Etching on wine bottles is a versatile and sophisticated technique used across industries to add aesthetic, functional, and branding elements to the product. This practice is especially prevalent in the beverage industry, where unique branding is essential for market differentiation. From artisanal wine producers to mass-market bottlers, the methods and materials used for etching vary widely, depending on the desired outcome and production scale. This article explores the intricate process of wine bottle etching, its techniques, materials, applications, and the industries involved.

Overview of Wine Bottle Etching
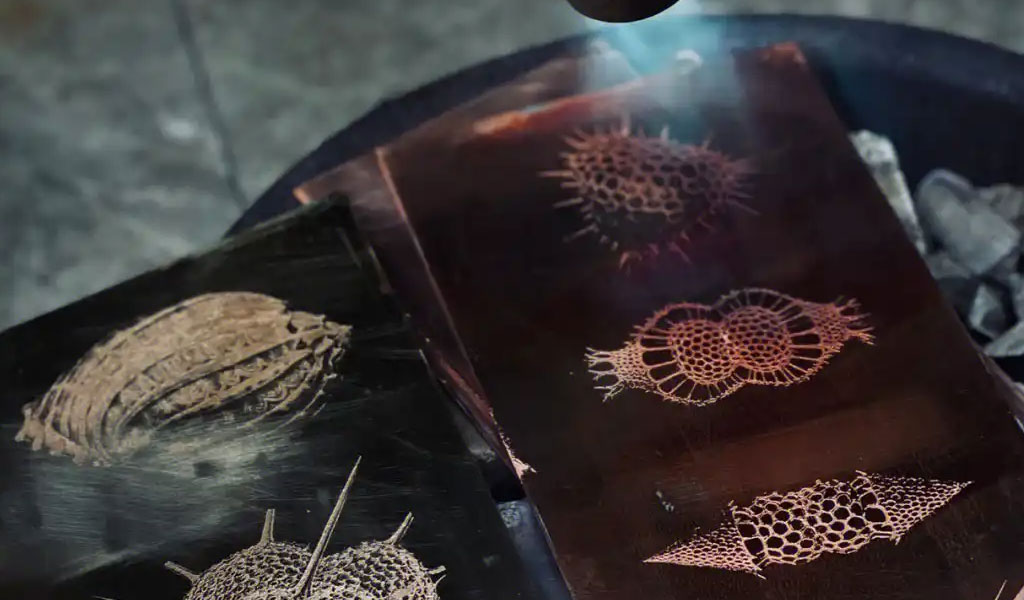
Etching involves engraving or marking the surface of a wine bottle to create permanent, decorative, or functional designs. Unlike labels that may peel off or deteriorate over time, etched designs are durable, resistant to environmental factors, and convey a sense of luxury and permanence.
This process can be employed for aesthetic embellishment, functional markings such as barcodes or QR codes, or regulatory information, including alcohol content and origin certification.
The etching process is typically applied to glass bottles, though some techniques may also work on polymer-based or coated glass substitutes. The methods used depend on the scale of production, budget, and design complexity. Wine bottle etching is also compatible with a variety of finishes, including frosted, clear, tinted, or coated surfaces.
Techniques Used for Etching Wine Bottles
Several methods are used to etch designs onto wine bottles, each with its advantages and limitations. The choice of method depends on the desired aesthetic, production efficiency, and cost constraints. Below are the most common techniques:
Sandblasting
Sandblasting is one of the most popular methods for etching wine bottles. This technique involves using pressurized air to propel an abrasive material, such as silica sand, aluminum oxide, or glass beads, against the bottle’s surface. The abrasive erodes the glass surface, creating a matte, frosted, or textured design. Stencils or masks are used to protect areas that should remain unetched, allowing for intricate patterns and sharp details.
Key Advantages:
- High level of detail and precision.
- Customizable depth and texture.
- Suitable for small or large production runs.
Challenges:
- Requires skilled labor and specialized equipment.
- Generates fine dust, necessitating proper safety measures.
Laser Etching
Laser etching employs a high-powered laser beam to create designs on the bottle’s surface. The laser heats the glass, causing localized melting or vaporization that results in a permanent mark. This technique is ideal for detailed patterns, logos, and text, and it can be automated for high-speed production.
Key Advantages:
- High precision and repeatability.
- Suitable for complex or small designs.
- No physical contact, reducing the risk of damage to the bottle.
Challenges:
- Expensive initial investment in laser equipment.
- Limited to certain glass compositions and coatings.
Acid Etching
Acid etching uses chemicals to corrode the surface of the glass, creating a frosted or textured appearance. Typically, hydrofluoric acid or other etching solutions are applied to the bottle using stencils, allowing for controlled patterns and designs. Acid etching is less common due to environmental and safety concerns but remains an option for specialized applications.
Key Advantages:
- Uniform and smooth finish.
- Excellent for large areas or simple patterns.
Challenges:
- Involves hazardous chemicals.
- Requires strict safety and disposal protocols.
Screen Printing with Etching Inks
Screen printing involves applying an etching ink containing abrasive particles to the bottle’s surface. The bottle is then processed to activate the ink, which chemically or mechanically etches the glass. This method combines the simplicity of screen printing with the durability of etching.
Key Advantages:
- Cost-effective for medium to large production runs.
- Allows for multicolored designs.
- Compatible with curved bottle surfaces.
Challenges:
- Limited resolution compared to sandblasting or laser etching.
- Requires curing or processing equipment.
Rotary Engraving
Rotary engraving involves using a diamond-tipped or carbide bit to physically engrave the glass surface. This technique is slower than other methods but offers a handcrafted appearance that is prized for high-end or artisanal products.
Key Advantages:
- Unique, handcrafted aesthetic.
- Suitable for personalized or one-off designs.
Challenges:
- Labor-intensive and time-consuming.
- Limited scalability for large production runs.
Materials and Equipment for Etching
The materials and equipment used for wine bottle etching depend on the chosen technique. Below is an overview of common tools and materials:
Stencils and Masks
Stencils are essential for creating precise designs in sandblasting, acid etching, and screen printing. They can be made from vinyl, paper, or other durable materials. Masks are used to protect areas of the bottle that should remain untouched during the etching process.
Abrasive Media
For sandblasting, various abrasive media are used depending on the desired finish. Fine abrasives create smoother textures, while coarser materials produce a more pronounced effect.
Lasers
Laser etching machines range from desktop units for small-scale production to industrial systems for high-volume operations. Modern lasers offer software integration for precise control of designs.
Etching Chemicals
In acid etching, hydrofluoric acid or commercially available etching creams are used. These chemicals must be handled with extreme caution and are subject to regulatory oversight.
Safety Equipment
Etching processes often involve hazardous materials or equipment. Safety gear such as gloves, goggles, respirators, and protective clothing is crucial. Proper ventilation systems and dust collection units are also necessary.
Applications of Wine Bottle Etching
Wine bottle etching is used for various purposes, ranging from branding and marketing to regulatory compliance. Below are common applications:
Branding and Marketing
Etched wine bottles convey luxury and exclusivity, making them ideal for premium brands. Logos, intricate designs, and embossed text enhance the visual appeal and create a memorable product.
Personalization
Personalized etched bottles are popular for weddings, anniversaries, and corporate gifts. Names, dates, and custom messages can be added for a unique touch.
Regulatory Information
Etching provides a permanent way to display mandatory information such as alcohol content, origin, and certification logos. This is particularly important for export markets with strict labeling requirements.
Limited Edition and Commemorative Releases
Limited-edition wines often feature etched designs to highlight their exclusivity. Commemorative releases for events or milestones also benefit from the added prestige of etching.
Industries Involved in Wine Bottle Etching
Wine bottle etching involves several industries, including glass manufacturing, graphic design, and industrial printing. Collaborative efforts among these industries ensure high-quality results.
Glass Manufacturers
Glass manufacturers produce bottles designed to withstand etching processes. This includes ensuring consistent glass quality and surface properties.
Graphic Designers
Designers create the templates, stencils, and digital files needed for etching. Their expertise ensures that designs are both visually appealing and technically feasible.
Printing and Etching Specialists
Specialized companies handle the actual etching process, offering expertise in various techniques. These companies may serve as subcontractors to wineries or branding agencies.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Wine bottle etching processes often involve materials and methods with environmental and safety implications. Proper disposal of chemicals, dust management, and compliance with regulations are critical for minimizing the impact on workers and the environment.
Sustainable Practices
To address environmental concerns, many companies are adopting sustainable practices such as using eco-friendly abrasives, recycling etching media, and reducing chemical use.
Worker Safety
Worker safety is a priority in facilities where etching takes place. Training, protective gear, and adherence to safety standards are essential for preventing accidents and exposure to hazardous materials.
Future Trends in Wine Bottle Etching
Advancements in technology are driving innovation in wine bottle etching. Emerging trends include:
- Digital Integration: Smart wine bottles featuring etched QR codes for interactive experiences.
- Eco-Friendly Techniques: Increased use of lasers and sustainable abrasives to reduce environmental impact.
- Customization at Scale: Automated systems enabling personalized designs for mass production.
Conclusion
Etching on wine bottles combines artistry, technology, and craftsmanship to create visually striking and functional designs. Whether for branding, personalization, or compliance, etched wine bottles continue to captivate consumers and enhance the value of the product. As technologies evolve and sustainability becomes a focus, the future of wine bottle etching promises exciting possibilities for industries and consumers alike.4o