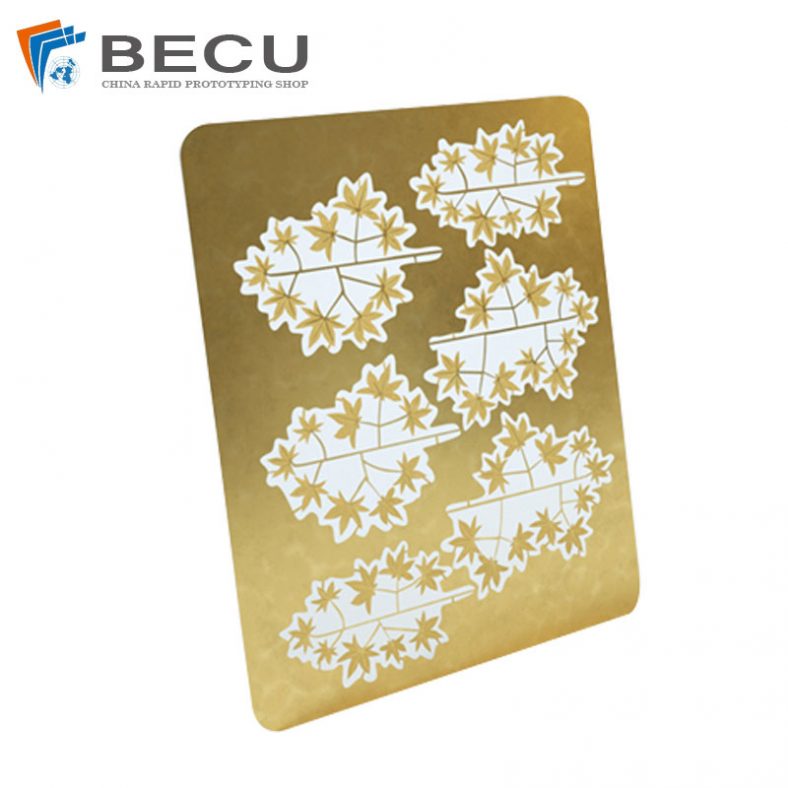
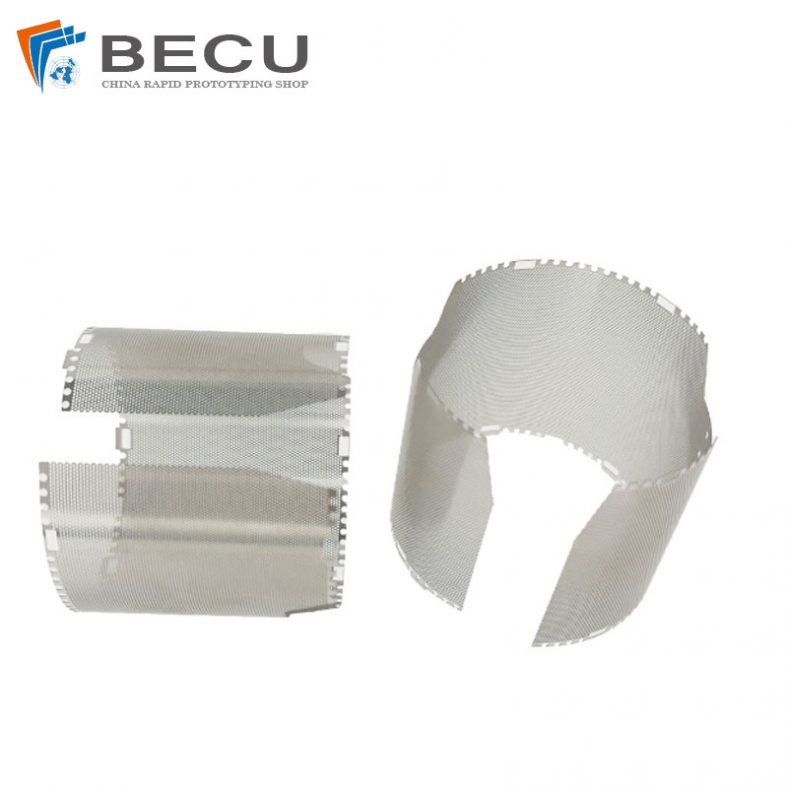
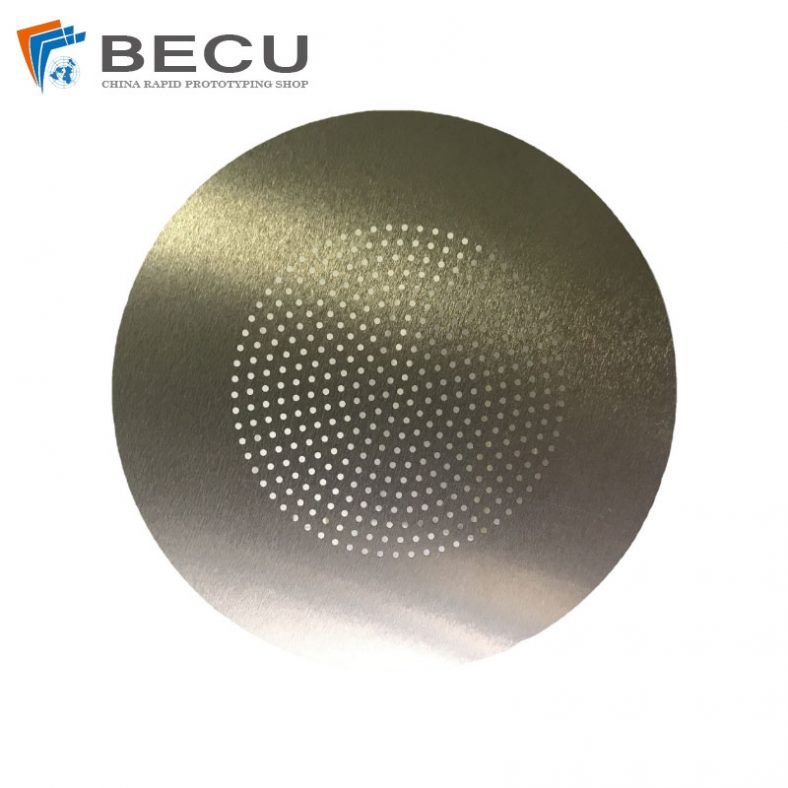
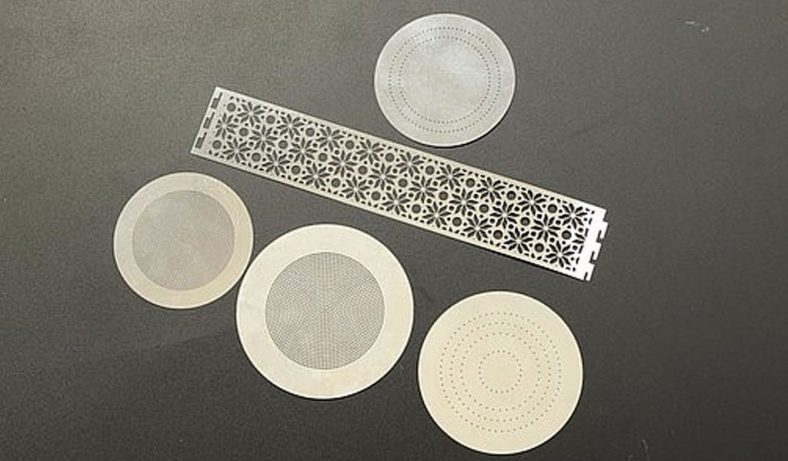
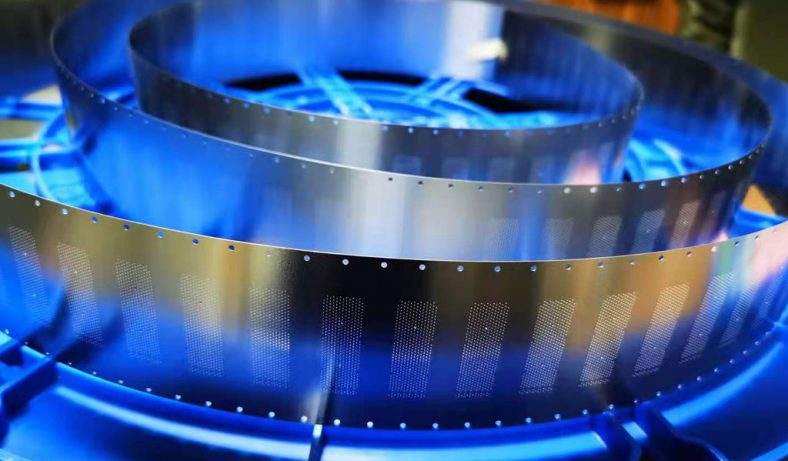
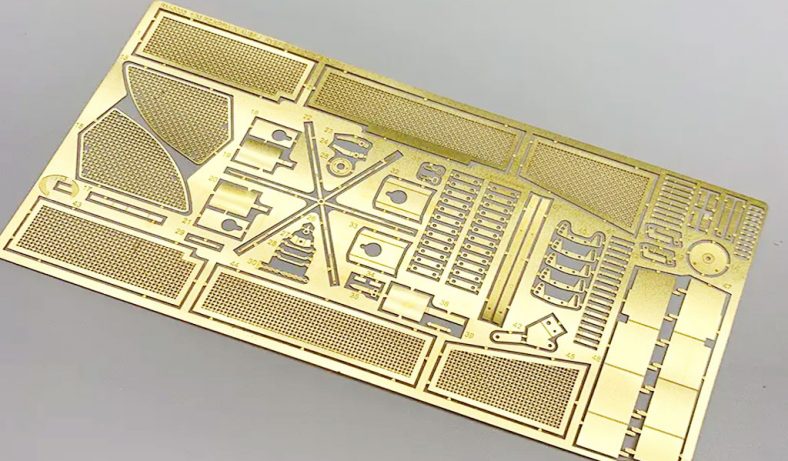
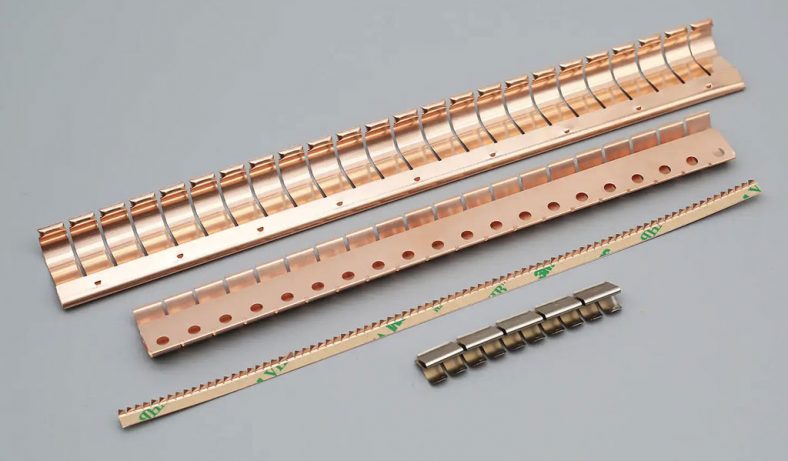
Etching is a widely used process for creating detailed patterns and designs on various materials, including metals like brass. Among the different etching methods, using ferric chloride (FeCl3) as an etching agent is particularly popular due to its effectiveness and relatively straightforward application. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the etching process for brass using ferric chloride, covering its history, chemistry, preparation, and safety considerations, as well as a detailed step-by-step guide to achieving high-quality etching results.
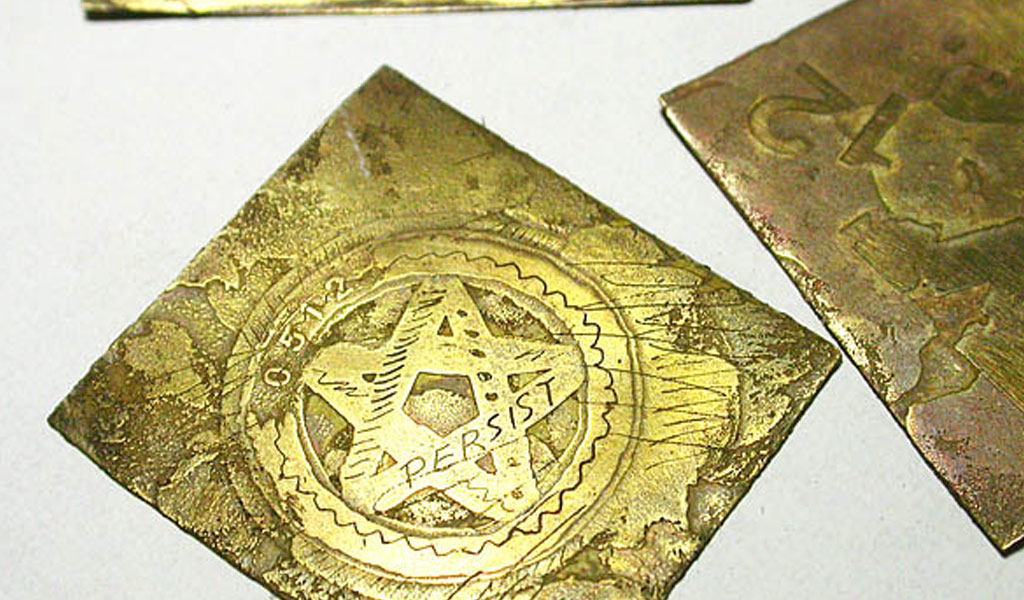

History
Etching as a method for decorating metals dates back several centuries. Early examples of etched metalwork can be traced to the medieval period, where artisans employed acids derived from naturally occurring substances to create intricate designs on armor and weaponry. By the Renaissance, etching had evolved significantly, becoming a favored technique among artists and craftsmen for its ability to produce fine lines and complex patterns.
The use of ferric chloride in metal etching emerged in the 19th century, coinciding with advances in chemistry and industrial processes. Ferric chloride, a compound with the formula FeCl3, was discovered to be highly effective in dissolving metals such as copper and brass. Its adoption for etching was driven by its efficiency and the relatively safer handling compared to more volatile acids. Over time, ferric chloride etching has become a standard technique in both artistic and industrial applications.
Chemistry of Ferric Chloride Etching
Ferric Chloride Properties
Ferric chloride is a versatile etchant known for its strong oxidizing properties. It appears as a yellowish-brown crystalline solid and is highly soluble in water.
When dissolved, it forms a brownish solution capable of etching metals by oxidizing and dissolving their surfaces. The chemical reaction involved in the etching process can be represented by the following equation:

FeCl3+Cu (or Zn in brass) → CuCl2(orZnCl2)+FeCl2
In this reaction, ferric chloride reacts with the metal to form metal chlorides and ferrous chloride.
Mechanism of Etching
The etching process using ferric chloride involves the removal of metal through oxidation. When ferric chloride comes into contact with the brass surface, it reacts with the copper and zinc components of the alloy. This reaction results in the dissolution of the metal, creating grooves and patterns on the surface. The depth and precision of the etching can be controlled by varying the concentration of the ferric chloride solution and the duration of exposure.
Preparation for Etching
To etch brass using ferric chloride, the following materials and tools are required:
- Brass sheet or object
- Ferric chloride solution (available in various concentrations)
- Protective gear (gloves, goggles, apron)
- Plastic or glass container for the etching solution
- Brushes or sponges for applying resist
- Resist material (such as wax, paint, or specialized etching resist)
- Cleaning supplies (detergent, acetone, or alcohol)
- Masking tape
- Fine abrasive paper or steel wool
- Neutralizing agent (baking soda solution)
- Running water for rinsing
Surface Preparation
Proper preparation of the brass surface is crucial for achieving high-quality etching results. The following steps outline the preparation process:
- Cleaning: Thoroughly clean the brass surface to remove any dirt, grease, or oxidation. Use detergent and warm water, followed by a rinse with acetone or alcohol to ensure the surface is free from contaminants.
- Sanding: Lightly sand the surface with fine abrasive paper or steel wool to create a uniform, slightly rough texture. This helps the resist adhere better to the brass.
- Applying Resist: Apply a resist material to the areas that should remain unetched. This can be done using various methods such as brushing on a resist paint, using wax, or applying a specialized etching resist. Ensure the resist is applied evenly and allows for intricate detailing if needed.
- Masking: Use masking tape to cover any areas of the brass that should not come into contact with the etching solution.
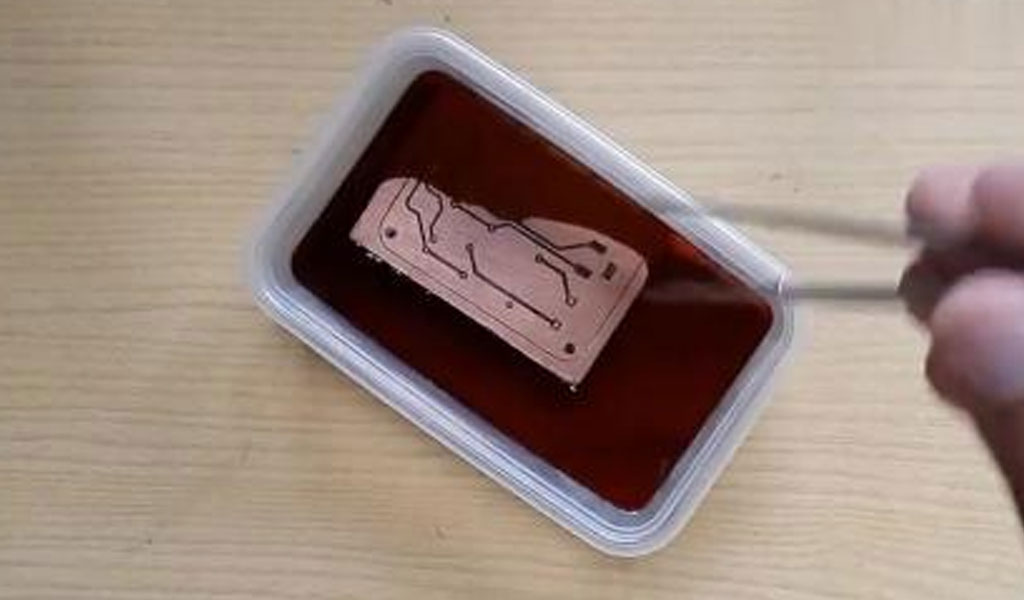
Etching Process
Ferric chloride is typically available as a concentrated solution or in crystalline form that needs to be dissolved in water. The recommended concentration for etching brass is around 30-40%. To prepare the solution:
- Dilution: If using a concentrated ferric chloride solution, dilute it with water according to the manufacturer’s instructions to achieve the desired concentration. For crystalline ferric chloride, dissolve the crystals in water while stirring to ensure complete dissolution.
- Safety Precautions: Always add ferric chloride to water, not the other way around, to prevent exothermic reactions. Wear protective gear and work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling fumes.
Etching Procedure
Once the brass and ferric chloride solution are prepared, follow these steps to etch the brass:
- Submersion: Place the brass object or sheet into the container with the ferric chloride solution. Ensure that the entire surface to be etched is submerged.
- Agitation: Gently agitate the solution or use a brush to help the etchant penetrate evenly across the brass surface. This helps in achieving a more uniform etch.
- Monitoring: Monitor the etching process closely. The duration of etching can vary depending on the concentration of the solution, temperature, and desired depth of etch. Typical etching times range from 15 minutes to several hours.
- Inspection: Periodically remove the brass from the solution and inspect the progress. If deeper etching is required, return the brass to the solution and continue the process.
- Neutralizing: Once the desired etching depth is achieved, remove the brass from the solution and rinse it thoroughly with running water. Neutralize any remaining ferric chloride on the surface by immersing the brass in a baking soda solution.
Post-Etching Cleanup
After etching, it is essential to clean and finish the brass to enhance its appearance and durability:
- Resist Removal: Remove the resist material using a suitable solvent or by mechanical means such as scrubbing with a brush.
- Final Cleaning: Clean the brass with detergent and water to remove any residual etchant and neutralizing agent.
- Polishing: If desired, polish the etched brass surface to achieve a smooth and shiny finish. This can be done using metal polish and a soft cloth.
Safety Considerations
Etching with ferric chloride involves handling chemicals that can be hazardous if not managed properly. The following safety measures should be observed:
- Protective Gear: Always wear gloves, goggles, and an apron to protect against splashes and fumes.
- Ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area or use a fume hood to avoid inhaling harmful fumes.
- Storage: Store ferric chloride in a secure, labeled container away from incompatible substances.
- Disposal: Dispose of used ferric chloride solution and other waste materials according to local regulations. Neutralize the solution with baking soda before disposal to minimize environmental impact.
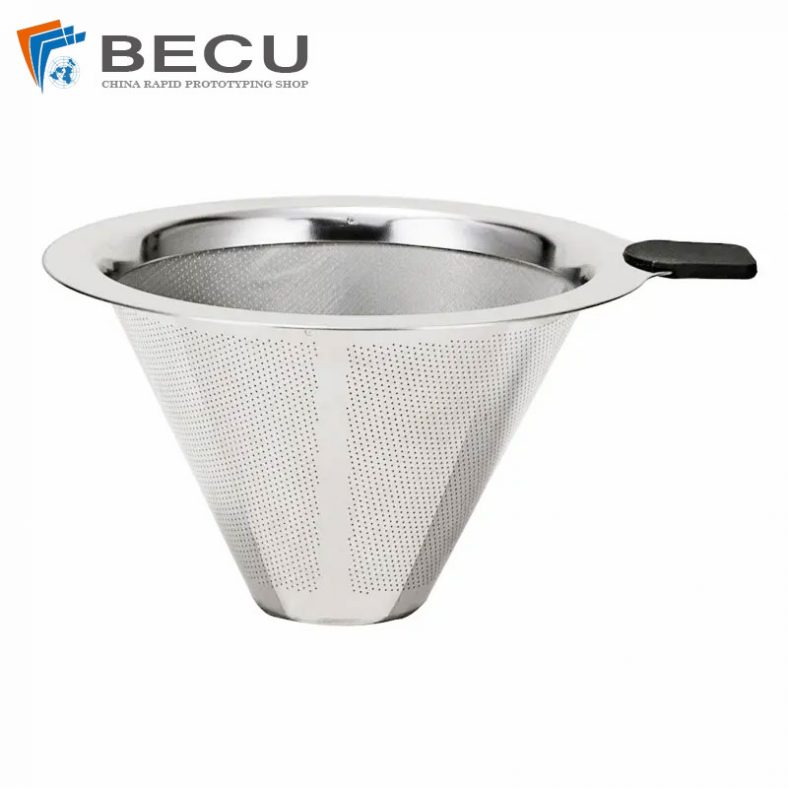
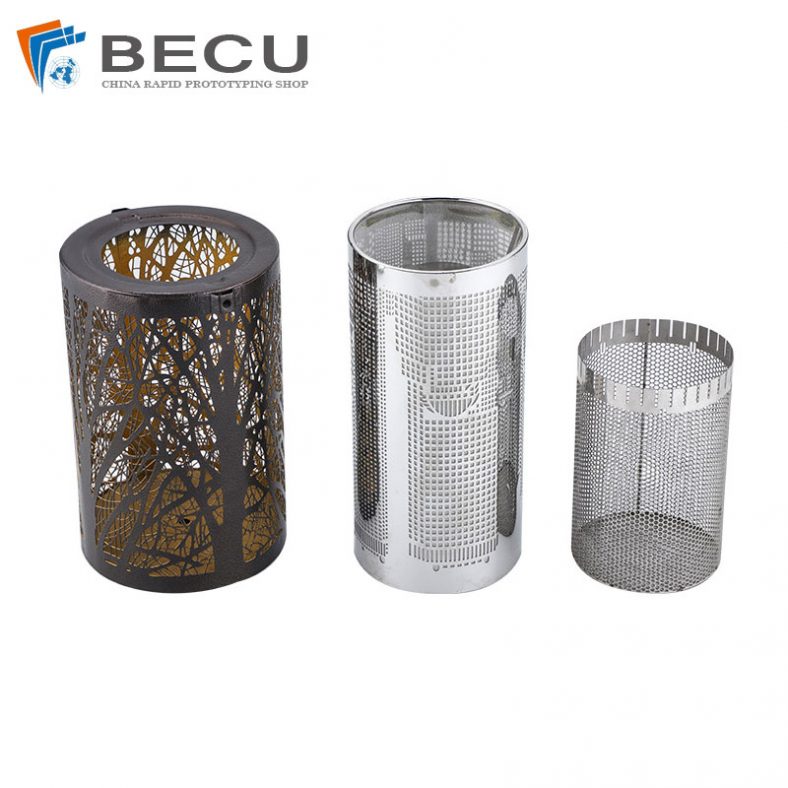
Applications and Uses
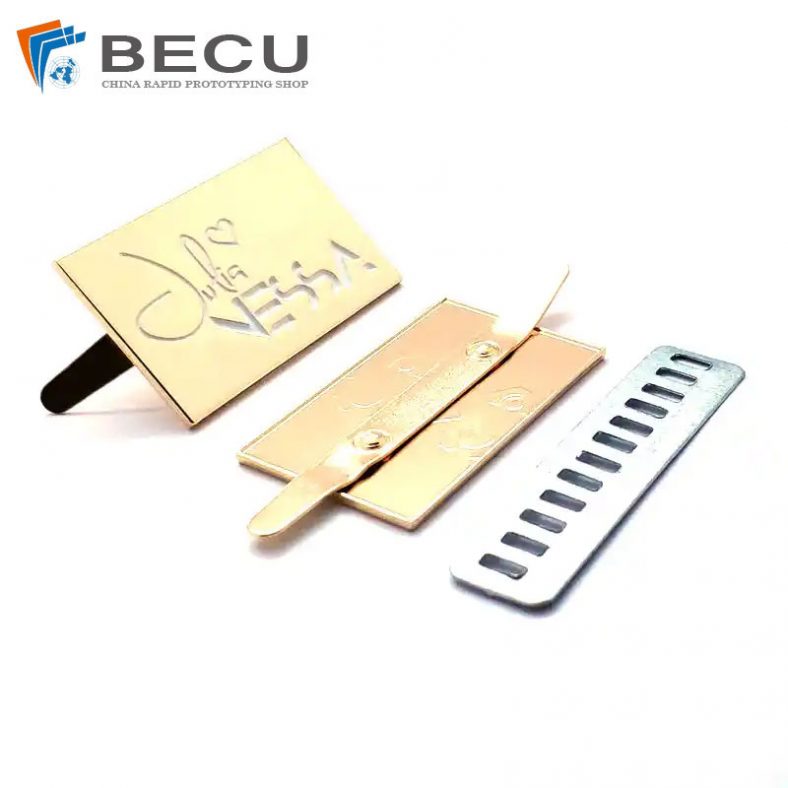
Etching brass with ferric chloride is widely used in the creation of artistic and decorative items. Artists and craftsmen use this technique to produce detailed designs on jewelry, plaques, and ornamental pieces.
The ability to create fine lines and intricate patterns makes ferric chloride etching a favored method for personalizing and enhancing the aesthetic appeal of brass items.
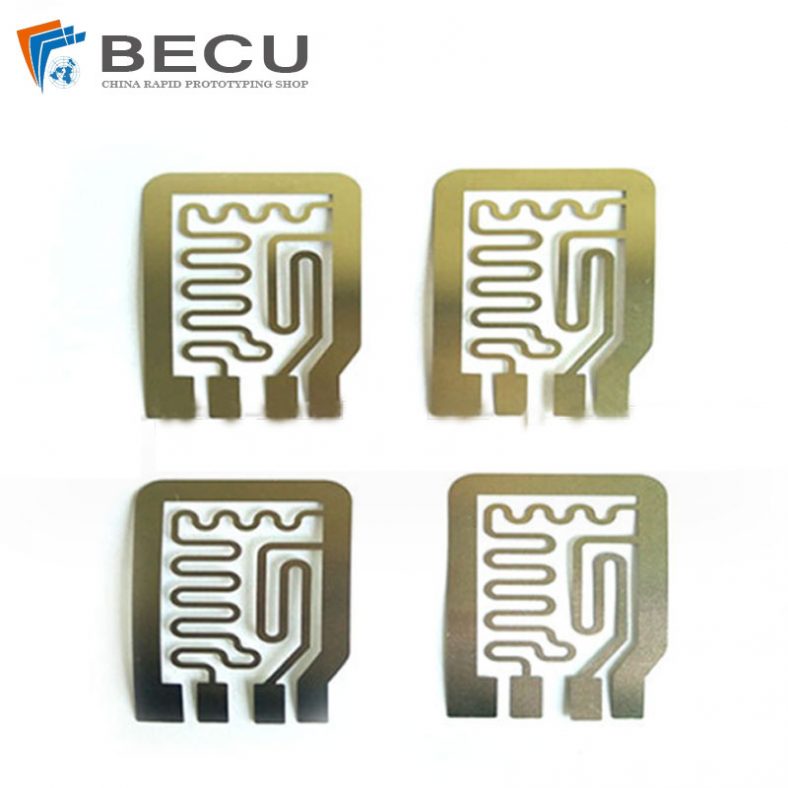
In addition to artistic uses, ferric chloride etching is employed in various industrial applications. It is used in the manufacture of printed circuit boards (PCBs), where precise etching is required to create intricate circuitry on copper-clad substrates. Ferric chloride is also utilized in the production of nameplates, signage, and other components where detailed and accurate metalwork is essential.
Conclusion
Etching brass with ferric chloride is a versatile and effective method for creating detailed and precise designs on brass surfaces. By understanding the chemistry involved, preparing the materials properly, and following safety guidelines, artisans and manufacturers can achieve high-quality etching results. Whether for artistic creations or industrial applications, ferric chloride etching remains a valuable technique in the world of metalwork.