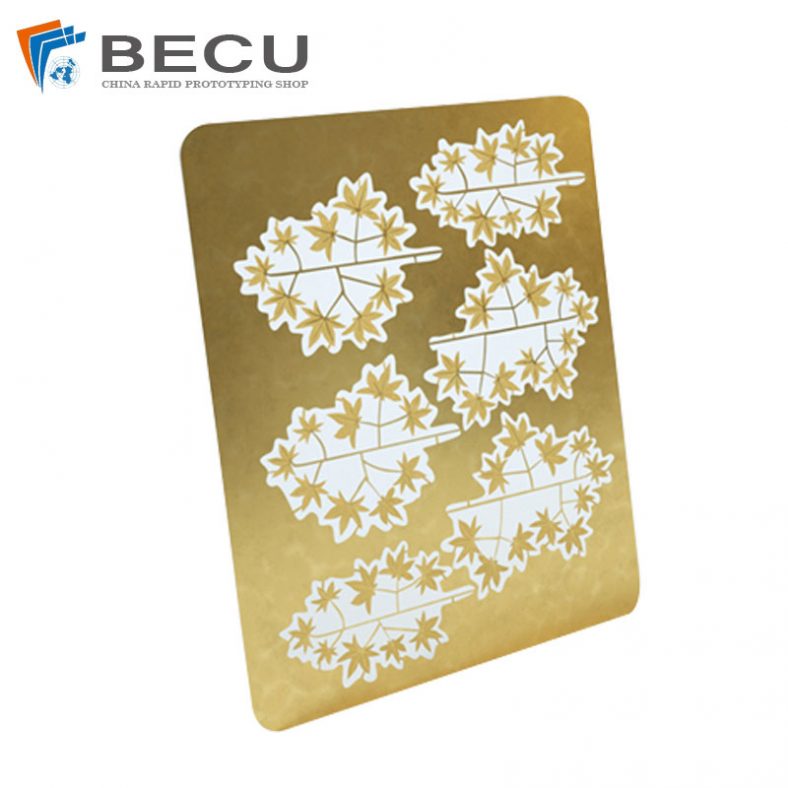
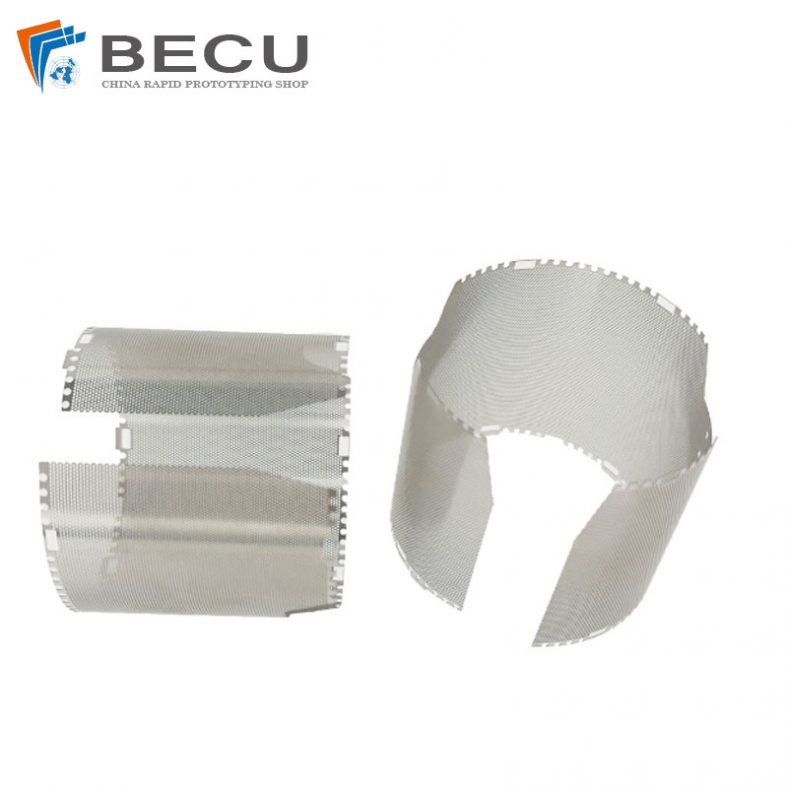
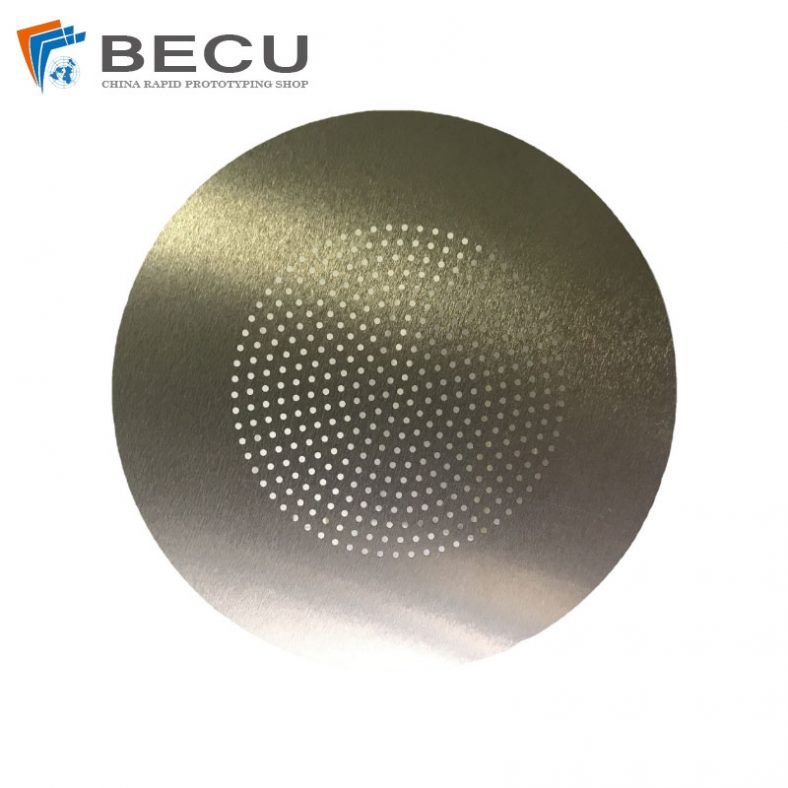
Chemical etching, also known as chemical milling or photochemical machining, stands as a pivotal process in various industries such as electronics, aerospace, automotive, and more. It involves selectively removing material from a metal surface to create intricate designs, patterns, or finely detailed parts. The success and quality of chemical etching highly depend on the choice of metals used in the process. This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse range of metals suitable for chemical etching, their unique properties, and their applications across industries.
Understanding Chemical Etching For Metal
Before delving into the ideal metals for chemical etching, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental process. Chemical etching is a subtractive manufacturing technique that involves several steps:

- Cleaning and Preparation: The metal surface must be thoroughly cleaned to remove any contaminants that could interfere with the etching process. This step ensures uniform etching.
- Application of Mask: A resistant mask, often a photoresist or a protective film, is applied to the metal surface. This mask is designed to protect specific areas of the metal from the etchant.
- Etching: The metal is exposed to a corrosive chemical (etchant), which selectively removes the unprotected areas, leaving behind the desired pattern or design.
Factors Affecting Metal Suitability for Chemical Etching
Several factors influence the choice of metals for chemical etching:
- Chemical Reactivity: Metals react differently to various etchants. Some metals are more susceptible to corrosion, while others display resistance to certain etching solutions.
- Surface Finish: The surface finish of the metal greatly impacts the quality and precision of the etched patterns. Metals with smoother surfaces generally yield finer details.
- Material Thickness: Etching thicker metals might require longer exposure to the etchant, impacting production time and cost-effectiveness.
- Cost and Availability: The cost of the metal and its availability in desired quantities play a crucial role in industrial applications.
Suitable Metals for Chemical Etching
- Stainless Steel: Renowned for its corrosion resistance and durability, stainless steel (grades like 304, 316) is a popular choice for chemical etching. Its versatility allows for intricate designs while maintaining structural integrity.
- Copper: Due to its excellent electrical conductivity and malleability, copper finds applications in electronics and decorative arts. Chemical etching reveals detailed patterns on copper surfaces.
- Brass: A copper-zinc alloy, brass, offers an attractive golden hue and is highly malleable. It etches well, making it a preferred choice for ornamental applications.
- Aluminum: Known for its lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion, aluminum undergoes chemical etching for creating lightweight, intricate parts used in aerospace and automotive industries.
- Nickel and Nickel Alloys: With exceptional resistance to extreme temperatures and corrosion, nickel and its alloys like Inconel® are suitable for harsh environments and precision parts.
- Titanium: Recognized for its high strength-to-weight ratio and biocompatibility, titanium undergoes chemical etching in medical devices and aerospace components.
Applications across Industries
- Electronics: Copper and stainless steel find applications in electronic components due to their conductivity and durability.
- Aerospace: Aluminum, titanium, and nickel alloys are extensively used in aerospace for lightweight parts with intricate designs.
- Medical Devices: Titanium’s biocompatibility makes it ideal for surgical instruments and implants.
- Automotive: Stainless steel and aluminum are prevalent in automotive parts due to their strength and corrosion resistance.
Conclusion
The selection of metals for chemical etching plays a crucial role in achieving precise and high-quality results across various industries. Understanding the properties and characteristics of different metals helps in choosing the most suitable material for specific applications, ensuring efficient and accurate manufacturing through the chemical etching process.