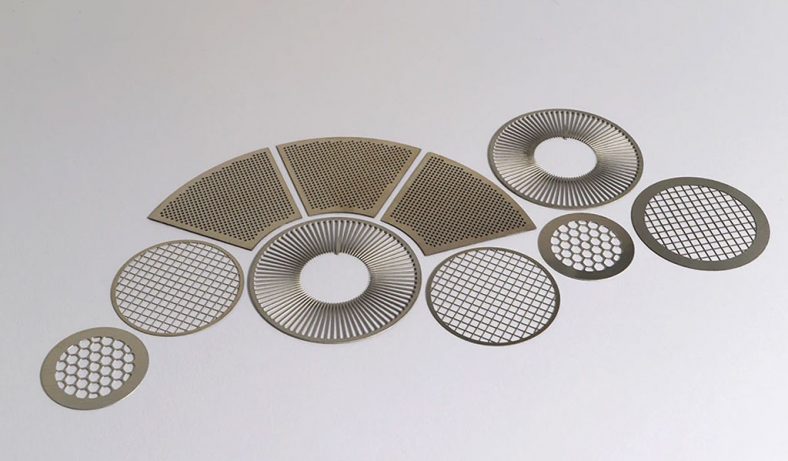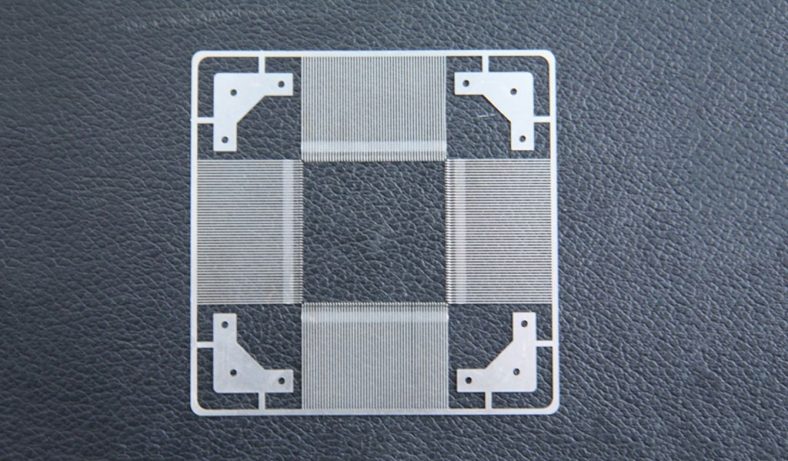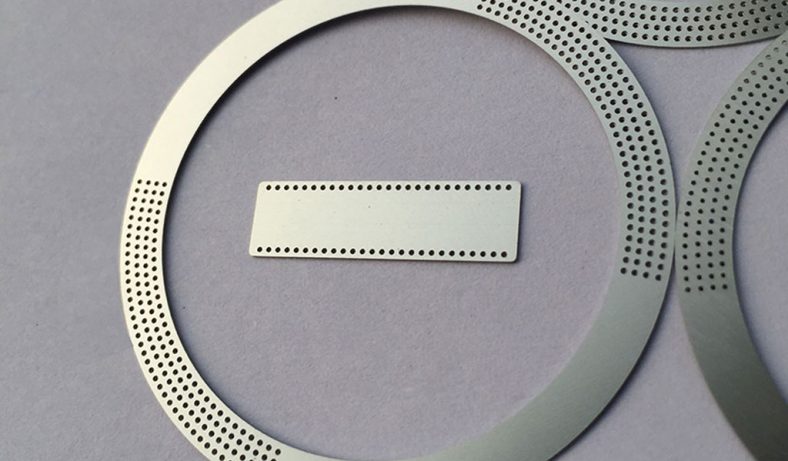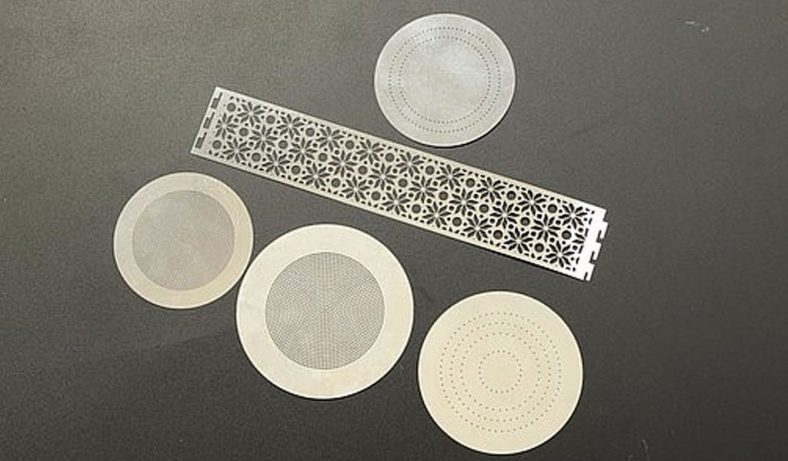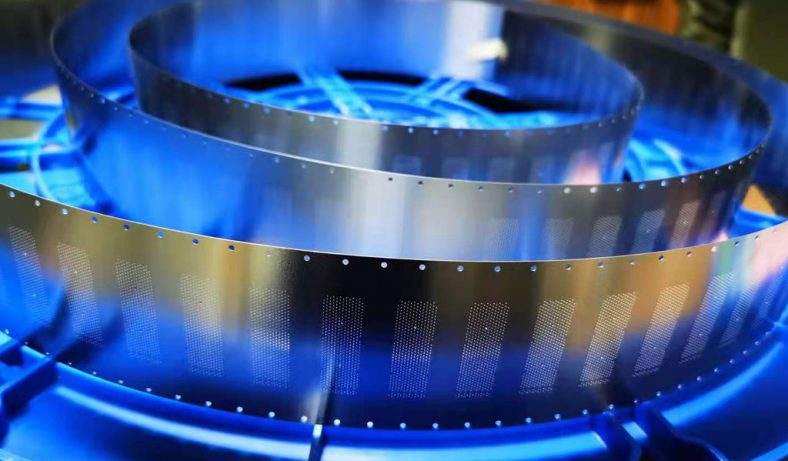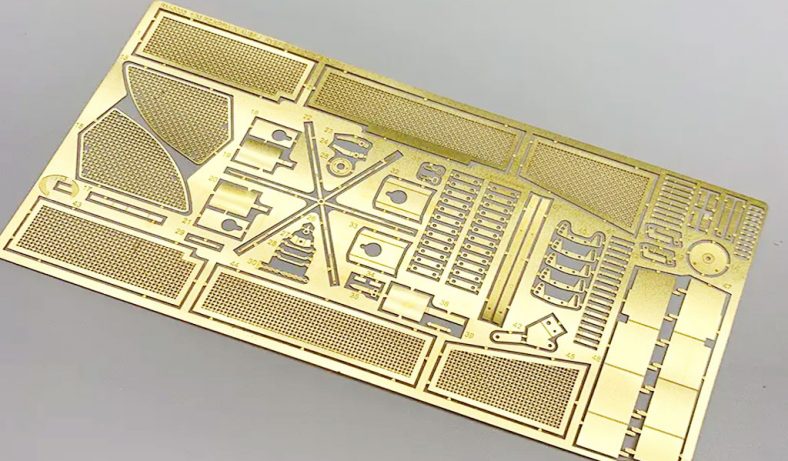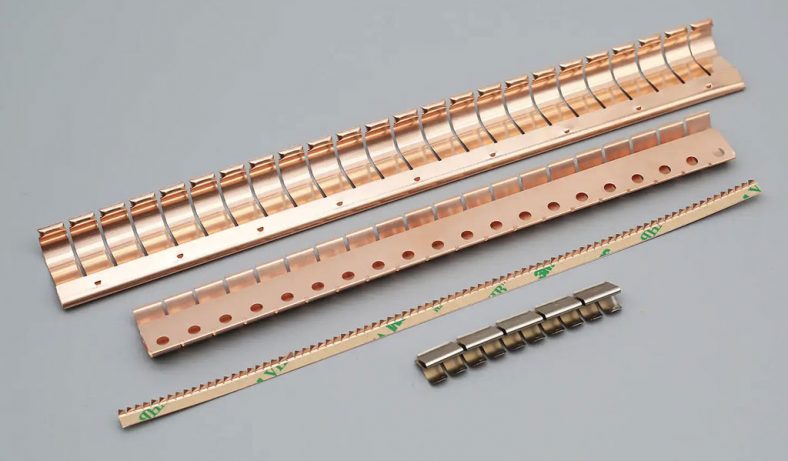
Metal etching, a precise and versatile manufacturing process, plays an integral role in the electronics industry, contributing to the production of a variety of essential components. The process involves selectively removing material from a metal surface to create intricate patterns, designs, or markings. This ability to produce high-precision parts with complex geometries makes metal etching particularly valuable for electronics, where miniaturization and accuracy are paramount. Etched metal parts are widely used in diverse applications, ranging from circuit boards to heat sinks, connectors, and more. Below, we explore the top 20 metal etching parts for electronics, examining their functions, benefits, and applications in the field of electronics.
1. Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs)
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are arguably the most common and crucial components in electronics, serving as the backbone for most electronic devices. Metal etching is used in the fabrication of PCBs, particularly in the creation of copper traces that form the electrical connections between components. The etching process allows for the precise removal of excess copper from the board, leaving behind intricate pathways that are essential for signal transmission.
PCBs are found in nearly every electronic device, from smartphones and computers to televisions and automotive systems. The ability to create highly complex and fine-featured circuit patterns using metal etching has led to the development of smaller, more efficient PCBs, which are a key enabler of modern electronics.
2. Microelectromechanical Systems (MEMS) Components
Microelectromechanical Systems (MEMS) represent a class of devices that integrate mechanical elements, sensors, actuators, and electronics on a single chip. Etching is a crucial step in MEMS manufacturing, particularly for the creation of microscale structures, such as sensors, mirrors, and actuators. These etched parts are essential for various applications, including accelerometers in smartphones, pressure sensors in automotive systems, and optical mirrors in lasers.
Etching allows for the precise fabrication of tiny, intricate features required for MEMS components, with high repeatability and reliability. The ability to create 3D structures at a microscopic scale has enabled the development of MEMS-based devices that are smaller, faster, and more efficient than traditional mechanical systems.
3. Heat Sinks
Heat sinks are components used to dissipate heat from electronic devices, preventing overheating and ensuring efficient performance. Metal etching is often employed to produce heat sinks, particularly those with fine, intricate fin patterns. The etched fins increase the surface area available for heat dissipation, improving the efficiency of the heat sink.
In electronics, heat sinks are used in devices such as power supplies, processors, LED lighting, and radio frequency (RF) equipment. Etched heat sinks are preferred due to their ability to provide high thermal conductivity, custom shapes, and fine surface finishes that enhance heat transfer.
4. Connectors
Connectors are critical components in electronics, allowing for the transmission of power, signals, or data between different parts of a system. Metal etching is used to manufacture precise connector components, such as pins, sockets, and contact pads. Etched metal connectors are known for their reliability, durability, and high electrical conductivity.
Metal etching allows manufacturers to create connectors with very fine features, which is especially important in miniaturized electronic devices where space is limited. The precision of the etching process ensures that connectors can be tightly packed into devices without compromising their functionality or performance.
5. RF Shields
Radio frequency (RF) shields are used in electronics to block electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure that devices function correctly without interference from external RF signals. Metal etching is employed to produce RF shields with fine, intricate patterns that are effective at blocking unwanted frequencies while allowing for efficient airflow and cooling.
RF shields are essential in applications such as mobile phones, wireless communication devices, and satellite systems, where minimizing interference is crucial for maintaining signal integrity and device performance. Etching allows for the precise control of the shield’s shape and design, ensuring it meets the specific needs of each application.
6. Enclosures and Casings
Enclosures and casings provide protective housing for electronic devices, safeguarding sensitive components from physical damage, environmental factors, and electromagnetic interference. Metal etching is often used to create intricate designs on the surface of these enclosures, allowing for customized features such as ventilation slots, mounting holes, and decorative patterns.
The precision of metal etching allows for the creation of enclosures that are not only functional but also aesthetically pleasing. Etched metal enclosures are widely used in industries such as telecommunications, medical devices, and consumer electronics, where both form and function are important.
7. Battery Contacts
Battery contacts are essential components in battery-operated electronic devices, ensuring the efficient transfer of power from the battery to the device’s circuitry. Metal etching is used to manufacture these contacts with high precision, allowing for the creation of thin, flexible, and highly conductive parts that fit into the tight spaces of battery compartments.
Etched battery contacts are found in devices ranging from hearing aids and remote controls to electric vehicles and portable electronics. The use of etching allows for the mass production of battery contacts with consistent quality and performance.
8. EMI Shields for Circuit Boards
In addition to the RF shields mentioned earlier, electromagnetic interference (EMI) shields for circuit boards are also critical in ensuring the proper functioning of electronic systems. These shields protect sensitive components on PCBs from external electromagnetic radiation that could disrupt their operation.
Metal etching is used to produce these shields with fine features, allowing them to be integrated directly onto the surface of a PCB or housed in separate shield enclosures. This ensures a cost-effective and space-efficient solution for mitigating EMI in compact electronic devices.
9. Flexible Printed Circuits (FPCs)
Flexible Printed Circuits (FPCs) are a type of PCB designed to be flexible and lightweight, making them ideal for use in compact, mobile, and wearable electronics. Metal etching is used in the manufacturing of FPCs to create the conductive traces that connect components on the flexible substrate.
The etching process enables the creation of intricate and precise circuit patterns that are both durable and capable of bending without breaking. FPCs are widely used in applications such as smartphones, tablets, wearables, and automotive electronics, where flexibility and space constraints are important considerations.
10. Stencils for Soldering
Solder stencils are used in the assembly of PCBs, particularly for the application of solder paste onto the board in preparation for component placement. Etching is used to create precise stencil apertures that correspond to the locations where solder paste is required. This ensures accurate and uniform paste deposition, which is critical for achieving reliable solder joints.
Solder stencils are a key part of the PCB assembly process, particularly in high-volume manufacturing, where precision and repeatability are paramount. Etched stencils are preferred due to their accuracy, consistency, and ability to handle high-volume production runs.
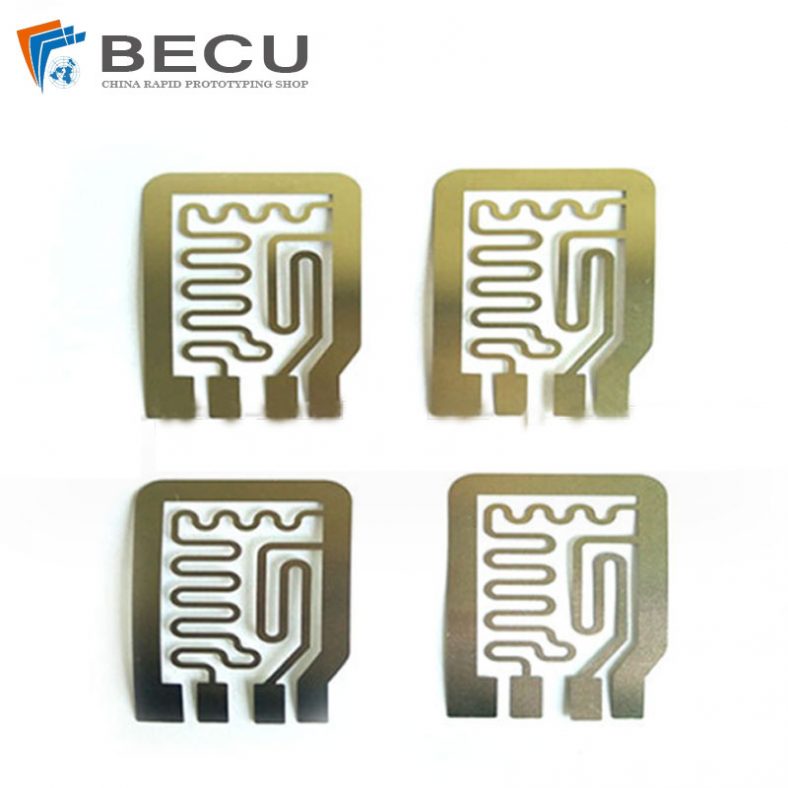
11. Inductors
Inductors are passive electronic components that store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current flows through them. Metal etching is used in the production of inductors, particularly in the creation of etched metal patterns that form the coils or windings. This method allows for the creation of inductors with precise coil geometries and low resistance.
Etched inductors are commonly used in applications such as power supplies, RF circuits, and signal processing, where compactness, efficiency, and high performance are crucial. The precision of the etching process ensures that inductors can be manufactured with high repeatability and minimal variation.
12. Transistor Leads
Transistors are fundamental components in electronic circuits, used for switching and amplifying electrical signals. Metal etching is employed to create the leads (or pins) of transistors, which are used to connect the transistor to the PCB and other components in the circuit. The etching process allows for the production of thin, precise leads that can be easily inserted into PCB holes.
Transistor leads are typically made from high-conductivity metals such as copper or gold and are etched to achieve the necessary shape and size for proper connection. The accuracy of the etching process ensures that the leads maintain consistent electrical performance across large production runs.
13. Antenna Elements
Antenna elements are crucial in electronic devices that rely on wireless communication, such as mobile phones, radios, and Wi-Fi devices. Metal etching is often used to create the intricate designs of antenna elements, particularly for microstrip antennas and patch antennas used in compact devices.
The ability to etch precise patterns onto metal surfaces allows for the creation of antennas with optimal performance characteristics, such as bandwidth, gain, and radiation pattern. Etched antennas are lightweight, cost-effective, and ideal for integration into compact electronic devices.
14. Beryllium Copper Springs
Beryllium copper is a high-performance alloy known for its excellent electrical conductivity, strength, and corrosion resistance. Etching is used to create intricate designs for beryllium copper springs, which are commonly used in electronic devices to provide reliable electrical connections and mechanical support.
These springs are used in applications such as connectors, battery contacts, and switch mechanisms, where precision, reliability, and long-term performance are essential. The etching process allows for the creation of springs with fine tolerances and uniform mechanical properties.
15. Shunt Resistors
Shunt resistors are used in electronic circuits to measure current by providing a low-resistance path for electrical flow. Metal etching is used to manufacture these resistors, particularly in the creation of the fine patterns that define the resistance value. Etched resistors offer high precision, low tolerances, and minimal heat dissipation.
Shunt resistors are widely used in power measurement applications, battery management systems, and current sensing in devices such as electric vehicles and industrial machinery. Etching enables the production of shunt resistors with consistent resistance values and high accuracy.
16. Capacitor Plates
Capacitors are passive components that store and release electrical energy. The plates of capacitors are typically made from etched metal, and the etching process allows for the creation of finely detailed patterns on the plates to achieve specific capacitance values.
Etched capacitor plates are commonly used in applications such as power supplies, signal filtering, and energy storage systems. The ability to etch precise patterns onto metal plates ensures that capacitors can meet the demanding performance requirements of modern electronic circuits.
17. Speaker Grills
Speaker grills protect the delicate internal components of speakers while allowing sound to pass through. Metal etching is often used to create intricate patterns on speaker grills, providing both functional and aesthetic benefits. Etched speaker grills are lightweight, durable, and can be designed to match the appearance of the surrounding device.
Speaker grills are used in a wide range of electronic devices, including smartphones, home audio systems, and automotive sound systems. The precision and design flexibility offered by metal etching make it an ideal solution for creating high-quality speaker grills.
18. Metalized Foils for Flexible Circuits
Metalized foils are used in the production of flexible circuits, where the metal layer serves as the conductive medium for electrical signals. Metal etching is used to create precise circuit patterns on these foils, enabling the creation of flexible and lightweight circuits for use in portable electronics, medical devices, and wearables.
The etching process ensures that the metalized foils maintain high conductivity while retaining their flexibility, making them ideal for integration into compact and flexible devices. Etched metal foils are increasingly used in applications where space and weight are limited.
19. Signal Filters
Signal filters are essential components in electronics that help to remove unwanted frequencies from signals. Metal etching is used to manufacture the conductive traces and patterns required for signal filters, allowing for the precise tuning of filter characteristics such as cut-off frequency and impedance.
Signal filters are widely used in communication systems, audio equipment, and medical devices, where clean and accurate signal transmission is crucial. The precision of metal etching ensures that the filters perform consistently and effectively across a broad range of frequencies.
20. Thermal Interface Materials
Thermal interface materials (TIMs) are used to enhance the heat transfer between electronic components and heat sinks or other thermal management solutions. Metal etching is used to create the fine patterns that are required for the production of TIMs, ensuring that they provide efficient heat conduction and uniform coverage.
TIMs are used in a variety of electronic devices, including processors, power transistors, and LED lighting, where effective heat dissipation is essential for maintaining performance and reliability. Etching allows for the creation of TIMs with precise thicknesses and surface finishes, ensuring optimal thermal management.