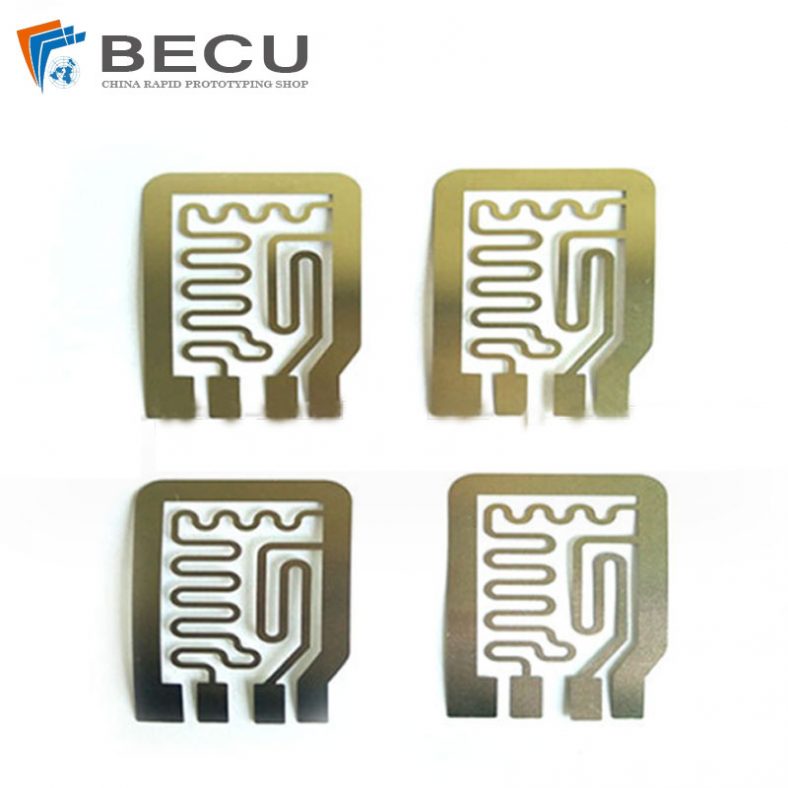
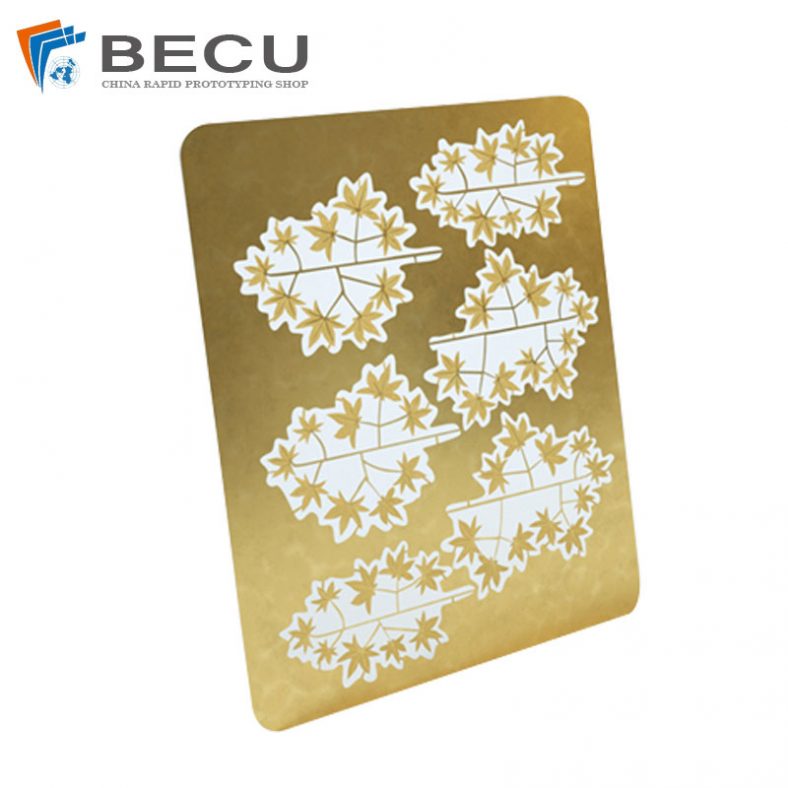
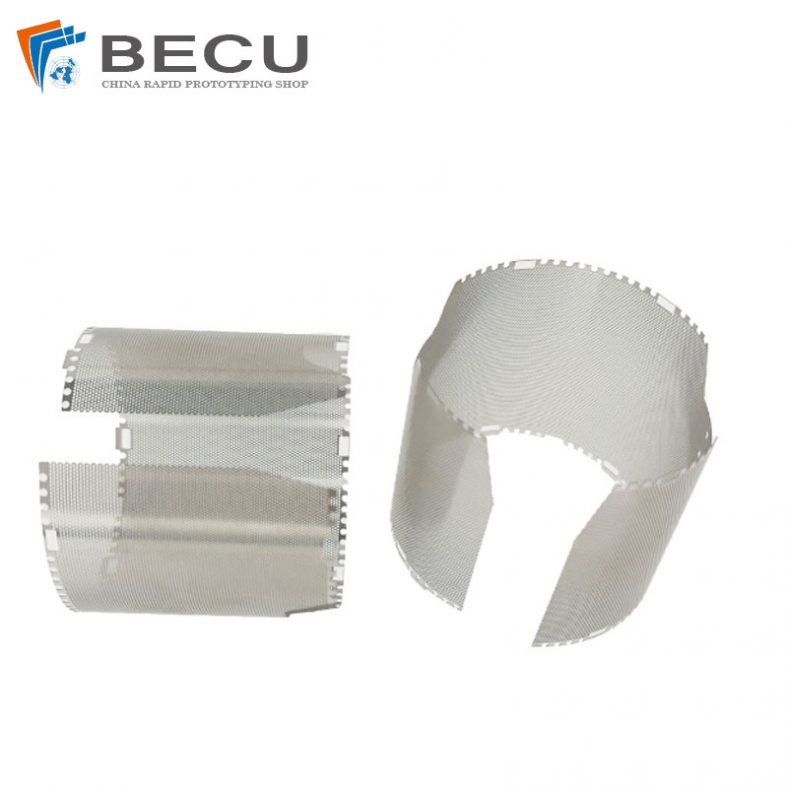
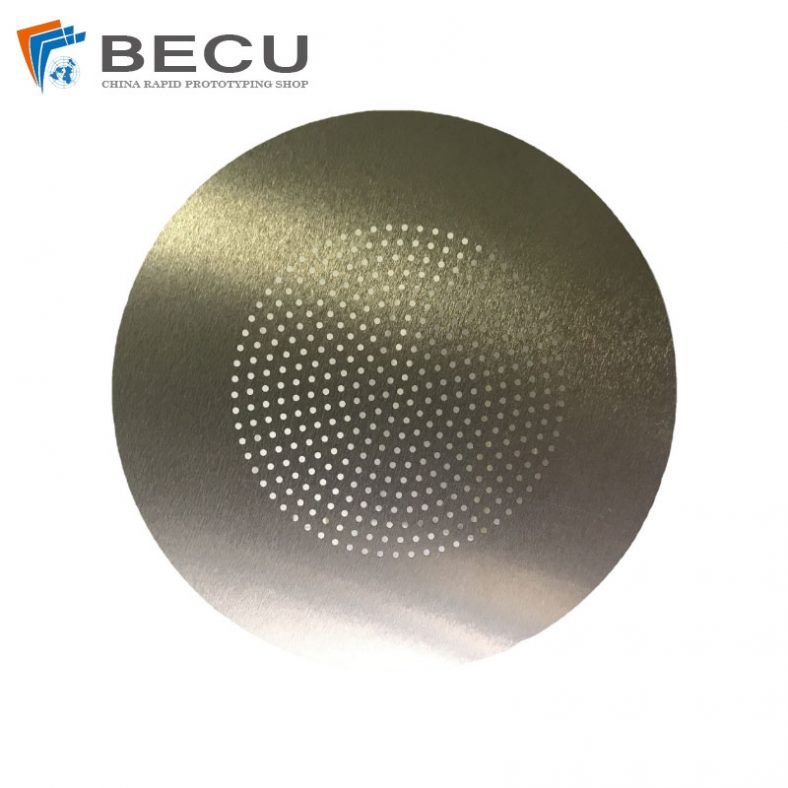
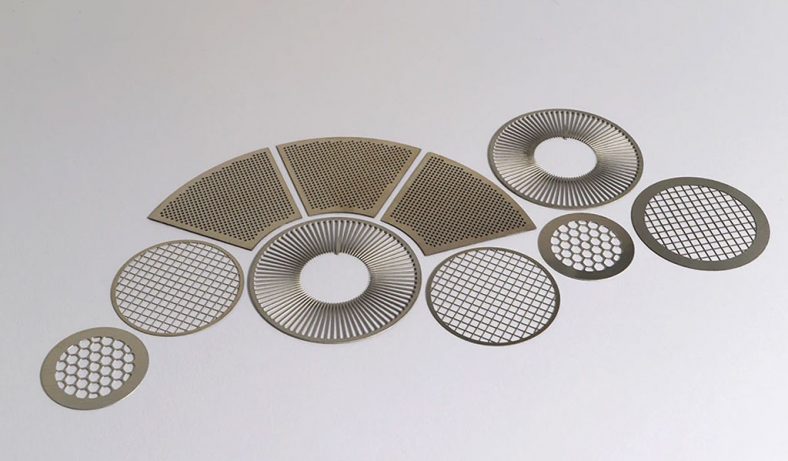
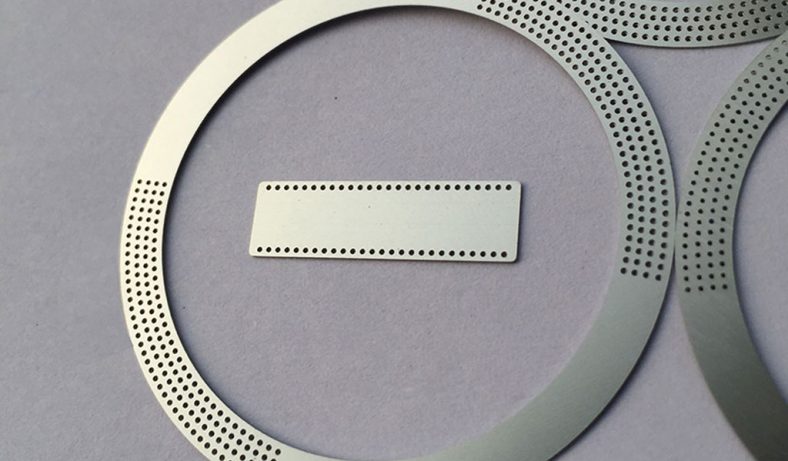
Motor laminations are an integral part of electric motors, particularly in the stator and rotor cores, where they help in minimizing energy losses and enhancing the efficiency of electrical machines. These laminations are made from high-quality, thin sheets of electrical steel, which are stacked together to form a core that is both magnetically efficient and resistant to eddy current losses. The manufacturing of motor laminations requires a range of precise processes, one of which is etching. This article will explore the etching process for motor laminations, its importance, and the various techniques used in this field. It will also look into the materials involved, the role of etching in motor performance, and the future developments in this area of technology.
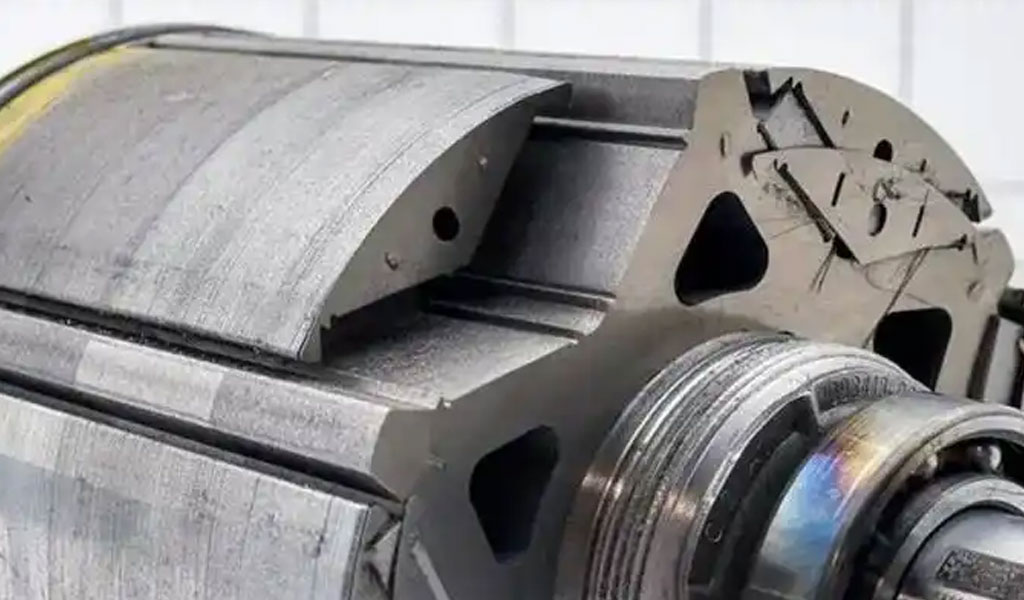

The Role of Laminations in Electric Motors
Laminations are thin sheets of magnetic material, typically made from silicon steel, which are used in the construction of motor cores. Their primary purpose is to reduce the eddy currents that occur when an electric motor operates. Eddy currents are unwanted currents that flow in the core material when exposed to a changing magnetic field, which results in energy losses in the form of heat. To combat this, the core is made of multiple thin sheets or laminations that are electrically insulated from each other. This construction minimizes eddy currents and reduces power losses.
In the context of electric motors, laminations are critical to ensuring that the motor operates efficiently, with minimal heat generation and energy wastage. These laminations are arranged in a stack and are often coated with an insulating layer to further prevent electrical conductivity between the layers. The performance of these laminations has a direct impact on the motor’s overall efficiency, durability, and effectiveness.
Etching in Motor Laminations Manufacturing
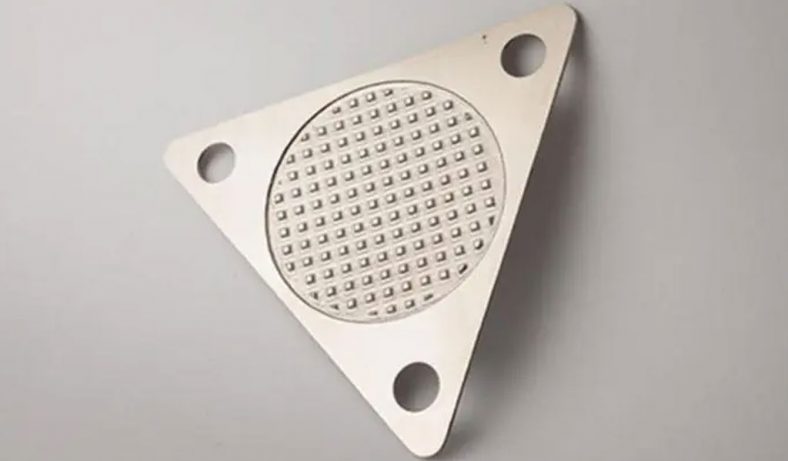
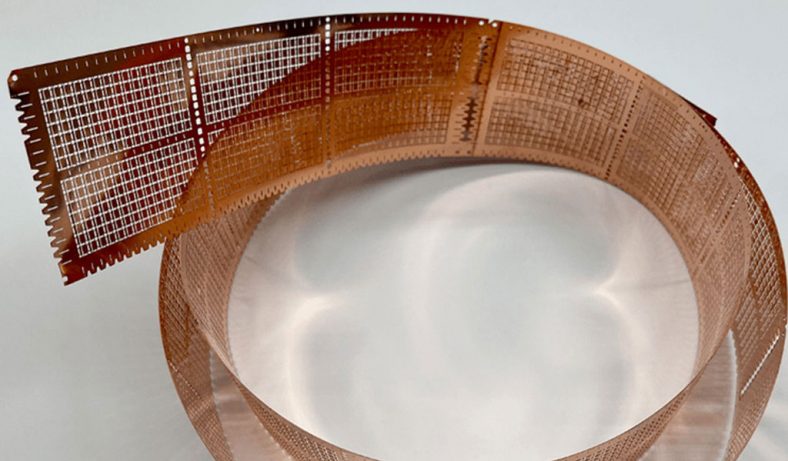
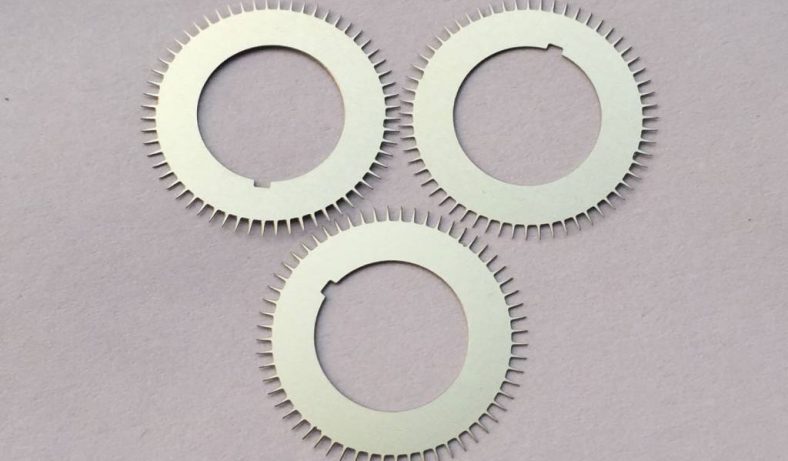
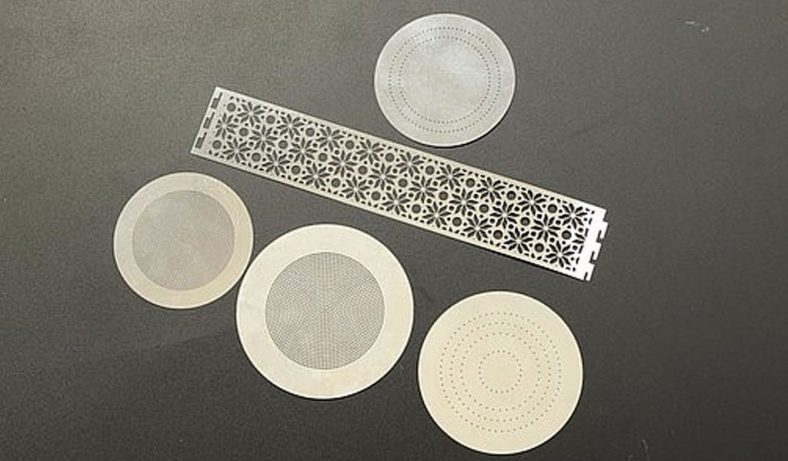
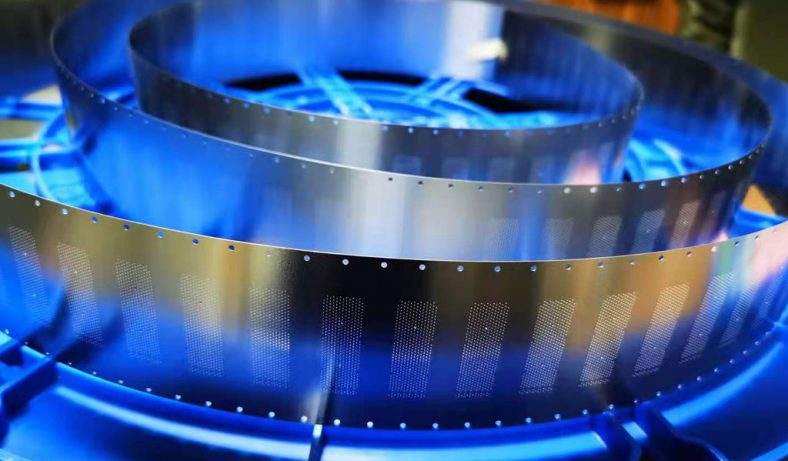
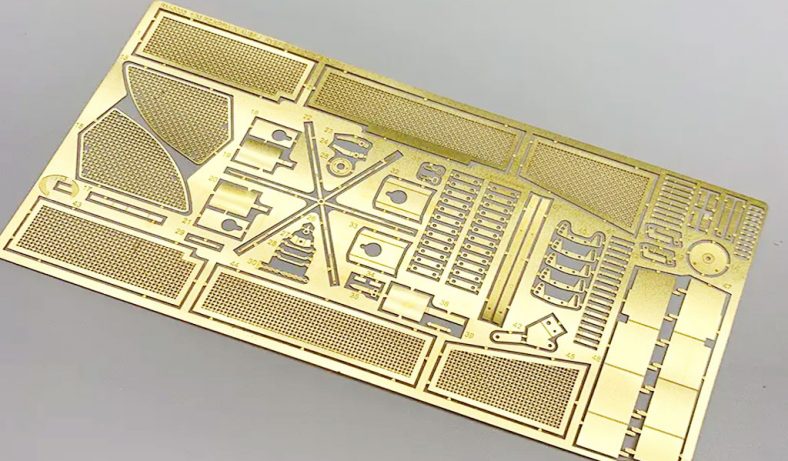
Etching is a process used in the production of motor laminations to create specific patterns or features on the surface of the steel sheets. This technique is critical in the manufacturing process as it helps in achieving the desired magnetic properties, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy of the laminations. The etching process is typically used to produce detailed patterns, such as slots, holes, or grooves, which are necessary for the motor’s electrical and mechanical functions.
The etching process involves the use of chemicals or lasers to remove specific portions of the surface material, exposing areas of the base material or leaving behind a desired pattern. In the case of motor laminations, etching can be used to create grooves that reduce eddy current formation and improve the magnetic flux density. The etching process can also be employed to create specific patterns for winding the motor, which is essential for ensuring the correct alignment of the motor’s components.
Types of Etching Methods
Several etching techniques are used in the production of motor laminations, each of which offers specific advantages depending on the requirements of the motor’s design and the material properties. The most common etching methods used in this field include:
- Chemical Etching Chemical etching, also known as photochemical etching or photochemical machining (PCM), is one of the most widely used methods for etching motor laminations. This process involves applying a photoresist to the surface of the material, which is then exposed to ultraviolet light to create a pattern on the surface. The areas that are exposed to light become hardened, while the unexposed areas remain soft. The unexposed portions are then removed using a chemical etchant, leaving behind the desired pattern on the lamination.One of the significant advantages of chemical etching is its ability to create very fine details with high precision. It also allows for the production of complex shapes without the need for mechanical tooling, which can reduce production time and costs. Chemical etching is particularly effective when it comes to etching thin materials like those used in motor laminations, where precision is paramount.
- Laser Etching Laser etching is another technique used to modify the surface of motor laminations. This method uses a high-powered laser beam to remove material from the surface of the steel sheets. The laser can be precisely controlled to create intricate patterns and markings, making it ideal for applications that require high precision and minimal material loss. Laser etching is particularly useful for producing fine, high-contrast markings on motor laminations, which can help in both functional and aesthetic applications.While laser etching offers many advantages, including high speed and the ability to handle complex designs, it can be more expensive compared to other methods. The precision of the laser allows for the creation of very fine and accurate patterns, which are essential for motor performance, as they can help reduce eddy current losses and improve the overall magnetic properties of the laminations.
- Mechanical Etching Mechanical etching involves the use of abrasive tools, such as rotary brushes, sandblasting, or milling tools, to etch the surface of the steel sheets. While this technique is less commonly used for high-precision applications compared to chemical and laser etching, it can still be effective for certain motor lamination designs. Mechanical etching is typically used for simpler, larger-scale etching tasks, where the need for fine detail is less critical.This method is more commonly used in industries where cost-effectiveness is prioritized over precision. However, it is worth noting that mechanical etching may not offer the same level of control or surface finish quality as chemical or laser etching, making it less suitable for motor laminations requiring highly detailed patterns or high magnetic efficiency.
- Electrochemical Etching Electrochemical etching is a process that uses an electrolyte solution and an electric current to remove material from the surface of the motor lamination. In this process, the material to be etched serves as the anode in an electrochemical cell, and the current causes the material to corrode in the pattern defined by a mask. This technique is useful for creating complex patterns on the surface of motor laminations, and it is often used in conjunction with other methods to enhance the etching process.Electrochemical etching offers high precision and can be used on a wide range of materials. It also produces minimal waste and is considered environmentally friendly compared to some chemical etching methods. However, it can be slower than other etching techniques and may require more specialized equipment.
Benefits of Etching Motor Laminations
Etching plays a significant role in improving the performance and efficiency of electric motors. The key benefits of etching motor laminations include:
- Reduction of Eddy Currents One of the most important advantages of etching in motor laminations is its ability to reduce eddy current losses. By creating specific patterns or grooves on the surface of the laminations, etching reduces the path that eddy currents can follow, thus minimizing energy losses. This leads to a more efficient motor with reduced heat generation and improved overall performance.
- Improved Magnetic Properties Etching can also be used to optimize the magnetic properties of motor laminations. By precisely controlling the surface texture and pattern, etching enhances the magnetic flux density, which improves the efficiency of the motor. This is particularly important in high-performance motors used in applications such as electric vehicles, industrial machinery, and renewable energy systems.
- Enhanced Motor Durability The ability to create fine, uniform patterns on the motor laminations can help improve the durability of the motor. By reducing the formation of cracks and other structural weaknesses in the material, etching ensures that the motor can withstand the stresses of continuous operation without premature failure. This is especially crucial in motors used in demanding applications, where reliability is key.
- Cost-Effectiveness Etching, especially chemical and laser etching, can be more cost-effective than other methods of creating patterns on motor laminations. The precision and speed of the process allow for higher throughput and reduced material waste, making it a more efficient choice for large-scale manufacturing. Additionally, the ability to create intricate designs without the need for mechanical tooling reduces setup and production costs.
- Customization and Design Flexibility Etching provides manufacturers with the flexibility to create custom designs for motor laminations, which can be tailored to specific motor requirements. This can be especially valuable in the production of specialized motors used in applications such as aerospace, medical equipment, or robotics, where unique designs are often necessary.
Materials Used in Motor Laminations
Motor laminations are typically made from silicon steel, a type of steel that contains silicon in amounts ranging from 0.5% to 6.5%. The presence of silicon increases the electrical resistivity of the steel, which helps reduce eddy current losses and improve the magnetic properties of the material. Silicon steel is also known for its high permeability, which enhances its ability to conduct magnetic fields.
In addition to silicon, other alloying elements such as manganese, aluminum, and chromium may be added to further improve the material’s properties. The steel used in motor laminations is typically cold-rolled to produce thin, uniform sheets, which are then stacked and insulated to form the motor core.
Future Developments in Motor Laminations Etching
As electric motor technology continues to evolve, the methods and materials used in the production of motor laminations are also advancing. One area of development is the use of advanced etching techniques, such as high-resolution laser etching and advanced photochemical etching processes. These methods allow for even more precise and complex patterns to be created on motor laminations, which can further improve motor efficiency and performance.
Additionally, researchers are exploring the use of new materials for motor laminations, such as amorphous steels and nanocrystalline alloys, which offer even lower eddy current losses and improved magnetic properties. As the demand for energy-efficient motors grows, particularly in electric vehicles and renewable energy systems, the role of etching in the production of motor laminations will continue to be a critical aspect of motor design and manufacturing.
Conclusion
Motor laminations are essential components in the construction of electric motors, and the etching process plays a vital role in ensuring their efficiency and performance. Through various etching techniques, manufacturers can optimize the design of motor laminations to reduce eddy current losses, improve magnetic properties, and enhance overall motor durability. As motor technology continues to evolve, the role of etching will remain central to the development of high-performance, energy-efficient motors used in a wide range of applications.4o mini