the mechanical stirring method is not enough to completely discharge the bubbles at the edge of the anti-corrosion layer. However, when the processing reaches a certain depth, After the depth is reached, even the method of machine mold stirring is not enough to completely discharge the bubbles at the edge of the anti-corrosion layer. The most effective method for this kind of processing is to use a time-consuming manual method to smooth the anti-corrosion layer on the edge of the pattern. Another possible reason is the surface tension of the corrosive liquid. This situation will also cause corrosion failure on surfaces with narrow or small radius. For groove processing with large depth, the width is required to be no less than 4mm, and for deep groove processing, the width is not less than 4mm. Small grooves or round holes require a width or radius not less than 1.5 times the depth.
The Harm To Workers Caused By Acids And Alkalis In Etching And Their Treatment
1.Harm of hydrochloric acid to workers and treatment
High concentrations of hydrochloric acid can irritate the nasal mucosa and conjunctiva, causing corneal turbidity, hoarseness, suffocation, chest pain, rhinitis, cough, and sometimes blood in sputum. Hydrochloric acid mist can cause severe pain in the skin of the eyelids. If an accident occurs, the injured person should be immediately moved to fresh air to provide oxygen, clean the eyes and nose, and rinse the mouth with 2% soda water. If concentrated hydrochloric acid splashes on your skin, you should immediately rinse it with plenty of water for 5-10 minutes, and apply soda slurry to the burned surface. Severe cases should be sent to hospital immediately for treatment. The maximum allowable concentration of hydrochloric acid in the air is 5mg/m3
2.H3PO4 hazards to workers and treatment
H3PO4 vapor can cause atrophy of the nasal mucosa, has a strong corrosive effect on the skin, can cause skin inflammation and muscle damage, and even cause systemic poisoning. The maximum allowable amount of H3PO4 in the air is 1mg/m3. If you accidentally come into contact with your skin during work, you should immediately rinse it with plenty of water. After washing away the H3PO4, you can generally apply mercurochrome or gentian violet solution to the affected area. In severe cases, you should be sent to the hospital for treatment.
3.Commonly used materials for metal etching
stainless steel SUS304 SUS301 Introduction to mechanical properties: For the etching process, the material properties of SUS304 are more suitable for etching processing. The performance of SUS301 is relatively hard, and the etching will have defects such as burrs and uneven hole walls.
The Choice Of Metal Etching Methods
There are two main methods of metal etching based on the contact form of the workpiece with the solution, namely spray etching and bubble etching. There are two principles for selecting etching methods.
- Production volume: Spray etching has high efficiency, fast speed and high precision, and is suitable for certain batch production. The production is easy to realize automatic control, but the equipment investment is large, and it is not suitable for etching special-shaped workpieces and large workpieces; The investment of bubble etching equipment is small, etching is convenient, and the range of workpieces used is wide.
- Workpiece shape and size: Due to equipment limitations, it is difficult to use spray etching for large workpieces, while the immersion etching method will not be affected by the size of the workpiece. The shape of the workpiece is complex. During spraying, some parts may not be sprayed in place, which will affect the normal progress of etching. The soaking type soaks the entire workpiece in the etching solution. As long as the dynamic between the solution and the workpiece is maintained , it can ensure that all parts of the heterogeneous workpiece can be filled with etching liquid and the new liquid and old liquid can be continuously replaced, so that etching can proceed normally.
For small flat or nearly flat workpieces, if conditions permit, spray etching is superior to bubble etching in terms of efficiency and accuracy. Therefore, for workpieces with a large batch size, moderate size, and simple shape, the spray type is the first choice; if the workpiece is large in shape, it is difficult to use an etching machine, the workpiece has a complex shape, and the batch size is not large, the soaking type is the best choice. The formula is appropriate.
The Post-processing Issues Of Metal Etching Workpieces
After the protective film on the etched workpiece is removed, the shiny metal color is revealed. For example, brass decorative parts, nameplates, and unetched convex areas are bright golden yellow. The etched recesses are matte or matte, with clear layers. After rinsing and passivation, the surface is covered with protective paint, which is the finished product. The etched recesses are also filled with various colored paints to form colorful patterns and then covered with protective paint. After the high-end handicrafts are stripped, they often need to be electroplated, plated with alloy or real gold or silver, and then filled with paint or directly varnished. There is also partial electroplating. For example, the protective film is not removed, and other colors are plated on the etched parts, and then the protective film is removed. This is a two-color product of gold and silver. It looks exquisite, gorgeous and noble. In the past, some people used self-drying paint for varnishing, which looked good but was not durable. Nowadays, drying paint, UV-curable paint or electrophoretic paint are mostly used. For parts made of stainless steel used in industrial products, the protective film is usually removed and cleaned. Of course, if there are special requirements, surface coloring, passivation or coating may also be required.
Environmental Issues During Metal Etching Processes
The factors affecting the metal etching process are mainly acid, alkali and ferric chloride. The waste coating must be properly disposed of and cannot be discharged casually. Acid and alkali wastewater are generally treated by neutralization methods. During the etching process, there are alkaline wastewater and acidic wastewater. They can neutralize each other. Of course, it is impossible to have an acid-base balance, so PH needs to be detected. Value, make up for whatever is missing, so that the pH value meets the discharge requirements. At the same time, excess metal ions must be removed. After precipitation, the clean water can be discharged. The environmental pollution caused by ferric chloride waste liquid is mainly due to its image. Wherever it touches, there will be a piece of yellow rust, which is very ugly and damages the environment. The waste coating should be canned and recycled by professional processing units. For the treatment of wastewater containing ferric chloride, the most common treatment method is to add lime milk, which not only neutralizes acid, but also precipitates ferric iron and other metal ions in the wastewater, and has a positive effect on the wastewater. The impurities have agglomeration effect.
The Role Of Degreasing Before Etching
The purpose of degreasing is to remove grease from the metal surface. As a job that requires metal etching, whether it is processing circuit boards, general mechanical parts or decorative workpieces, or whether it is processing aerospace parts or high-demand workpieces such as ships. . Among these workpieces to be processed, some require graphic etching, some require structural etching, and some only require overall chemical etching on one or both sides of the workpiece. The surfaces of these workpieces must first be effectively cleaned. An ideal clean surface must be a surface that is free of grease, rust, and oxide scale, and at the same time washes away various markings, symbols, and other insoluble foreign substances. The purpose of this cleaning action is to ensure the adhesion of the anti-corrosion layer on the metal surface and the indispensable conditions for uniform etching rate.
The Role Of Water Washing In The Etching Process
Water washing is a frequently used step in the entire process of metal etching. Water washing must be performed after each treatment. The purpose of water washing: 1. To wash away the alkaline or acidic liquid film attached to the surface of the workpiece taken out from the alkaline or acidic solution and replace it with a clean water film, thereby becoming a clean surface; 2. To transfer the workpiece from a process When going to the next process, the solution of the previous process will not be brought into the solution of the next process. Therefore, water washing is an important process that affects the quality of the metal etching process.
The Control Of Metal Etching Process
The guarantee of metal etching quality mainly comes from the control of the etching process. The control of the metal etching process is divided into chemical parameter control and physical parameter control.
1.Chemical Parameter Control
Chemical parameter control is very critical to maintaining a uniform etching rate of the etching solution. Chemical parameter control mainly includes the control of the solution concentration and the proportion control between the components in the solution. Regarding the control of these two aspects, the concentration of the former is easy to control, and the consumption of components in the solution can be determined through analytical methods. The latter is more difficult to control mainly because the content of added substances in the etching solution is low, and may be some materials that are difficult to analyze, or it is difficult to separate from the main materials in the etching solution.
The basis for chemical parameter control comes from the analysis of solution components rather than empirical estimates. Of course, for some small factories, it is not excluded that the operator can make further adjustments by observing the intensity of the etching process, the state of the etched metal surface, and changes in the color of the solution. Make adjustments based on experience and satisfy a certain degree of controllability. This method has certain practicability for etching solutions with a single composition. However, for workpieces with complex composition and high requirements for uniformity of metal etching depth, this method has great limitations and is difficult to ensure mass production. need. From the perspective of ensuring stable product quality, the etching factory is required to use the analysis results as a basis for adjusting the etching solution.
The analysis cycle of chemical etching solutions is mainly affected by the following factors:
- The volume of the solution;
- The initial concentration of the solution;
- The load per unit volume;
- The etching amount (generally in days).
It is easy to understand the influencing factors in these aspects. When the solution volume is small, the initial concentration of the solution is low, and the load per unit volume is large, the faster the change rate of the etching solution composition is, the shorter the analysis period will be, and vice versa. Generally speaking, if the volume of etching solution is not large, it should be analyzed once per shift in the case of mass production (the shift here is calculated based on a production cycle of 8 hours).
2.Physical Parameter Control
The control of physical parameters is divided into general parameter control and other parameter control determined by the etching method. General parameter control is mainly to control time and temperature during the etching process: other parameter controls determined by the etching method include control of the degree of stirring of the solution for immersion etching and control of the spray pressure for spray etching. Within the controllable range of chemical parameters, the control of physical parameters is very important to maintain a constant etching rate and etching uniformity. The control of physical parameters is much easier and more intuitive than the control of chemical parameters. At the same time, some equipment has automatic control devices for temperature, time and injection pressure. You only need to input these parameters in advance.
Any metal etching must have two indicators that need to be controlled, namely depth and surface smoothness. Although changes in physical and chemical factors will have an impact on the etching depth and surface smoothness, under the determined etching liquid composition and concentration, the impact on the depth is mainly physical factors. Under the premise of constant temperature and pressure, The factor that ensures the etching depth index is the etching time. In actual production, the etching depth is also controlled by time. As for surface smoothness, although changes in temperature will have a certain impact, it is mainly affected by the chemical composition of the etching solution. Adding substances to the chemical group has a greater impact on surface smoothness than the main etching agent. At the same time, adjustment is more difficult, but it can be controlled by determining an empirical value of consumption per unit area through experiments.
Metal Etching Certification,Equipment List and Quality
We are committed to enlisting the full support of all employees to continuously improve our processes and enhance quality, thereby fulfilling our customer's needs with defect free products and services, on time and every time
- ISO 9001:2015 certified
- Compliance in DFARS materials sourcing requirements
- Strict compliance with PPAP and Process FMEA
- Fully compliant with the exacting requirements of our customers
- ITAR registered
- NIST cybersecurity standard compliant
- Proprietary Patented quality systems
- Skilled in KanBan and other customer driven quality and inventory management systems
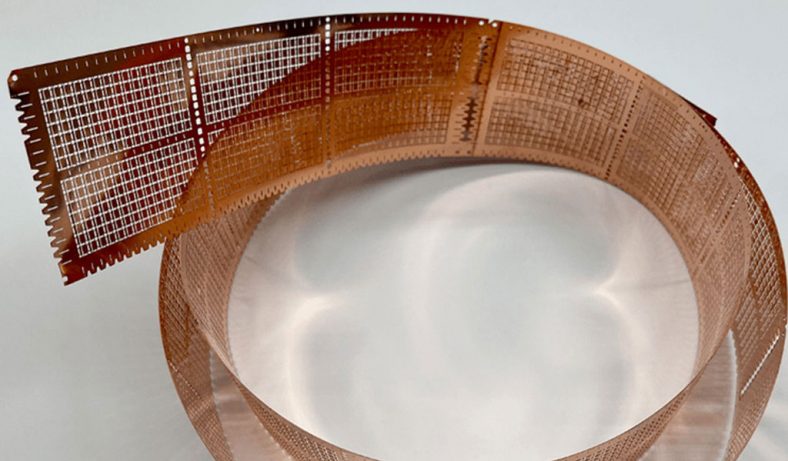
Metal Etching Material
BE-CU is experienced in precision etching various metals, allowing customers the freedom to specify components in hundreds of different materials.
The Surface Treatment Of Metal Etching Parts
Do you want your etching parts to be more corrosion-resistant or get a specific look? Metal finishing service is a essential choice to achieve your design perfectly. BE-CU – metal-etch.com is an accomplished finished parts manufacturer, our workers and craftsman are capable to provide precision metal etching services and a wide range of finishing services including aluminum anodizing, painting, passivation, electroplating, powder coating, polishing, black oxide, conversion coating, abrasive blasting, etc. We offers several common surface finishes to help improve functionality and aesthetics.
- Anodizing (Anodized)
- Passivation
- Plating (Electroplating)
- Painting
- Black Oxide (Hot Blackening)
- Polishing
- Powder Coating
- Heat Treatment
- Satin Finish
- Abrasive blasting (Sandblasting)
- Conversion coating
- Tungsten carbide coating
After browsing a list of metal finishing services, select a process based on essential considerations, like production time, cost-effectiveness, part tolerance, durability and applications. High-tolerance metal etching parts are not recommended to apply secondary metal surface finish, because the treatment may change the sizes of the finished part through removing or adding a small amount of materials.
Other requirements or custom designs, welcome to contact us for a free quote fast!