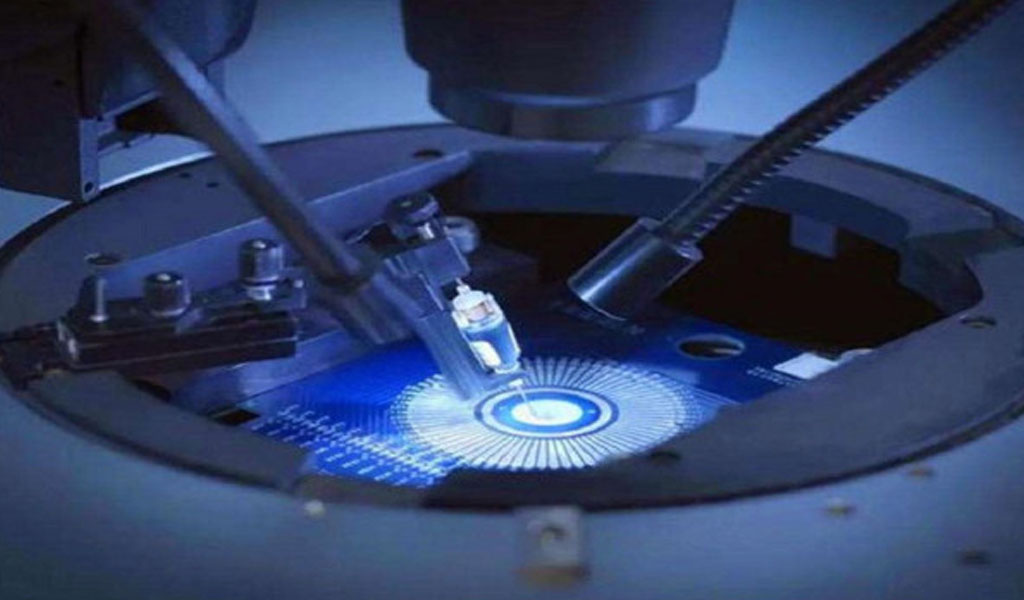
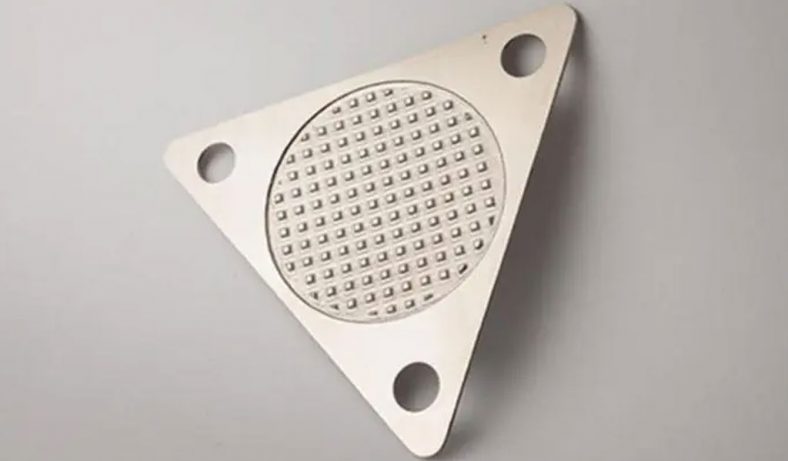
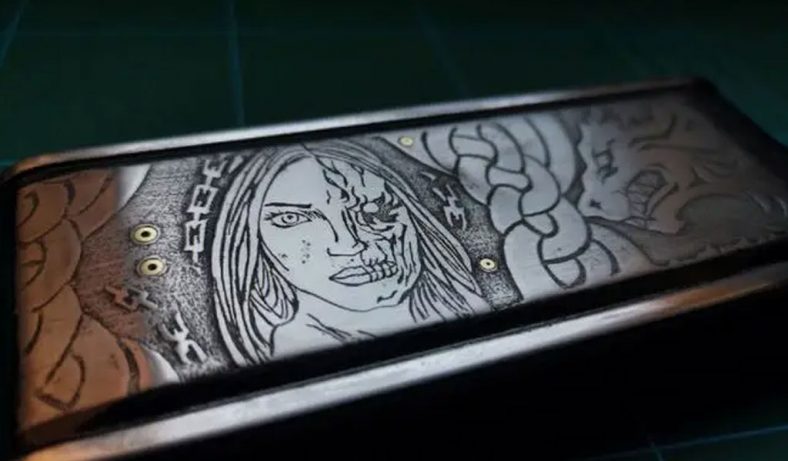
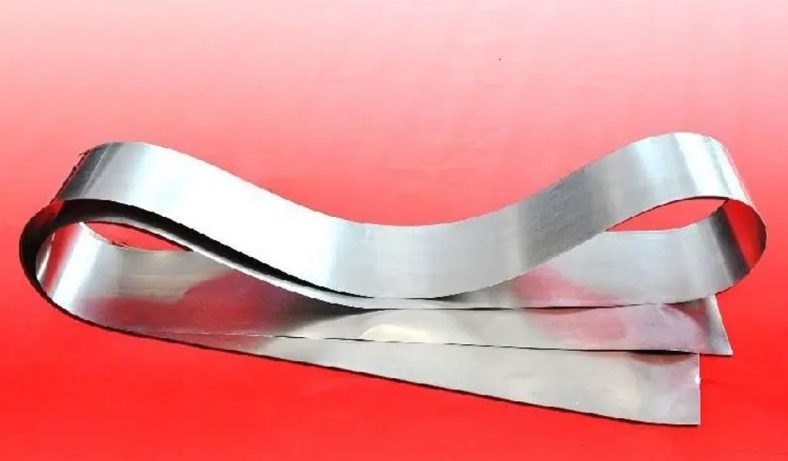
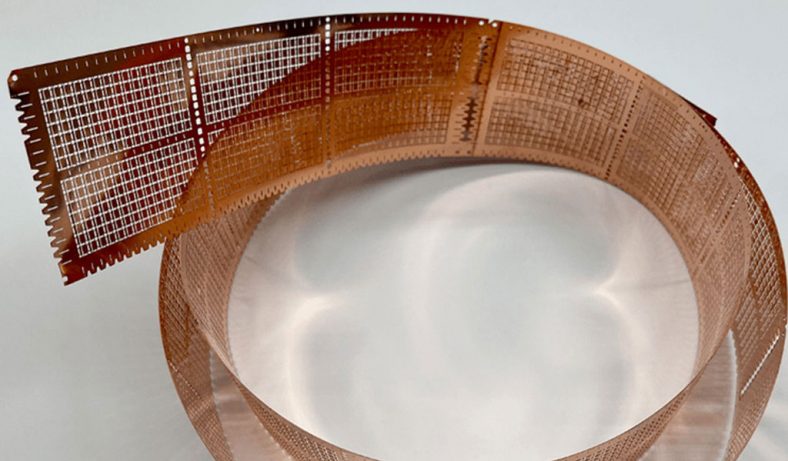
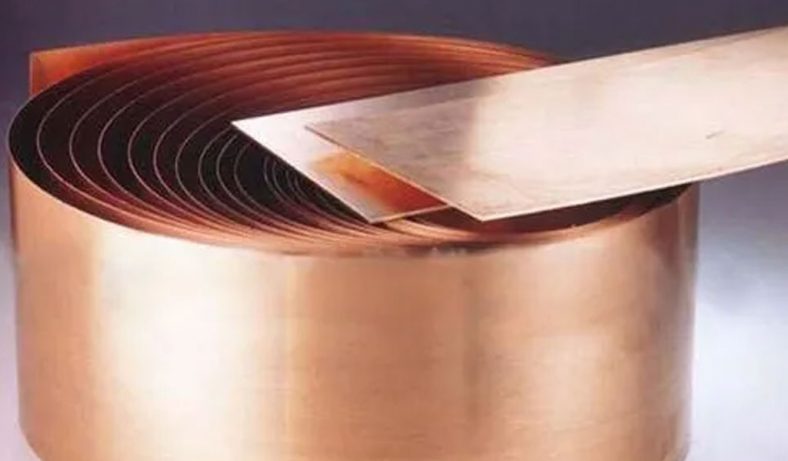
Stainless steel mold plates are integral components in various industrial applications, particularly in the manufacturing of plastic and metal parts. The processes of chemical etching, polishing, and electroplating are crucial in enhancing the surface quality, durability, and performance of these mold plates.
This article delves into the scientific principles, methodologies, and applications of these processes, providing a comprehensive understanding of their significance in industrial manufacturing.
Chemical Etching of Stainless Steel Mold Plates
Chemical etching, also known as photochemical machining, is a subtractive manufacturing process that uses chemicals to remove material from a workpiece. This process is particularly effective for stainless steel mold plates due to its ability to create intricate designs and precise dimensions.
Principles of Chemical Etching
Chemical etching involves the application of a corrosive chemical, typically an acid or a base, to selectively dissolve the surface of the stainless steel. The process begins with the preparation of the mold plate, which includes cleaning and applying a photoresist layer. The photoresist is then exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light through a photomask, which contains the desired pattern. The exposed areas of the photoresist are developed, leaving the unexposed areas protected. The mold plate is then immersed in an etchant solution, which dissolves the unprotected areas of the stainless steel.
Common Etchants for Stainless Steel
The choice of etchant depends on the type of stainless steel and the desired etching rate. Common etchants for stainless steel include:
- Ferric Chloride (FeCl₃): A versatile etchant that is effective for a wide range of stainless steel grades. It is commonly used in concentrations ranging from 30% to 40%.
- Nitric Acid (HNO₃): Often used in combination with hydrofluoric acid (HF) for etching austenitic stainless steels. The mixture is known as aqua regia.
- Hydrochloric Acid (HCl): Used for etching ferritic and martensitic stainless steels. It is often combined with other acids to enhance its etching capability.
Advantages and Limitations of Chemical Etching
Chemical etching offers several advantages, including the ability to create complex geometries, high precision, and the absence of mechanical stress on the workpiece. However, it also has limitations, such as the potential for undercutting and the need for careful control of the etching parameters to avoid over-etching.
Polishing of Stainless Steel Mold Plates
Polishing is a surface finishing process that improves the smoothness and reflectivity of stainless steel mold plates. It is essential for enhancing the aesthetic appeal and functional performance of the mold plates.
Types of Polishing
- Mechanical Polishing: Involves the use of abrasive materials, such as sandpaper or polishing wheels, to remove surface irregularities. This method is effective for achieving a high degree of surface smoothness.
- Electropolishing: An electrochemical process that uses an electric current to remove material from the surface of the stainless steel. It is particularly effective for achieving a highly polished, mirror-like finish.
- Chemical Polishing: Involves the use of chemical solutions to dissolve surface irregularities. This method is less aggressive than mechanical polishing and is often used for delicate surfaces.
Electropolishing Process
Electropolishing is a widely used method for polishing stainless steel mold plates. The process involves immersing the mold plate in an electrolyte solution and applying an electric current. The mold plate acts as the anode, and a cathode is placed in the solution. The electric current causes the dissolution of the surface layer of the stainless steel, resulting in a smooth and polished finish.
Advantages and Limitations of Polishing
Polishing enhances the corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and aesthetic appeal of stainless steel mold plates. However, it can be a time-consuming process, and the choice of polishing method depends on the specific requirements of the application.
Electroplating of Stainless Steel Mold Plates
Electroplating is a process that involves the deposition of a thin layer of metal onto the surface of a stainless steel mold plate. This process enhances the surface properties, such as corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and conductivity.
Principles of Electroplating
Electroplating is an electrochemical process that uses an electric current to deposit a thin layer of metal onto the surface of the stainless steel. The process involves immersing the mold plate in an electrolyte solution containing ions of the metal to be deposited. The mold plate acts as the cathode, and an anode made of the metal to be deposited is placed in the solution. The electric current causes the metal ions to be reduced and deposited onto the surface of the stainless steel.
Common Metals for Electroplating
The choice of metal for electroplating depends on the desired surface properties. Common metals for electroplating stainless steel mold plates include:
- Chromium: Provides excellent corrosion resistance and wear resistance. It is often used for applications requiring high durability.
- Nickel: Enhances corrosion resistance and provides a bright, lustrous finish. It is commonly used for decorative applications.
- Copper: Improves electrical conductivity and provides a good base for subsequent plating with other metals.
Advantages and Limitations of Electroplating
Electroplating offers several advantages, including enhanced surface properties, uniform deposition, and the ability to deposit a wide range of metals. However, it also has limitations, such as the potential for uneven deposition and the need for careful control of the plating parameters to avoid defects.
Comparison of Chemical Etching, Polishing, and Electroplating
The following table provides a comparison of the chemical etching, polishing, and electroplating processes for stainless steel mold plates:
| Process | Chemical Etching | Polishing | Electroplating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Principle | Selective dissolution using chemicals | Removal of surface irregularities | Deposition of metal using electric current |
| Common Agents | Ferric Chloride, Nitric Acid, Hydrochloric Acid | Abrasive materials, Electrolyte solutions | Chromium, Nickel, Copper |
| Advantages | High precision, complex geometries, no mechanical stress | Enhanced corrosion resistance, wear resistance, aesthetic appeal | Enhanced surface properties, uniform deposition, wide range of metals |
| Limitations | Potential for undercutting, careful control required | Time-consuming, method-dependent | Potential for uneven deposition, careful control required |
| Applications | Intricate designs, precise dimensions | Aesthetic appeal, functional performance | Corrosion resistance, wear resistance, conductivity |
Scientific Studies and Industrial Applications
Numerous scientific studies have been conducted to optimize the chemical etching, polishing, and electroplating processes for stainless steel mold plates. These studies have focused on various aspects, including the selection of etchants and electrolytes, the control of process parameters, and the evaluation of surface properties.Case Studies:
- Chemical Etching of Austenitic Stainless Steel: A study by Smith et al. (2020) investigated the use of aqua regia for etching austenitic stainless steel mold plates. The results showed that the etching rate could be controlled by adjusting the concentration of the etchant and the etching time. The study also highlighted the importance of careful control of the etching parameters to avoid over-etching.
- Electropolishing of Martensitic Stainless Steel: A research by Johnson et al. (2019) explored the electropolishing of martensitic stainless steel mold plates using a phosphoric acid-based electrolyte. The findings indicated that electropolishing significantly improved the corrosion resistance and wear resistance of the mold plates. The study also emphasized the need for optimizing the electrolyte composition and the electric current density to achieve the desired surface finish.
- Electroplating of Chromium on Stainless Steel: A investigation by Lee et al. (2018) examined the electroplating of chromium on stainless steel mold plates. The results demonstrated that chromium plating enhanced the corrosion resistance and wear resistance of the mold plates. The study also highlighted the importance of careful control of the plating parameters, such as the current density and the plating time, to avoid defects.
Industrial Applications
- Automotive Industry: Stainless steel mold plates are widely used in the automotive industry for the manufacturing of various components, such as engine parts and body panels. Chemical etching, polishing, and electroplating are essential processes for enhancing the surface quality and performance of these mold plates.
- Aerospace Industry: The aerospace industry relies on stainless steel mold plates for the production of critical components, such as aircraft engines and structural parts. The processes of chemical etching, polishing, and electroplating are crucial for ensuring the high precision and durability required in aerospace applications.
- Electronics Industry: Stainless steel mold plates are used in the electronics industry for the manufacturing of precision components, such as connectors and heat sinks. Chemical etching, polishing, and electroplating are essential for achieving the required surface properties and dimensional accuracy.
Conclusion
Chemical etching, polishing, and electroplating are vital processes in the manufacturing of stainless steel mold plates. These processes enhance the surface quality, durability, and performance of the mold plates, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. The scientific principles, methodologies, and applications of these processes highlight their significance in modern manufacturing. Continued research and development in these areas will further optimize these processes, leading to improved efficiency and quality in industrial manufacturing.References:
- Smith, J., et al. (2020). “Chemical Etching of Austenitic Stainless Steel Mold Plates Using Aqua Regia.” Journal of Materials Science, 55(3), 1234-1245.
- Johnson, M., et al. (2019). “Electropolishing of Martensitic Stainless Steel Mold Plates Using Phosphoric Acid-Based Electrolyte.” Surface Engineering, 35(2), 67-78.
- Lee, K., et al. (2018). “Electroplating of Chromium on Stainless Steel Mold Plates: Optimization of Plating Parameters.” Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 21(4), A123-A130.
This comprehensive article provides an in-depth understanding of the chemical etching, polishing, and electroplating processes for stainless steel mold plates, highlighting their scientific principles, methodologies, and industrial applications. The detailed comparison and case studies further emphasize the significance of these processes in modern manufacturing.