Laser etching and laser engraving are two widely used methods in the field of material processing, especially in industries requiring precise and detailed marks on surfaces, such as manufacturing, art, aerospace, automotive, and medical industries. These methods rely on focused laser beams to alter the surface of a material in distinct ways. Despite both involving lasers to create markings, the processes differ in terms of depth, technique, and application. This article delves deeply into the differences, similarities, applications, advantages, and limitations of laser etching and laser engraving, as well as their technological advancements, historical background, and future prospects.
Introduction to Laser Marking Techniques
Laser marking encompasses a range of technologies that use lasers to create permanent markings on various materials.
Among the most commonly used techniques are laser etching and laser engraving, both of which involve the use of laser energy to alter the surface of a material. These two processes are often confused because they both create marks using laser beams, but they differ significantly in how they affect the surface of the material.

In laser etching, the laser beam is focused on the surface of the material, causing a reaction that leads to a slight change in the surface texture or color without significant material removal. In contrast, laser engraving involves the use of higher laser energy, which physically removes a portion of the material to create a deeper mark or design. Both processes can be used on a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, glass, ceramics, and wood, each of which responds differently to laser energy depending on its composition.
The Basics of Laser Etching
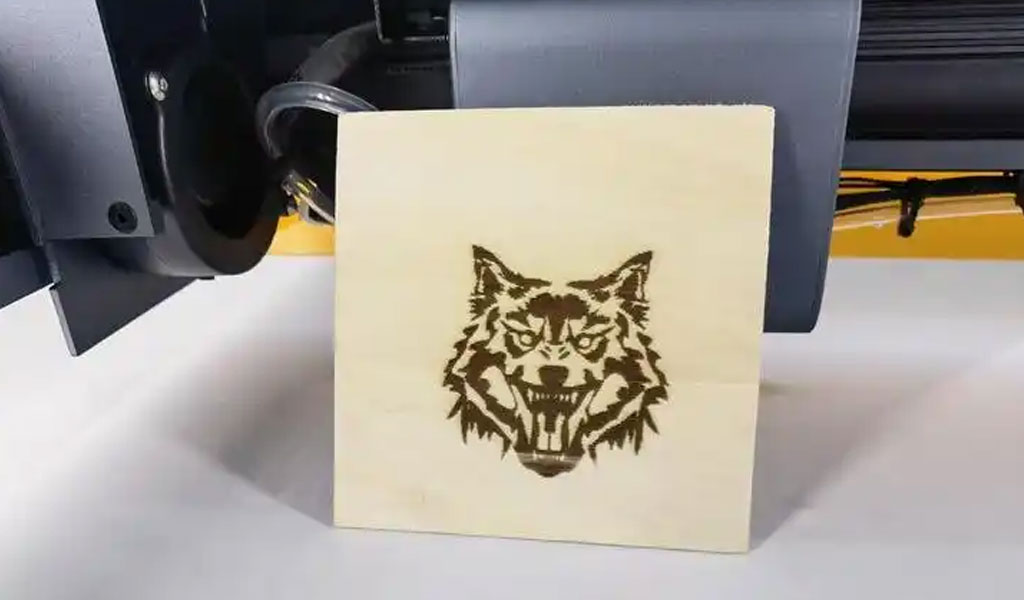
Laser etching is a technique in which a laser beam is focused on the surface of a material, causing it to heat up and expand, creating a shallow, high-contrast mark.
The process works by modifying the chemical composition or physical structure of the material’s surface, often through a process known as thermal reaction. This modification can result in a change in color, texture, or surface finish.
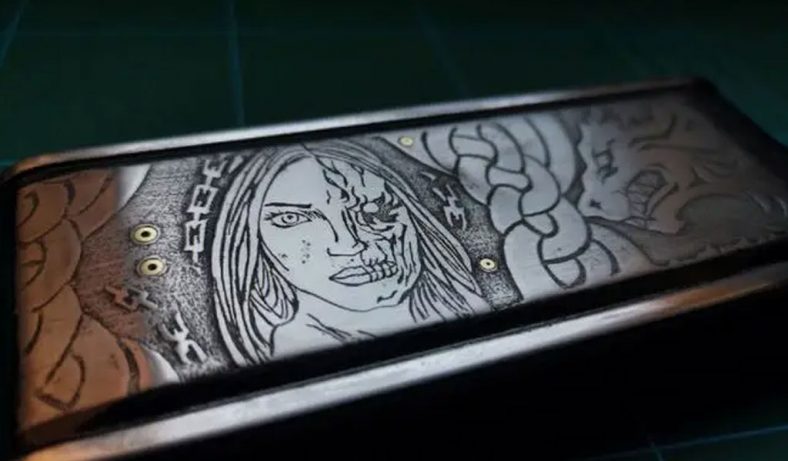
Laser etching is most commonly used for applications requiring surface marks that are not deep but still visible and permanent. This includes tasks like branding, marking serial numbers, logos, and barcodes. Unlike laser engraving, etching typically does not involve the removal of material, making it less intrusive to the material’s integrity.
Mechanism of Laser Etching
In laser etching, a focused beam of high-energy light is directed onto the surface of the material. The intense heat generated by the laser causes a rapid expansion of the material, which results in the creation of a micro-texture on the surface. The heat also often leads to chemical reactions that change the color of the material. For example, etching on metals such as stainless steel can result in a darkened mark due to oxidation, while etching on plastics may cause the surface to turn white or frosted.
Laser etching is commonly done with carbon dioxide (CO2) lasers for non-metallic materials like wood, plastics, and ceramics, while fiber lasers are more commonly used for metals. The power and frequency of the laser are carefully controlled to achieve the desired etching effect without deep penetration into the material.
Advantages of Laser Etching
- Minimal Material Removal: Since laser etching involves minimal material removal, it preserves the integrity of the base material, which is important in applications where the strength or functionality of the material must remain intact.
- Precision and Detail: Laser etching can produce highly detailed marks with precision, allowing for intricate designs, logos, and text to be etched onto various materials.
- Fast Processing: Laser etching is typically faster than engraving due to the reduced depth of the mark and the less intensive laser settings required.
- Variety of Materials: Laser etching can be applied to a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, glass, and ceramics, making it a versatile solution in manufacturing and product customization.
- Low Operational Costs: Laser etching machines are generally less expensive to operate than engraving machines, especially when large quantities of items need to be marked with minimal depth.
Limitations of Laser Etching
- Shallow Marks: The marks created by laser etching are shallow and may not be suitable for applications that require more permanent or deep markings.
- Limited Contrast: In some materials, the contrast between the etched area and the rest of the surface can be relatively low, especially when etching on reflective surfaces like polished metals or glass.
- Surface Sensitivity: Because the process alters only the surface of the material, laser etching may not be as effective on materials with highly reflective surfaces, such as mirror-finish metals.
The Basics of Laser Engraving
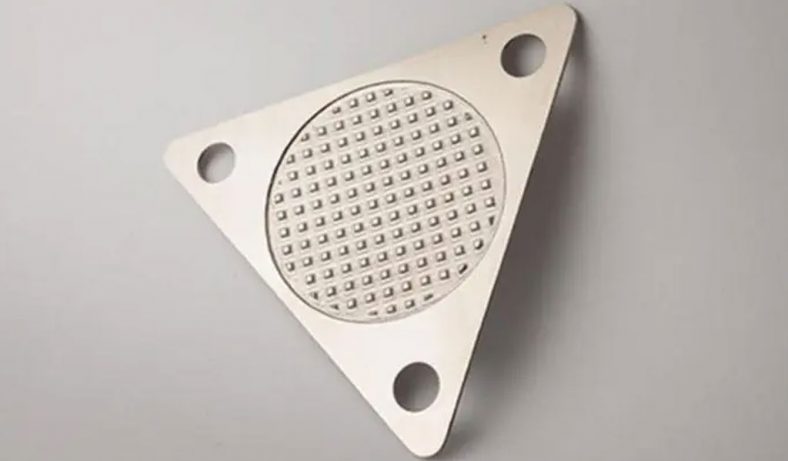
Laser engraving, on the other hand, involves the use of a high-powered laser that removes material from the surface to create a deeper, more permanent mark. In this process, the laser beam focuses on the material, melting, vaporizing, or ablating a thin layer of the material’s surface, creating a cavity or depression. The depth of the engraving is determined by the intensity and duration of the laser pulse, which can be adjusted depending on the material and the desired outcome.
Laser engraving is ideal for applications requiring deeper, more permanent markings, such as identification tags, custom gifts, awards, and intricate designs that need to withstand wear and tear over time.
Mechanism of Laser Engraving
Laser engraving works by using a concentrated laser beam to target the surface of the material. As the laser beam moves across the surface, it vaporizes or burns away the material, creating a depression or groove in the shape of the design. The depth of the engraving can be controlled by adjusting the power, speed, and focus of the laser beam.
Engraving can be done on a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, glass, and leather. For metals, fiber lasers are often used, while CO2 lasers are more commonly employed for materials like wood, acrylic, and glass.
Advantages of Laser Engraving
- Deep and Permanent Marks: One of the primary advantages of laser engraving is its ability to create deep, permanent marks that will not fade over time, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability.
- High Precision: Laser engraving can produce fine details and intricate designs, even in small spaces, making it suitable for detailed logos, text, and artwork.
- Durability: The deep marks produced by laser engraving are more resistant to wear, corrosion, and environmental factors, making it ideal for industries that require long-lasting identification or branding.
- Wide Material Compatibility: Like etching, laser engraving can be applied to a broad range of materials, including metals, plastics, glass, wood, and leather, giving it significant versatility.
Limitations of Laser Engraving
- Material Removal: Because laser engraving involves material removal, the process can be more costly and time-consuming compared to laser etching. In addition, removing material can affect the strength or appearance of the material, particularly in thin or delicate items.
- Heat-Affected Zones: Laser engraving can cause heat-affected zones (HAZ) around the engraved area, leading to color changes or warping in some materials. This can be problematic when working with heat-sensitive materials.
- Slower Process: Laser engraving tends to be slower than laser etching due to the depth of material removal required, especially for larger designs or thicker materials.
Key Differences Between Laser Etching and Laser Engraving
While both laser etching and laser engraving involve the use of a focused laser beam, there are several key differences between the two techniques:
- Depth of Marking: Laser etching creates shallow marks, while laser engraving involves deeper material removal. Etching is typically used for lighter marks, while engraving is suited for deeper, more permanent designs.
- Material Removal: Laser etching involves minimal material removal, while laser engraving physically removes material to create a depression in the surface.
- Surface Texture: Laser etching can create a textured or discolored surface, whereas engraving creates a more pronounced groove or cavity on the material.
- Applications: Laser etching is used for tasks requiring subtle marks or high-contrast designs, while laser engraving is preferred for applications where a deeper, more durable mark is needed.
- Speed: Laser etching is generally faster than laser engraving because it requires less energy and time to create a mark.
- Cost: Because laser engraving involves material removal, it is generally more expensive and slower than laser etching, which can be done more efficiently and with less material loss.
Applications of Laser Etching and Laser Engraving
Both laser etching and laser engraving find applications across various industries, from manufacturing to customization. The choice of technique depends on the specific requirements of the application, including the desired depth, permanence, and material.
Applications of Laser Etching
- Product Branding and Marking: Laser etching is commonly used for marking logos, serial numbers, and barcodes on products, especially in industries like electronics, automotive, and aerospace.
- Customization: Laser etching is often employed in personalized products such as jewelry, trophies, and gifts, where surface-level markings are required.
- Industrial Applications: Laser etching is also used for labeling components in the automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing sectors, providing clear, legible marks without affecting the material’s strength.
Applications of Laser Engraving
- Identification and Security: Laser engraving is widely used for creating identification plates, tags, and security markings on products, particularly in industries where durability and permanence are crucial.
- Awards and Trophies: Laser engraving is commonly used in the production of awards, trophies, and plaques, where detailed designs and logos need to be engraved into materials like wood, glass, and metal.
- Medical Devices: In the medical field, laser engraving is used for marking surgical instruments, implants, and other devices that require permanent identification and tracking.
- Industrial Parts and Tools: Laser engraving is ideal for tools and components that require deep markings, such as serial numbers, logos, or barcodes, ensuring that these markings are durable and remain visible throughout the part’s life cycle.
Technological Advancements in Laser Marking
Both laser etching and laser engraving have evolved significantly with advancements in laser technology. Modern lasers offer higher precision, faster processing speeds, and improved material compatibility. The development of fiber lasers has been particularly important, as they provide higher power output and efficiency, making both etching and engraving faster and more precise, especially when working with metals.
Furthermore, advancements in computer numerical control (CNC) technology and software have enabled greater control over the laser beam’s movement and intensity. This has led to more detailed and complex engravings and etchings, as well as improvements in automation for large-scale production.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Both laser etching and engraving are considered environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional marking methods like chemical etching or mechanical engraving, as they produce minimal waste and do not require harmful chemicals. Additionally, because the laser beam is highly focused, the amount of energy consumed can be controlled, reducing overall environmental impact.
However, the heat generated by the laser can still result in fumes or smoke, particularly when working with certain materials such as plastics or composites. To mitigate this, proper ventilation and filtration systems are often employed in laser marking systems.
Conclusion
The future of laser etching and engraving looks promising, with continued advancements in laser technology, materials, and automation. As industries continue to demand more efficient, precise, and sustainable marking solutions, the role of laser marking techniques will likely expand. With the ongoing development of new lasers, including green lasers and ultraviolet (UV) lasers, it is expected that laser etching and engraving will become even more versatile, enabling new applications across a wider range of materials and industries.
Laser etching and laser engraving are two distinct yet complementary techniques used to mark materials with high precision and durability. While laser etching creates shallow, high-contrast marks with minimal material removal, laser engraving involves deeper marks that are permanent and highly durable. Each technique has its advantages and limitations, making them suitable for different applications across industries. The choice between the two methods depends on factors such as material type, mark depth, speed, and cost considerations. As laser technology continues to evolve, both laser etching and engraving will remain indispensable tools in modern manufacturing, product customization, and industrial marking.4o